mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline conditions
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions
11 juin 2013 Esters hydrolyze through a variety of mechanisms depending on their substitution pattern and the reaction conditions. Ingold proposed a widely ... |
|
Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline
9 juin 2021 Cyclobutane shows a perfect stability to keep the polymer's backbone when the ester groups are hydrolyzed under alkaline and acidic conditions. |
|
Stability of gamma-valerolactone under pulping conditions as a
1 déc. 2021 substitution mechanism in both acid and basic catalyzed solutions. ... of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline conditions. |
|
The transition state conformational effect on the activation energy of
9 mars 2021 "Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions" The. Journal of Organic Chemistry |
|
Stability of Gamma-valerolactone Under Pulping Conditions as a
3 mars 2021 The hydrolysis reactions in alkaline conditions were conducted at ... J (2013b) Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline ... |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
3 juin 2013 The existing mechanisms of acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis ... As occurs in neutral and alkaline hydrolyses these species lay at. |
|
Hydroxyl Group Participation in Amide Hydrolysis. The Influence of
Both mechanisms could be Abstract: The hydrolysis of 4-hydroxybutyranilide in weakly alkaline ... lactone 2-phenyliminotetrahydrofuran in neutral or. |
|
Comparative stability of cephalosporins in aqueous solution
Solution: Kinetics and Mechanisms of Degradation. TSUKINAKA YAMANAX and AKIRA TSUJI. Abstract 0 The acidic neutral |
|
Readily Degradable Aromatic Polyesters from Salicylic Acid
7 janv. 2020 the detailed polymerization mechanism (iii) evaluation of ... lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline conditions. J. Org. Chem. |
|
HYDROLYSIS 2016.pdf
mechanisms account for neutral acid and base hydrolysis. general |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions
