 Proof of Correctness for Prims Algorithm
Proof of Correctness for Prims Algorithm
Nov 15 2016 Theorem 1 If S is the spanning tree selected by Prim's algorithm for input graph G = (V
 14.1 Introduction 14.2 Prims Algorithm
14.1 Introduction 14.2 Prims Algorithm
Oct 21 2014 1 Prim's algorithm correctly computes an MST. Proof: We'll prove this by induction. The induction hypothesis will be that after each iteration
 Prims Algorithm
Prims Algorithm
Prim's Algorithm Dense Graphs procedure prim(G
 ‣ Prims algorithm demo
‣ Prims algorithm demo
Feb 12 2013 GREEDY ALGORITHMS (PART II). ‣ Prim's algorithm demo. Page 2. 2. Prim's algorithm demo. Initialize S = any node. Repeat n – 1 times: ・Add to ...
 Prime Object Proposals with Randomized Prims Algorithm
Prime Object Proposals with Randomized Prims Algorithm
In this paper we introduce a novel and very efficient method for generic object detection based on a randomized version of Prim's algorithm. Using the
 Prims Algorithm.pdf
Prims Algorithm.pdf
Prim's Algorithm was originally discovered in 1930 by Vojtech Jarnik and was then independently discovered by Robert Clay Prim in 1957. 1. To begin pick any
 Comparative of prims and boruvkas algorithm to solve minimum
Comparative of prims and boruvkas algorithm to solve minimum
By comparing two algorithms Prim's and Boruvka's algorithm
 Modification of Prims algorithm on complete broadcasting graph
Modification of Prims algorithm on complete broadcasting graph
The method that will be applied is the algorithms of minimum spanning tree. Kruskal's and Prim's algorithms are considered. In Kruskal's algorithm the edges
 Greedy Algorithms
Greedy Algorithms
What's the cheapest way to connect a graph? ○ Prim's Algorithm. ○ A simple and efficient algorithm for finding minimum spanning trees.
 Kruskals and Prims algorithm
Kruskals and Prims algorithm
Theorem 1 Kruskal's algorithm yields a minimum weight spanning tree. Proof: Assume Kruskal's algorithm has selected the edges e1
 Prime Object Proposals with Randomized Prims Algorithm
Prime Object Proposals with Randomized Prims Algorithm
Prim's (RP) algorithm is designed to sample random par- tial spanning trees of a graph with lection of edges in Prim's algorithm with multinomial sam-.
 Prime Object Proposals with Randomized Prims Algorithm
Prime Object Proposals with Randomized Prims Algorithm
In this paper we introduce a novel and very efficient method for generic object detection based on a randomized version of Prim's algorithm. Using the
 14.1 Introduction 14.2 Prims Algorithm
14.1 Introduction 14.2 Prims Algorithm
21 oct. 2014 Both of them are greedy algorithms but they work in slightly different ways. 14.2 Prim's Algorithm. The first algorithm we'll talk about is ...
 Proof of Correctness for Prims Algorithm
Proof of Correctness for Prims Algorithm
15 nov. 2016 Theorem 1 If S is the spanning tree selected by Prim's algorithm for input graph G = (VE)
 Prims algorithm demo
Prims algorithm demo
?Add to T the min weight edge with exactly one endpoint in T. ?Repeat until V - 1 edges. 3. Prim's algorithm demo. 5. 4.
 Introduction to Algorithms
Introduction to Algorithms
The second due to Prim
 Prims Algorithm
Prims Algorithm
Note: It can be helpful to write a visited list to keep track of nodes that are already in the minimum spanning tree. The purpose of Prim's Algorithm is to find
 Comparative of prims and boruvkas algorithm to solve minimum
Comparative of prims and boruvkas algorithm to solve minimum
Prim's algorithm is suitable for trees with a large number of vertices and will always be able to find a minimum spanning tree but the resulting spanning tree
 Correctness analysis of Prims algorithm
Correctness analysis of Prims algorithm
The proof of correctness follows because Prim's Algorithm outputs Un?1. Proof of Claim 1. We will proof the claim by induction on k. Base case: k=0. U0 = ?
