hydrolysis of disaccharides
|
Thermodynamics of hydrolysis of disaccharides
Mar 5 2022 Additional pathways for calculating thermodynamic parameters for these hydrolysis reactions are discussed. The disaccharides cellobiose |
|
Enzymatic hydrolysis of disaccharides and halogenosalicins
In agreement with the Weidenhagen theory the enzymes of almond emulsin hydrolyze all of the disaccharides with p-glucosidic linkages which have thus far. |
|
The uptake and hydrolysis of disaccharides by fast-and slow
disaccharide uptake systems in fast-growing rhizobia one transporting sucrose |
|
In vitro Inhibition of Rat Intestinal Surface Hydrolysis of
Feb 18 1980 hydrolysis of maltose and phenylalanylglycine. On the basis of kinetic experiments |
|
In vitro Inhibition of Rat Intestinal Surface Hydrolysis of
Feb 18 1980 hydrolysis of maltose and phenylalanylglycine. On the basis of kinetic experiments |
|
London S.E. 1
osmoreceptors occurring after the hydrolysis of the disaccharides. 3. Glucose was slightly more effective per osmole |
|
STUDIES ON REACTIONS RELATING TO CARBOHYDRATES AND
The problem of the relative ease of hydrolysis of disaccharides and of polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose is an important one not only. |
|
Hydrolysis of Glycosides
FIGURE 7.2. Hydrolysis of thioglycosides. TABLE 7.1. Acid hydrolysis of disaccharides. Disaccharide. Hydrolysis product. (+)-sucrose. D-(+)-glucose. |
|
Decomposition Kinetics of Maltose in Subcritical Water