11 jui 2013 · The neutral and base-catalyzed hydrolysis of nine carboxylic acid esters was studied using a hybrid supermolecule-PCM approach including six |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions
11 jui 2013 · ABSTRACT: The neutral and base-catalyzed hydrolysis of nine carboxylic acid esters was studied using a hybrid supermolecule-PCM approach |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions
7 avr 2023 · The molecules studied included two linear esters four beta-lactones two gamma-lactones and one delta-lactone: ethyl acetate and methyl formate |
|
Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline conditions
2 juil 2013 · The neutral and base-catalyzed hydrolysis of nine carboxylic acid esters was studied using a hybrid supermolecule-PCM approach including six |
|
Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline
9 jui 2021 · Cyclobutane shows a perfect stability to keep the polymer's backbone when the ester groups are hydrolyzed under alkaline and acidic conditions |
|
Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline - PubMed
19 juil 2013 · The neutral and base-catalyzed hydrolysis of nine carboxylic acid esters was studied using a hybrid supermolecule-PCM approach including six |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions
The neutral and base-catalyzed hydrolysis of nine carboxylic acid esters was studied using a hybrid supermolecule-PCM approach including six explicit water |
|
HYDROLYSIS
Epoxides undergo hydrolysis by neutral and acid catalyzed mechanisms under environmentally relevant conditions The hydrolysis of epoxides generally leads |
|
Stability of gamma-valerolactone under pulping conditions as a
1 déc 2021 · The hydrolysis in an alkaline environment is more detrimental for the lactone ring due to the irreversible salt formation the 4-hydroxyvalerate |
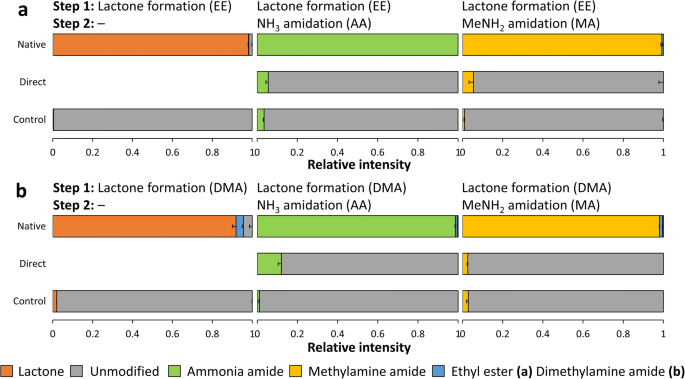
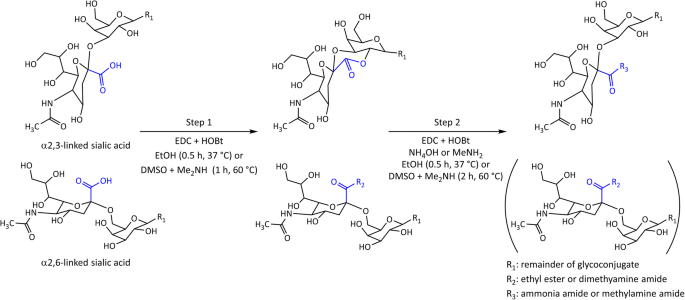
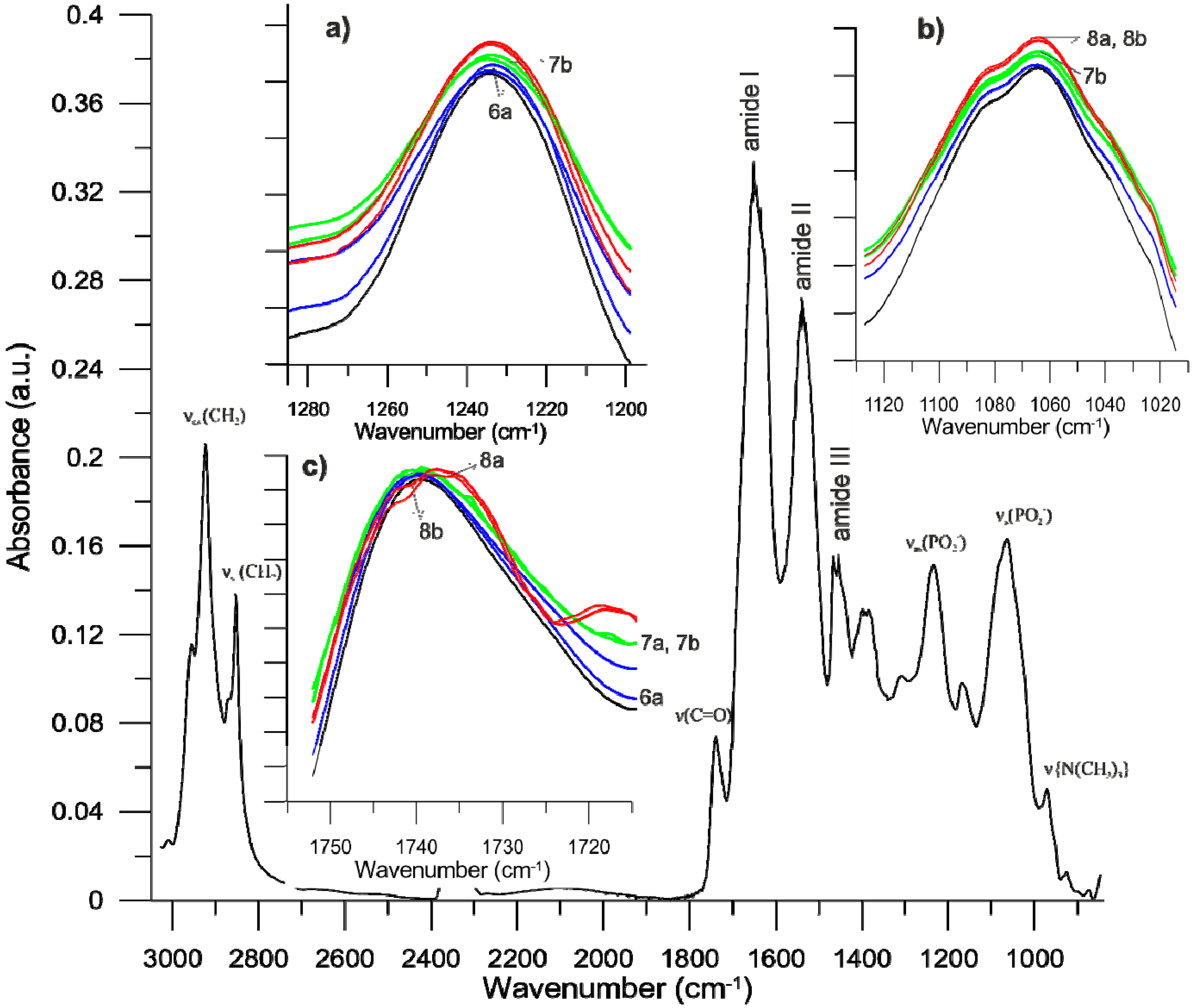
What is the mechanism of lactone hydrolysis?