 Review and Analysis of Minimum Spanning Tree Using Prims
Review and Analysis of Minimum Spanning Tree Using Prims
Keywords:- Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) Prim's Algorithm
 Overview 141 Prim’s Algorithm - Duke University
Overview 141 Prim’s Algorithm - Duke University
When implementing Prim’s Algorithm we want to e ciently nd 1) a cut that does not go through any edges we have chosen and 2) a min-cost edge in the cut We can choose the cut such that F = S and use a data structure similar to that in Dijkstra’s algorithm The only di erence is in the key values by which the priority queue is ordered
 Greedy Algorithms - Stanford University
Greedy Algorithms - Stanford University
Prim's Algorithm A simple and efficient algorithm for finding minimum spanning trees Exchange Arguments Another approach to proving greedy algorithms work correctly Trees tree is an undirectedacyclic connected graph An undirected graph is called minimally connected iff it is connected and removing any edge disconnects it
 Is Prim's algorithm greedy? Why? - Quora
Is Prim's algorithm greedy? Why? - Quora
Prim’s Algorithm CLRS Chapter 23 Outline of this Lecture Spanning trees and minimum spanning trees The minimum spanning tree (MST) problem The generic algorithm for MST problem Prim’s algorithm for the MST problem – The algorithm – Correctness – Implementation + Running Time 1
 Prim’s Algorithm
Prim’s Algorithm
Prim’s Algorithm • How the Prim’s algorithm works • Example from the book ?gure 23 5 • Step by step • Showing the queue and the values of the keys
 Lecture 18 - Duke University
Lecture 18 - Duke University
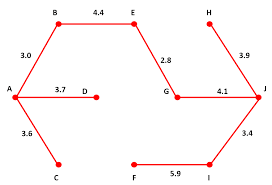
(a) Kruskal’s algorithm 3 7 5 4 6 2 (b) Prim’s algorithm Figure 1: Kruskal’s algorithm and Prim’s algorithm for minimum spanning tree The red edges are added this iteration 2 1 Kruskal’s Algorithm Kruskal’s algorithm maintains a spanning forest (starting with only singletons) and on each step connects
 Searches related to prim+s algorithm filetype:pdf
Searches related to prim+s algorithm filetype:pdf
Prim’s Algorithm: Proof of Correctness Theorem Upon termination of Prim’s algorithm F is a MST Proof (by induction on number of iterations) Base case: F = ??every MST satisfies invariant Induction step: true at beginning of iteration i – at beginning of iteration i let S be vertex subset and let f be the edge that Prim’s
How does the Prim algorithm work?
- The Prim algorithm, essentially, works by creating two components of the graph at each iteration and finding the minimum cost edge between them, knowing that such an edge has to be in the MST. This ensures that all the edges added using Prim's algorithm are edges of a valid MST of the graph.
What is your Prims algorithm a minimum spanning tree?
- Your Prims algorithm a minimum spanning tree that are implemented that being used are Kruskal algorithm... - 33 Prims algorithm ( MST ) is an important topic for GATE widely the algorithms that are that... Widely the algorithms that are implemented that being used are Kruskal 's....
What are the similarities between prim's and Kruskal's algorithms?
- First, the similarities: Prim’s and Kruskal’s algorithms both find the minimum spanning tree in a weighted, undirected graph. They are both considered greedy algorithms, because at each they add the smallest edge from a given set of edges. The best implementations of each also have the same big O time complexity: O ( E log ( V)).
How to prove Prim's algorithm correctly finds an MSt in G?
- Theorem:If Gis a connected, weighted graph, Prim's algorithm correctly finds an MST in G. Proof:Let Tbe the spanning tree found by Prim's algorithm and T*be any MST of G. We will prove c(T) = c(T*). If T= T*, then c(T) = c(T*) and we are done. Otherwise, T ? T*, so we have T– T*? Ø. Let (u, v) be any edge in T– T*.