decrease of pH affected the maltose decomposition rate and glucose formation. reactions such as the hydrolysis of esters4) epimeriza-. |
|
Experiment 11 – Carbohydrates
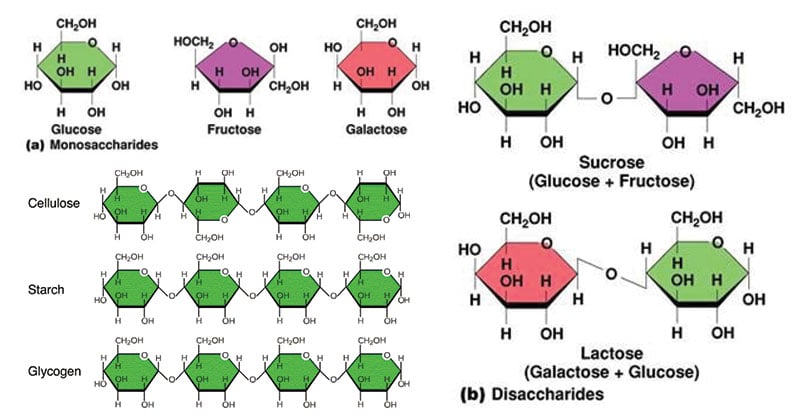
A disaccharide consists of two monosaccharides that are linked together. Disaccharides and polysaccharides can be hydrolyzed in the presence of acid or. |
|
Experiment 15 Carbohydrates - Moorpark College
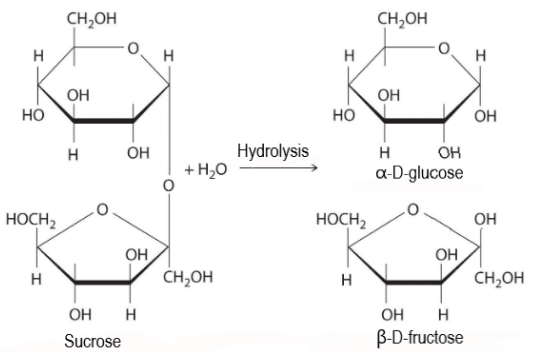
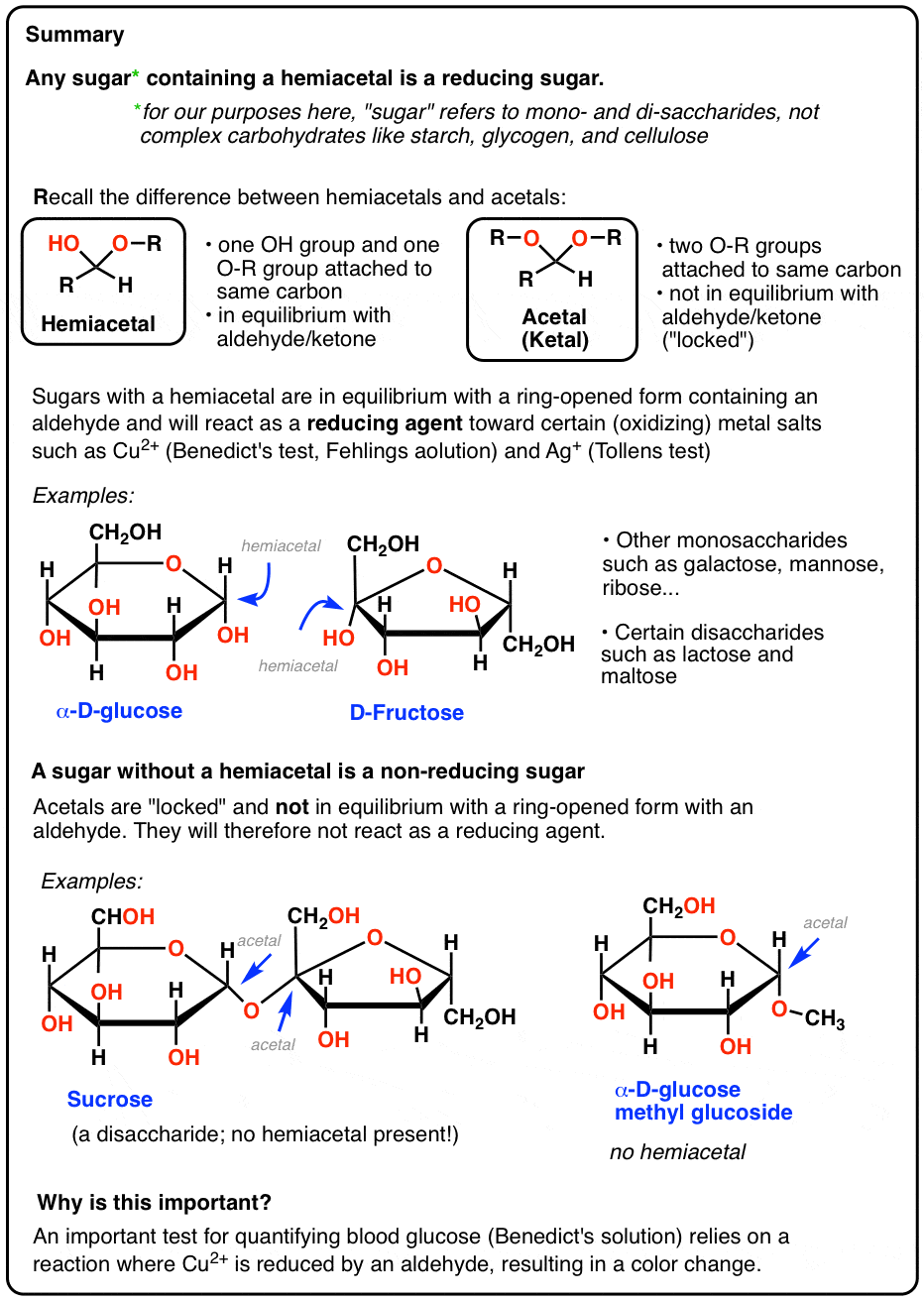
Hydrolysis of Acetal Groups Disaccharides and polysaccharides can be converted into monosaccharides by hydrolysis For example: Lactose + H 2 O catalyst ? D-galactose + D-glucose Procedure Reducing or Nonreducing Carbohydrates 1 Place approximately 2 mL (approximately 40 drops) of Fehling’s solution (20 drops each |
|
When disaccharide a is hydrolyzed which monosaccharide units are prod
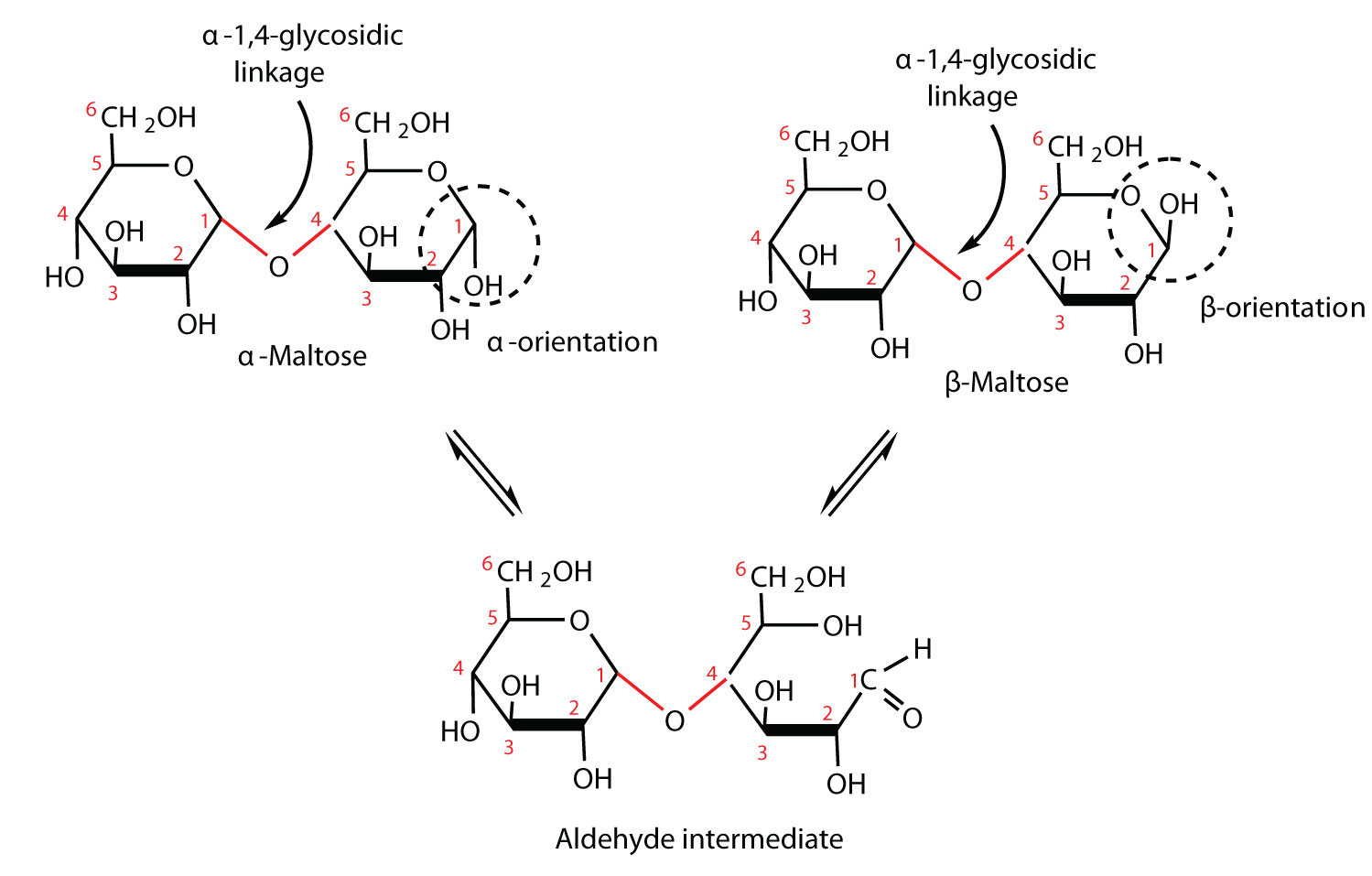
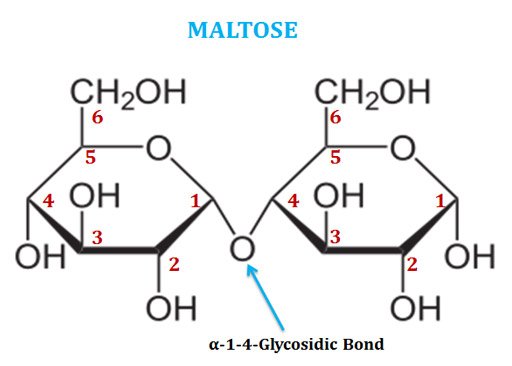
Disaccharides Disaccharides contain a glycosidic linkage between the C1 of one sugar and any position on another sugar (often C4) Some disaccharides Maltose Lactose Sucrose C Hydrolysis of Disaccharides Acid or enzyme hydrolysis of disaccharides yields monosaccharide subunits V Polysaccharides |
|
Enzymatic hydrolysis of disaccharides and halogenosalicins - NIST
ENZYMATIC HYDROLYSIS OF DISACCHARIDES AND HALOGENOSALICINS By William Ward Pigman ABSTRACT In agreement with the Weidenhagen theory the enzymes of almond emulsin hydrolyze all of the disaccharides with p-glucosidic linkages which have thus far been tried |
