 Hofstedes Cultural Dimensions Power Distance
Hofstedes Cultural Dimensions Power Distance
Power Distance culture and a culture that values the equal treatment of everyone is a Low Power Distance culture. In High Power Distance cultures
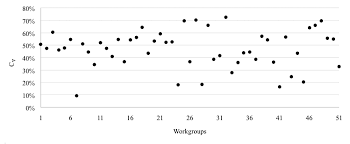 Effects of Power Distance Diversity within Workgroups on Work Role
Effects of Power Distance Diversity within Workgroups on Work Role
Secondly the most power distance diverse workgroups negatively influenced two dimensions of organizational citizenship behavior: altruism and civic virtue. In
 Case study - Power distance in cross-cultural environment
Case study - Power distance in cross-cultural environment
The. European countries involved have low power distances: Norway (31) Finland (33) and Germany. (35). In contrast
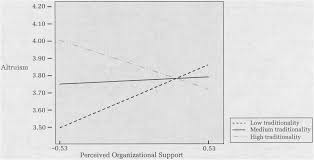 Individual-Level Cultural Values as Moderators of Perceived
Individual-Level Cultural Values as Moderators of Perceived
We found that both power distance and traditionality altered relationships of perceived organizational support to work outcomes in that these relationships
 Consequences of Power Distance Orientation in Organisations
Consequences of Power Distance Orientation in Organisations
(7) high power distance organisations are prone to unethical behaviour: This is because top managers have not to justify or defend their decisions to lower
 How Power Distance Interacts with Culture and Status to Explain
How Power Distance Interacts with Culture and Status to Explain
intercultural negotiation power distance
 The relationship between glass ceiling and power distance as a
The relationship between glass ceiling and power distance as a
Glass Ceiling Power. Distance. Glass ceiling symbolizes a variety of barriers and obstacles that arise from gender inequality at business life. With this mind
 Exploring the Nature of Power Distance: Implications for Micro-and
Exploring the Nature of Power Distance: Implications for Micro-and
After individualism/collectivism power distance is the most frequently studied cultural value in organizational research (Erez
 Classroom Interaction Affected by Power Distance
Classroom Interaction Affected by Power Distance
One of them Power Distance
 A Comparative Analysis of Chinese Cultural Values and Western
A Comparative Analysis of Chinese Cultural Values and Western
Large power distance culture gets higher. PDI. Hofstede found that countries such as China
 Hofstedes Cultural Dimensions Power Distance
Hofstedes Cultural Dimensions Power Distance
Power Distance. This is the way people in a society relate to each other on a hierarchical scale. A culture that gives great.
 Effects of Power Distance Diversity within Workgroups on Work Role
Effects of Power Distance Diversity within Workgroups on Work Role
Secondly the most power distance diverse workgroups negatively influenced two dimensions of organizational citizenship behavior: altruism and civic virtue. In
 Consequences of Power Distance Orientation in Organisations
Consequences of Power Distance Orientation in Organisations
(7) high power distance organisations are prone to unethical behaviour: This is because top managers have not to justify or defend their decisions to lower
 The Role of Job Satisfaction and Power Distance in Determining the
The Role of Job Satisfaction and Power Distance in Determining the
Power distance culture is an element of national culture that explains the difference in power between the employee and their boss (Wu 2006). Power distance
 Individual-Level Cultural Values as Moderators of Perceived
Individual-Level Cultural Values as Moderators of Perceived
mainland China we examined the moderating effect of power distance and Chinese traditionality on relationships between perceived organizational support and
 Impact of power distance on safety leadership on board
Impact of power distance on safety leadership on board
Power distance is one of the six primary dimensions that define. “cultures”. These parameters include;. •. Power distance index (PDI): “the extent to which the
 Relationship between power distance and autocratic- democratic
Relationship between power distance and autocratic- democratic
Key words: Power distance autocratic tendency
 Classroom Interaction Affected by Power Distance
Classroom Interaction Affected by Power Distance
One of them Power Distance
 The Moderating Role of Power Distance on the Relationship
The Moderating Role of Power Distance on the Relationship
12 jui. 2013 Results: Findings of the study showed that the level of power distance perceived by employees had a significant relationship with employee ...
 Moderating role of power distance in the relationship between
Moderating role of power distance in the relationship between
Keywords Knowledge workers Feedback-seeking behavior
 Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions Power Distance
Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions Power Distance
Power Distance This is the way people in a society relate to each other on a hierarchical scale A culture that gives great deference to a person of authority is a High Power Distance culture and a culture that values the equal treatment of everyone is a Low Power Distance culture
 What is Power Distance? - organizationalpsychologydegreescom
What is Power Distance? - organizationalpsychologydegreescom
Power distance is one of the factors shaping cultural perceptions of effective leadership For instance some For instance some cultures expect their leaders to be bold directive and decisive heroes whereas elsewhere a good leader may
 Relationships between Power Distance Organizational - ed
Relationships between Power Distance Organizational - ed
Power distance refers to the degree to which individuals organizations and societies accept inequalities in relation to power status and wealth (Hofstede 1980) It can be defined as the unequal distribution of power in organizations in the organizational field (Hofstede Hofstede & Minkov 2010)
 Power Distance and Facework Strategies - City University of
Power Distance and Facework Strategies - City University of
Power Distance and Facework Strategies Rebecca S Merkin This study utilized Hofstede’s (2001) study that tested whether Hofstede’s power distance (PD) dimension of culture is an important predictor for understanding cross-cultural facework It investigated how cultural groups differing in their level of PD negotiate
 Searches related to power distance filetype:pdf
Searches related to power distance filetype:pdf
Jul 12 2010 · Hofstede (1980 2001) under the label power distance Inhis seminal work based on a large survey of IBM employees located in 50 countries Hofstede defined power distance as the extent to which the less powerful members of institutions and organizations within a culture expect and accept that power is distributed un-equally
What does power distance mean?