Lecture 14: Minimum Spanning Tree II
Lecturer: Rong Ge Scribe: Haoming LiOverview
In the previous lecture, we introduced the denition of a Minimum Spanning Tree (MST), as well as some
properties of it. In this lecture, we will prove one of the properties (aka. Key Property, Key Lemma, or Cut
Property in the DPV textbook) and derive Prim's Algorithm, an algorithm for nding a MST. We will also
discuss Kurskal's Algorithm that does the same job.14.1 Prim's Algorithm
Say that in the process of building a MST, we have already chosen some edges and are so far on the right
track. Which edge should we add next? The following lemma gives us a lot of exibility in our choice14.1.1 Key Property
Lemma 14.1 (Key Property)SupposeFis a subset of edges of a MSTT. For every cut(S;S)that does not intersect withF,F[ fegis a subset of edges of some MSTT0(which may not be equal toT), wheree is an edge with minimum cost in the cut(S;S). A cut is any partition of the vertices into two groups,SandS=VS. What this property says is that itis always safe to add the lightest edge across any cut (that is, between a vertex inSand one inS), provided
Fhas no edges across the cut. Let prove why this holds. Proof:EdgesFare part of some MSTT; if the new edgeealso happens to be part ofT, then there is nothing to prove. So assume e is not inT. AddingetoTwill form a cycle, call itC. We know cycleCmust intersect with cut (S;S) in an even number of edges, so there must be another edgee02Cthat also crosses cut (S;S). We will swapeande0. DeneT0= (Tnfe0g)[feg. We havecost(T0) =cost(T)w(e0)+w(e)cost(T), sincew(e)w(e0) by theassumption thateis a min-cost edge across the cut. This means thatT0is a MST, and thatF[feg T014.1.2 Prim's Algorithm
What Key Property tells us in most general terms is that any algorithm conforming to the following greedy
schema is guaranteed to work.Algorithm:Prim(G= (V;E))
Initialize the treeFto be empty;
whilejFj14-2Lecture 14: Minimum Spanning Tree II
With the help of Key Property, we can quickly prove the correctness of Prim's Algorithm by induction.
Proof:
Inductive Hypothesis: At iterationi, the edges selected by the algorithm is a subset of some MST. Base Case: Wheni= 0, the set of edges selected is empty.Induction Step: see Key Property.When implementing Prim's Algorithm, we want to eciently nd 1) a cut that does not go through any
edges we have chosen, and 2) a min-cost edge in the cut. We can choose the cut such thatF=S, and use a
data structure similar to that in Dijkstra's algorithm. The only dierence is in the key values by which the
priority queue is ordered. In Prim's algorithm, the value of a node is the weight of the lightest incoming edge
from setS, whereas in Dijkstra's it is the length of an entire path to that node from the starting point. In
particular, we can maintaindis[u] for allunot visited, wheredis[u] is the min-cost of an edge (u;v) between
uand a visited vertexv.Nonetheless, the two algorithms are similar enough that they have the same running time, which depends
on the particular priority queue implementation. A naive implementaion of Prim's runs inO(n2), whereas
a Fibonacci heap version runs inO(m+nlogn).14.2 Kruskal's Algorithm
Kruskal's minimum spanning tree algorithm starts with the empty graph and then selects edges fromE according to the following rule:Repeatedly add the next lightest edge that doesn't produce a cycle.In other words, it constructs the tree edge by edge and, apart from taking care to avoid cycles, simply picks
whichever edge is cheapest at the moment. The proof of correctness of this algorithm centers on showing
that the output is a special case of general MST. We are going to show that, every time Kruskal's adds an
edge (u;v), we can nd a cut (S;S) whereu2Sandv2S, such that the cut does not contain any previous edges and that (u;v) is the min-cost edge in the cut. Proof:Consider when Kruskal's adds an edge (u;v). LetSbe the set of vertices that are connected touusing edges already selected by Kruskal's. By design ofv62S, therefore we only need to show that (u;v) is
the min-cost edge between (S;S).Assume towards contradiction that there is an edgeethat crosses the cut (S;S) such thatw(e)< w((u;v)).
By Kruskal's, edgeeis going to be considered before (u;v). Whenewas considered, (S;S) were not connected.
Therefore,ecannot create a cycle. Hence Kruskal's must have selectede. This is a contradiction.Sorting takesO(mlogm) time. For each edge, we need to check whether adding the edge creates a cycle.
This can be done very eciently (o(logm)).
14.3 Comparison of Running Time
Prim seems to be always faster (O(m+nlogn) vs. Kruskal'sO(mlogm)). However, theO(m+nlogn)version of Prim is not very easy to implement, and has a large hidden constant. If you use a regular binary
heap, the running time are the same, and Kruskal's is usually faster in practice, and easier to implement. If
the graph is dense,O(n2) version of Prim is easy to implement and faster than Kruskal's.quotesdbs_dbs3.pdfusesText_6[PDF] primary amine
[PDF] primary amine + naoh
[PDF] primary amine react with hcl
[PDF] primary amine synthesis
[PDF] primary and secondary sources examples
[PDF] primary and secondary sources lesson plan 5th grade
[PDF] primary and secondary sources powerpoint
[PDF] primary and secondary sources quiz
[PDF] primary and secondary sources worksheet
[PDF] primary and secondary sources worksheet 7th grade
[PDF] primary and secondary sources worksheet pdf
[PDF] primary arms 1 6 review
[PDF] primary arms 1x10
[PDF] primary arms 2020 catalog
