HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER Solved Problems By Mr P
HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER Solved Problems By Mr P annamalaiuniversity ac in/studport/download/engg/mech/oldqp/HMT 20University 20Solved 20Problems pdf Heat transfer co-efficient at innear side, hhf = 400 W/m2oC k = 0 51W/mK Find Heat loss from the pipe (Q/L) Solution We know that
Solutions to Chapter 2 of A Heat Transfer Textbook, 5th edition
Solutions to Chapter 2 of A Heat Transfer Textbook, 5th edition ahtt mit edu/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/AHTT_Chapter2_Solutions-v1 0 pdf 7 août 2020 From the example we get the formula for U Using the numbers We give the solution to the heat conduction equation for this case in
Heat Transfer: Exercises - IQY Technical College
Heat Transfer: Exercises - IQY Technical College www iqytechnicalcollege com/ME 20107 20heat-transfer-exercise-book pdf perfectly insulated on all sides except the top surface, what is the convective heat transfer coefficient? Solution Heat flux equals power supplied to
chapter 5 heat transfer theory - NZIFST
chapter 5 heat transfer theory - NZIFST nzifst nz/resources/unitoperations/documents/UnitopsCh5 pdf example of radiant heat transfer is when a foodstuff is passed below a bank Sugar solution is being heated in a jacketed pan made from stainless steel
Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer matermeer weebly com/uploads/3/2/0/5/32053441/heattransferpracticeworksheet__1_ pdf With ______ objects, heat transfers when the objects come In the boxes below, draw an example of each type of heat transfer the best answer
Staedy Conduction Heat Transferpdf
Staedy Conduction Heat Transfer pdf www sfu ca/~mbahrami/ENSC 20388/Notes/Staedy 20Conduction 20Heat 20Transfer pdf Steady Conduction Heat Transfer 6 Fig 4: Schematic for example 1 Solution: The rate of heat transfer through this composite system can be expressed as:
Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection, & Radiation
Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection, & Radiation www chester k12 sc us/cms/lib/SC50000477/Centricity/Domain/405/student 20share 20heat 20booklet 20answers pdf Circle the examples of convection Heater blowing warm air Walking on hot sand at beach Cuddling with your warm dog Smoke rising from campfire
Sample Test: Heat and Heat Transfer
Sample Test: Heat and Heat Transfer www cohassetk12 org/cms/lib/MA01907530/Centricity/Domain/345/Gr 209 20Physics/3 20Heat/Sample 20Unit 203 20Test 202015 pdf Heat transfer by convection occurs when atoms give off heat in the form of electromagnetic waves Explain your answer
HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER
HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER imartinez etsiae upm es/~isidoro/bk3/c11/Heat 20and 20mass 20transfer pdf and present at a later stage a briefing of similarities and differences between heat transfer and mass transfer, with some specific examples of mass
Methods of Heat Transfer - Maplesoft
Methods of Heat Transfer - Maplesoft www maplesoft com/content/EngineeringFundamentals/51/MapleDocument_49/heat_transfer pdf So the tube will lose 7 2 kW/ of thermal energy 1-D Heat Diffusion Equation In the previous example, we were able to obtain the temperature distribution by
 99674_3heattransferpracticeworksheet__1_.pdf
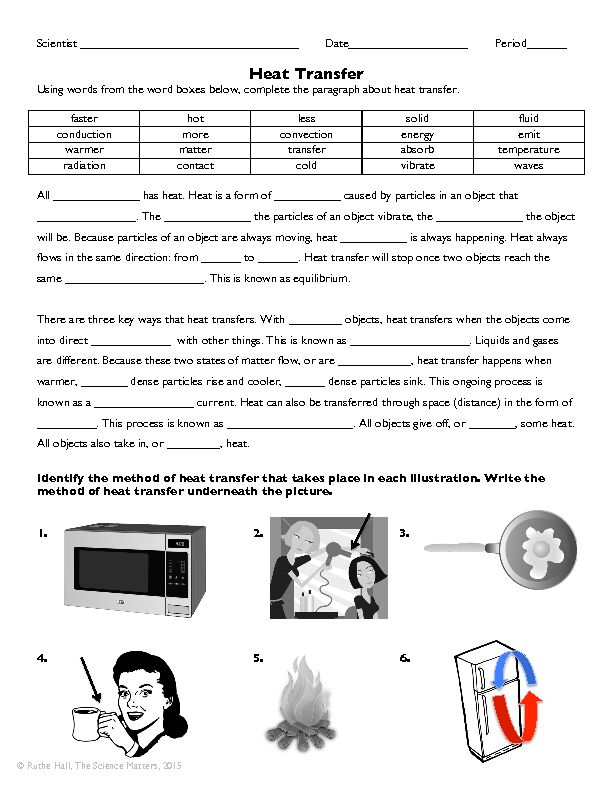
99674_3heattransferpracticeworksheet__1_.pdf Scientist _________________________________ Date__________________ Period______ Heat Transfer Using words from the word boxes below, complete the paragraph about heat transfer. faster
hot less solid fluid conduction more convection energy emit warmer matter transfer absorb temperature radiation contact cold vibrate waves All _____________ has heat. Heat is a form of __________ caused by particles in an object that _______________. The _____________ the particles of an object vibrate, the _____________ the object will be. Because particles of an object are always moving, heat __________ is always happening. Heat always flows in the same direction: from ______ to ______. Heat transfer will stop once two objects reach the same _____________________. This is known as equilibrium. There are three key ways that heat transfers. With ________ objects, heat transfers when the objects come into direct ____________ with other things. This is known as __________________. Liquids and gases are different. Because these two states of matter flow, or are ___________, heat transfer happens when warmer, _______ dense particles rise and cooler, ______ dense particles sink. This ongoing process is known as a _______________ current. Heat can also be transferred through space (distance) in the form of _________. This process is known as ___________________. All objects give off, or _______, some heat. All objects also take in, or ________, heat. Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Write the method of heat transfer underneath the picture. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. © Ruthe Hall, The Science Matters, 2015