- Power distance refers to the strength of a society’s social hierarchy. It measures the extent to which those people who are at the lower end of the hierarchy accept the fact that social stance or power is not distributed equally in the society. Both psychologists and sociologists use this measure.
What is the definition of power distance?
- Power distance refers to the relationship between higher-ranking and lower-ranking individuals that depends on how the latter react to the former. It is an anthropological concept used in cultural studies to understand the relationship between individuals with varying power, the effects, and their perceptions.
What is power distance culture?
- Power distance is one of five cultural dimensions developed by Geert Hofstede. It basically measures how a culture views power relationships between people. Cultures demonstrating high power distance view power as distributed unevenly, according to a hierarchy of authority.

Power Distance
Leadership
is found as an important function in human groups all over the world. E verywhere, the leadership role is associated with power and status. Most cultures have symbols that convey power and status. For example, in some cultures leaders may be recognizable by objects or clothing they alone are allow ed to carryor wear by virtue of their position. Such symbols are also found in the business world. Examples from that
sphere are company cars, job titles, or office location and size.Status
and power differentials are found everywhere, although they are more visibl e or stronger in some cultures than in others. Geert Hofstede, a cofounder of the Institute for Resear ch on Intercultural Cooperation, refers to culture as the collective programming of the mind. Power distance is one of the four dimensions of cultural variability that Hofstede discussed in his well-known 1980 stud y of IBM employees in forty countries. The other dimensions he discussed were individualism-collectivism, mascu linity-femininity, and uncertainty avoidance. In later research a fifth dimension emerged, labeled Confucia n dynamism (or a long versus short term orientation). This entry focuses on the impact of power distance o n leadership Hofstede defines power distance as the extent to which a society accepts the fact that power in institutions and organizations is distributed unequally. Research has shown that power di stance has a strong impact on organizational as well as personal functioning. For example, in a 1998 s tudy, the researchers Randall Schuler and Nikolai Rogovsky found that the greater the power distance in society ( that is, the more acceptance there is for unequal distribution of power in society), the less likely that companies in that society will have employeestock ownership plans. In the same year, the researcher Chet Robie and his colleagues reported that the
relationship between job satisfaction and job level was weaker in low power distance cultures than in high power distance cultures Hofstede is not the only one to have studied power differentials as an i mportant element of culture . All societies must find ways of eliciting responsible behavior from their me mbers, but there are many differentways of doing so. Hierarchical cultures emphasize the chain of authority and rely on hierarchically structured
roles. An unequal distribution of power and status is legitimate and expected. Employees are expected to comply with management's directives without questioning them. In contras t, egalitarian cultures encourage people to view each other as moral equals. Leaders motivate employees in a more participative manner and appeal to them to act on behalf of all. Employees typically have input i nto decisions and share in goal-setting activities. In cultures with large differences in power between individuals, organizations will typically have more layers and the chain of command is felt to be more important. There is clearly a c onnection between power distance and leadership . For example, compared with their counterparts in low power distance co untries, subordinates in high power distance countries are typically more reluctant to challen ge their supervisors and more fearful of expressing disagreement with their managers. Not only are people in high power distance countries less likely to provide negative feedback to superiors spontaneously, the very idea that subordinates would be allowed to provide feedback is more likely to be rejected in high power distance co untries, because such upward feedback may be perceived as threatening status positions. Thus, power distance has an impact on subordinates' expectations and preferences (people want and expect more guidance in societies with more power distance) as well as on acce ptable or typical patterns of leader behavior (autocratic leadership is more acceptable and effective in high power distance societies).BEING SEEN AS A LEADER: THE GLOBE STUDY
To be successful in a leadership role, leaders need to show characteristics or behave in ways that others
equate with leadership . The vastly different types of leaders one can find in the media worldw ide illustrate that people from different cultures associate different characteristics and behaviors with the leadership role. Power distance is one of the factors shaping cultural perceptions of eff ective leadership . For instance, some cultures expect their leaders to be bold, directive, and decisive heroes, whereas elsewhere a good leader may be someone who is calm, involves others in decision making, and seeks consensus before acting.The GLOBE (Global
Leadership
and Organizational Behavior Effectiveness) Project is one of the largest studies of leadership and culture carried out to date. The project involves researchers from some sixty c ountries working together to collect different kinds of data on leadership and culture. A large portion of the study involves a survey among middle managers in three different industries. I n total, more than sixteen thousand managers in more than sixty countries have participated in the survey.One of the results of the GLOBE study was a report that lists which leadership attributes are universally
endorsed as contributing to outstanding leadership , which are universally seen as undesirable, and which are culturally contingent. In all participating countries, an outstanding le ader is expected to be encouraging, motivational, dynamic, and to have foresight. Universally, a leader is also expected to be oriente d toward excellence, decisive, trustworthy, and intelligent. Several other attributes were universally viewed as impediments to outstanding leadership - for example, being noncooperative, ruthless, and dictatorial. The term autocratic leadership is often used to refer to leaders who do not allow subordinates to have any say in decision making. Dictatorial leadershipquotesdbs_dbs7.pdfusesText_5[PDF] power frequency 50hz or 60hz camera
[PDF] power line frequency tolerance
[PDF] power mac g4
[PDF] power mac g5
[PDF] power mac g5 a1047
[PDF] power of adjacency matrix
[PDF] power of board of directors
[PDF] power of ten
[PDF] power spectrum of discrete signal
[PDF] power tool abb knx
[PDF] power word activities
[PDF] power words for education
[PDF] powerful python pdf download
[PDF] powerful sentence starters