|
Searches related to hydrolysis of disaccharides filetype:pdf
for these hydrolysis reactions are discussed The disaccharides cellobiose gentiobiose isomaltose and maltose occur in living systems which use them both struc- turally and as energy sources |
Can a disaccharide be hydrolyzed?
- The human body is unable to metabolize maltose or any other disaccharide directly from the diet because the molecules are too large to pass through the cell membranes of the intestinal wall. Therefore, an ingested disaccharide must first be broken down by hydrolysis into its two constituent monosaccharide units.
What does the body do with disaccharides?
- Disaccharides such as lactose need some digestion to break them down to two 1-sugar units to facilitate absorption. When lactose is consumed in the human body, it is broken down into galactose and glucose by the lactase enzyme. These small sugars are then absorbed into the bloodstream from where they are absorbed by body cells to be used as energy.
Which disaccharides are reducing?
- reducing disaccharides, in which one monosaccharide, the reducing sugar of the pair, still has a free hemiacetal unit that can perform as a reducing aldehyde group; lactose, maltose and cellobiose are examples of reducing disaccharides, each with one hemiacetal unit, the other occupied by the glycosidic bond, which prevents it from acting as a …
What happens during a hydrolysis reaction?
- Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water.
|
Enzymatic hydrolysis of disaccharides and halogenosalicins
In agreement with the Weidenhagen theory, the enzymes of almond emulsin hydrolyze all of the disaccharides with p-glucosidic linkages which have thus far |
|
Thermodynamics of hydrolysis of disaccharides - Journal of
5 mar 2021 · The thermodynamics of the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellobiose, gentiobiose, isomaltose, and maltose have been studied using both high |
|
Transport and Hydrolysis of Disaccharides by - Journal of Bacteriology
Lactose, cellobiose, and melibiose are hydrolyzed by cell wall-bound glycosidase(s), suggesting hydrolysis of maltose, sucrose,or trehalose is not likely |
|
Q No 1 A disaccharide on hydrolysis gives Option 1 - MT Educare
A disaccharide on hydrolysis gives Similarly with fructose and maltose Acid or enzymatic hydrolysis of sucrose to give an equimolar mixture of glucose and |
|
Thermodynamics of hydrolysis of disaccharides - ScienceDirectcom
Thermodynamics of hydrolysis of disaccharides Lactulose, cu-D-melibiose, palatinose, D-trehalose, D-turanose and 3-o-j D-galactopyranosyl-D-arabinose |
|
SACCHARIDES OBTAINED FROM NATURAL SOURCES OR BY
OF NATURALLY OCCURRING DISACCHARIDES, OLIGOSACCHARIDES OR Enzymatic hydrolysis of saccharides is classified in C13K and C12P 19/00 |




















![PDF] Transport and hydrolysis of disaccharides by Trichosporon PDF] Transport and hydrolysis of disaccharides by Trichosporon](https://wou.edu/chemistry/files/2017/05/hydrolysis.png)