Mechanism: Lactones are cyclic esters and readily and irreversibly hydrolyze in alkaline media to produce a hydroxycarboxylate. Although carboxylic acids are weak acids they are completely ionized in basic media.What is the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis reaction?
The mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis is believed to be saponification of intermolecular ester bonds cross-linking xylan hemicelluloses and other components, for example, lignin and other hemicelluloses.What is the mechanism of lactone formation?
Lactones are cyclic organic esters of hydroxycarboxylic acids, usually formed by the reaction of a halogen atom or hydroxyl group with a carboxylic acid group present in the same molecule. These are formed by intramolecular esterification of respective hydroxycarboxylic acids.- Alkaline hydrolysis of nitriles generally results in the formation of the salt of the carboxylic acid and ammonia, and is conveniently applied to the simple alkyl cyanides and also to nitriles such as ?-cyanocarboxylic acids producing dicarboxylic acids which are unstable in hot mineral acid.
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Neutral and Alkaline Conditions
11 jui 2013 · mechanism, BPL and BBL are two of the rare instances of the neutral BAL2 hydrolysis, and BIVL follows the BAL1 mechanism Regarding the base-catalyzed mechanisms, BAC2 is exceedingly common and all the compounds studied hydrolyze through this mechanism in alkaline medium |
|
Mechanisms of Lactone Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
3 jui 2013 · 1 INTRODUCTION As is also the case with neutral and base-catalyzed mechanisms, the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of esters has seldom been |
|
HYDROLYSIS
Mechanisms analogous to SN1 and SN2 operate under neutral and acid catalyzed conditions neutral SN1 mechanism O O O O OH2+ O OH2+ |
|
Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids
a) “Downhill” hydrolysis: From acids or anhydrides with NEUTRAL WATER alone This reaction occurs routinely under biological conditions, in which enzymes catalyze the Draw the Mechanisms for the following Hydrolyses Ph O O Ph |
|
Mechanisms for the mutarotation and hydrolysis of the
A study has been made of the kinetics of the mutarotation and hydrolysis reactions of L-arabinosylamine, and 3 Thc process appears to be complicated Wldet· some conditions by the formation reaction in weakly alkaline or acid solutions, in which 'l'hus, if B in eq 6a is a neutral substance then H B becomes HB+ 136 |
|
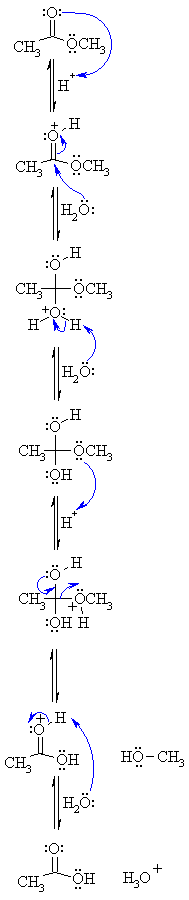
217 HYDROLYSIS OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
Ester hydrolysis in aqueous hydroxide is called saponification because it is used in the Specifically, the mechanisms of these reactions are classified as nucleophilic acyl substitu- lactone from a hydroxy acid is nothing more than an intramolecular stitution reaction that occurs under neutral or basic conditions |
|
Estimated carboxylic acid ester hydrolysis rate constants for - CORE
28 sept 2011 · Acid- (kA) and base- (kB) catalyzed and neutral (kN) hydrolysis rate acid- and base-catalyzed and neutral hydrolysis mechanisms [8-10] half-lives diverge rapidly under more acidic/basic conditions to 80041016 flower, lactone Holba, Effect of cosolvent on alkaline hydrolysis of monomethyl ester of |
![PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8b57fe7d6a5984cbeb43a275161918f8d7fa73b5/10-Figure6-1.png)
![PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8b57fe7d6a5984cbeb43a275161918f8d7fa73b5/9-Figure5-1.png)
![PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8b57fe7d6a5984cbeb43a275161918f8d7fa73b5/3-Figure1-1.png)
![PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8b57fe7d6a5984cbeb43a275161918f8d7fa73b5/3-Table1-1.png)
![PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline](http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/courses/350/Carey5th/Ch20/sapmech.gif)


![PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline PDF] Mechanisms of lactone hydrolysis in neutral and alkaline](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/17111101_Hydrolysis_of_aspirin_Intramolecular_general_base_catalysis_of_ester_hydrolysis/links/5cd9201092851c4eab99fec3/largepreview.png)