In the boxes below, draw an example of each type of heat transfer. Explain how heat is being transferred in your example. Conduction Convection Radiation Explanation: ________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Explanation: ________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Explanation: ________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ In each of the following situations, identify the method of heat transfer taking place. Write conduction, convection, or radiation on the line next to the statements. Choose the best answer. 1. You are stirring a bowl of hot soup with a metal spoon. The spoon starts to feel warmer because of ______________________. 2. You buy a lava lamp from the store. As the lamp heats up, blobs of liquid rise to the top then sink back down to the bottom. This process continues because of ______________________. 3. You are doing your homework at a desk that is underneath a lamp. You start to feel hotter because of ______________________ from the lamp. 4. Your best friend has a bunk bed. You move from the bottom bunk to the top bunk and notice that the air is warmer. The warm air rises because of _________________. 5. You are in science class and want to see if the hot plates were used recently. You place your hand over the hot plate. Without touching the hot plate, your hand feels warmer. Heat is transferred to your hand by ______________________. 6. You are roasting marshmallows at a campfire. The metal skewer (stick) that you're cooking your marshmallow on burns your hand because of _______________________. © Ruthe Hall, The Science Matters, 2015
Scientist _________________________________ Date__________________ Period______ Heat Transfer Using words from the word boxes below, complete the paragraph about heat transfer. faster hot less solid fluid conduction more convection energy emit warmer matter transfer absorb temperature radiation contact cold vibrate waves All _____________ has heat. Heat is a form of __________ caused by particles in an object that _______________. The _____________ the particles of an object vibrate, the _____________ the object will be. Because particles of an object are always moving, heat __________ is always happening. Heat always flows in the same direction: from ______ to ______. Heat transfer will stop once two objects reach the same _____________________. This is known as equilibrium. There are three key ways that heat transfers. With ________ objects, heat transfers when the objects come into direct ____________ with other things. This is known as __________________. Liquids and gases are different. Because these two states of matter flow, or are ___________, heat transfer happens when warmer, _______ dense particles rise and cooler, ______ dense particles sink. This ongoing process is known as a _______________ current. Heat can also be transferred through space (distance) in the form of _________. This process is known as ___________________. All objects give off, or _______, some heat. All objects also take in, or ________, heat. Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Write the method of heat transfer underneath the picture. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. KEY matter energyvibrate faster warmer hot transfer cold temperature solid contact conduction fluid less more convection waves radiation emit absorb radiation radiation convectionconvectionconductionconduction© Ruthe Hall, The Science Matters, 2015
In the boxes below, draw an example of each type of heat transfer. Explain how heat is being transferred in your example. Conduction Convection Radiation Explanation: ________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Explanation: ________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ Explanation: ________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ In each of the following situations, identify the method of heat transfer taking place. Write conduction, convection, or radiation on the line next to the statements. Choose the best answer. 1. You are stirring a bowl of hot soup with a metal spoon. The spoon starts to feel warmer because of ______________________. 2. You buy a lava lamp from the store. As the lamp heats up, blobs of liquid rise to the top then sink back down to the bottom. This process continues because of ______________________. 3. You are doing your homework at a desk that is underneath a lamp. You start to feel hotter because of ______________________ from the lamp. 4. Your best friend has a bunk bed. You move from the bottom bunk to the top bunk and notice that the air is warmer. The warm air rises because of _________________. 5. You are in science class and want to see if the hot plates were used recently. You place your hand over the hot plate. Without touching the hot plate, your hand feels warmer. Heat is transferred to your hand by ______________________. 6. You are roasting marshmallows at a campfire. The metal skewer (stick) that you're cooking your marshmallow on burns your hand because of _______________________. conductionconductionconvectionconvectionradiation radiation Answers should vary © Ruthe Hall, The Science Matters, 2015
Copyright © Ruthe Hall. All rights reserved by author. This product is to be used by the original downloader only. Copying for more than one teacher, classroom, department, school, or school system is prohibited. This product may not be distributed or displayed digitally for public view. Failure to comply is a copyright infringement and a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). Clipart and elements found in this PDF are copyrighted and cannot be extracted and used outside of this file without permission or license. Intended for classroom and personal use ONLY.