 Standard Reduction Potentials of Half-Cells - F2(g) + 2e- 2F-(aq) +
Standard Reduction Potentials of Half-Cells - F2(g) + 2e- 2F-(aq) +
Standard Reduction Potentials of Half-Cells. (Ionic concentrations are at 1M in water @ 250 C). Oxidizing Agents. Reducing Agents. E0 (Volts). F2(g) + 2e-. 2F-(
 APPENDIX H Standard Reduction Potentials*
APPENDIX H Standard Reduction Potentials*
APPENDIX H Standard Reduction Potentials. APPENDIX H. Standard Reduction Potentials*. Reaction. E (volts). dE /dT (mV/K). Aluminum. Al3+ + 3eJ. T Al(s). J1.677.
 Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C - Half-Reaction E° (V)
Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C - Half-Reaction E° (V)
Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C. Half-Reaction. E° (V). Ag. +. (aq) + e. - → Ag (s). +0.799. AgBr (s) + e. - → Ag (s) + Br. -. (aq). +0.095. AgCl (s) +
 CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics
CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics
Table 3 lists only those reduction potentials which have E° negative with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode. In Table 3 the reactions are listed in
 One-Electron Standard Reduction Potentials of Nitroaromatic and
One-Electron Standard Reduction Potentials of Nitroaromatic and
Reduction of explosives becomes less thermodynamically favorable as the one-electron standard reduction potential decreases from di- and tri-nitroaromatic
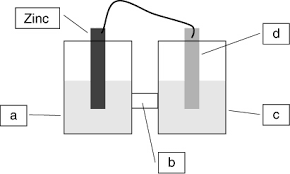 Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-Marked
Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-Marked
Using the Table of Standard Reduction Potentials table shown above what is the standard cell potential for an electrochemical cell that has iron (Fe) and
 Redox Potential Chart SELECTED STANDARD REDUCTION
Redox Potential Chart SELECTED STANDARD REDUCTION
Redox Potential Chart. SELECTED STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIALS @ 25◦C. Reduction Half-Reaction. E◦ (V). Au3+(aq) + 3 e−. → Au(s). +1.50. Hg2+(aq) + 2 e−. →
 Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell E°(V)
Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell E°(V)
Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell. E°(V). Na. +. (aq) + e. - → Na(s). -2.7144. Y. 3+. (aq) + 3e. - → Y(s). -2.370. Mg. 2+. (aq)+ 2e. - → Mg(s). -
 Standard Reduction Potentials from Chang 10th edition.pdf
Standard Reduction Potentials from Chang 10th edition.pdf
Page 1. Standard Reduction Potentials from Chang 10th edition.
 THE REDUCTION POTENTIAL OF THE COUPLE O3 /O
THE REDUCTION POTENTIAL OF THE COUPLE O3 /O
According to the Handbook of Chemistry and Physics [2] the ozone molecule is a powerful two-electron oxidant with a standard reduction potential of 2.07 V. The.
 Standard Reduction Potentials of Half-Cells - F2(g) + 2e- 2F-(aq) +
Standard Reduction Potentials of Half-Cells - F2(g) + 2e- 2F-(aq) +
Standard Reduction Potentials of Half-Cells. (Ionic concentrations are at 1M in water @ 250 C). Oxidizing Agents. Reducing Agents. E0 (Volts). F2(g) + 2e-.
 Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C - Half-Reaction E° (V)
Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C - Half-Reaction E° (V)
Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C. Half-Reaction. E° (V). Ag. +. (aq) + e. - ? Ag (s). +0.799. AgBr (s) + e. - ? Ag (s) + Br. -. (aq). +0.095.
 Environmental Standard Reduction Potentials
Environmental Standard Reduction Potentials
Environmental Standard Reduction Potentials. We will consider a simple reversible redox reaction for which we are able to measure.
 THE REDUCTION POTENTIAL OF THE COUPLE O3 /O
THE REDUCTION POTENTIAL OF THE COUPLE O3 /O
with a standard reduction potential of 2.07 V. The products of this reaction are oxygen and water. Since two-electron reactions are normally slow
 APPENDIX H Standard Reduction Potentials*
APPENDIX H Standard Reduction Potentials*
1964 and 1971); G. Milazzo and S. Caroli Tables of Standard Electrode Potentials (New York: Wiley
 Standard Reduction Potentials for Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Standard Reduction Potentials for Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Dec 7 2015 standard reduction potential of the O2 + 4e. ?. + 4H+ ? 2H2O couple in organic solvents. The values are +1.21 V in acetonitrile.
 Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell E°(V)
Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell E°(V)
Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell. E°(V). Na. +. (aq) + e. - ? Na(s). -2.7144. Y. 3+. (aq) + 3e. - ? Y(s). -2.370. Mg. 2+. (aq)+ 2e. - ? Mg(s).
 F2 (g) + 2e - ? 2F 2.87 PbO2 (s) + 4H + SO4 + 2e
F2 (g) + 2e - ? 2F 2.87 PbO2 (s) + 4H + SO4 + 2e
Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C. Reduction. E°r ed (V). F2 (g) + 2e. - ? 2F. -. 2.87. PbO2 (s) + 4H. +. + SO4. 2-. + 2e. - ? PbSO4(s) + 2H2O 1.69.
 Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-Marked
Test4 ch19 Electrochemistry Practice-answers-Marked
For the cell shown the standard reduction potentials are +0.80 V for Ag+ and –0.76 V for Zn2+. Based on the reduction potentials
 Standard Reduction Potentials
Standard Reduction Potentials
Standard Reduction Potentials. Alan D. Earhart. 11/22/2016. Standard Reduction Potentials. E°(V). Standard Reduction Potentials.
 [PDF] APPENDIX H Standard Reduction Potentials* - CSUN
[PDF] APPENDIX H Standard Reduction Potentials* - CSUN
1964 and 1971); G Milazzo and S Caroli Tables of Standard Electrode Reduction potentials for 1 200 free radical reactions are given by P Wardman
 [PDF] Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C - Half-Reaction E° (V)
[PDF] Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C - Half-Reaction E° (V)
Standard Reduction Potentials at 25°C Half-Reaction E° (V) Ag + (aq) + e - ? Ag (s) +0 799 AgBr (s) + e - ? Ag (s) + Br
 [PDF] CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics
[PDF] CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics
There are three tables for this electrochemical series Each table lists standard reduction potentials E° values at 298 15 K (25° C) and at a pressure
 [PDF] Chapter 18
[PDF] Chapter 18
The important characteristics of the standard electrode potential is: 1 It is a relative quantity---the potential of an electrochemical cell in which the
 [PDF] Standard Reduction Potential
[PDF] Standard Reduction Potential
The standard reduction potential is in a category known as the standard cell potentials or standard electrode potentials The standard cell potential is the
 [PDF] Standard Reduction Potentials - Alans Chemistry Site
[PDF] Standard Reduction Potentials - Alans Chemistry Site
Standard Reduction Potentials Alan D Earhart 11/22/2016 Standard Reduction Potentials E°(V) Standard Reduction Potentials
 [PDF] ElEctrochEmical SEriES - Petr Vanýsek - Chm Ulaval
[PDF] ElEctrochEmical SEriES - Petr Vanýsek - Chm Ulaval
Table 3 lists only those reduction potentials which have E° negative with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode In Table 3 the reactions are listed in
 [PDF] Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell E°(V) - (aq) + e
[PDF] Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell E°(V) - (aq) + e
Standard Reduction Potentials: Half Cell E°(V) Na + (aq) + e - ? Na(s) -2 7144 Y 3+ (aq) + 3e - ? Y(s) -2 370 Mg 2+ (aq)+ 2e - ? Mg(s)
 [PDF] Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr AO
[PDF] Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr AO
A redox reaction is an electrochemical reaction in which both reduction and oxidation take place together The redox potential data are extensively used for
What is standard reduction potential?
The standard reduction potential is the potential in volts generated by a reduction half-reaction compared to the standard hydrogen electrode at 25 °C, 1 atm and a concentration of 1 M. The standard reduction potential is defined relative to a standard hydrogen electrode, which is assigned the potential 0.00 V.How is standard reduction potential calculated?
The standard reduction potential can be determined by subtracting the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the anode from the standard reduction potential for the reaction occurring at the cathode. The minus sign is needed because oxidation is the reverse of reduction.What is standard reduction potential e0?
What is a Standard Redox Potential? A standard redox potential, symbol Eo, is the electric potential of an electrochemical half-cell relative to a standard electrochemical half-cell under standard conditions. Standard redox potential is also known as the standard reduction potential.- Reason: Standard reduction potential (SRP) of water is +1.23 V.
----------------------
[PDF] standard vs control chemistry
[PDF] standard vs control in laboratory
[PDF] standardization of tools
[PDF] standards for cosmetics
[PDF] standards for cosmetics in india
[PDF] standards for online learning
[PDF] standing alone rule in braille
[PDF] standstill period procurement ireland
[PDF] stanford encyclopedia of philosophy de beauvoir
[PDF] stanford hospital board internal message covid 19 snopes
[PDF] stanford house glendale
[PDF] stanford ib requirements
[PDF] stanley bijective proofs
[PDF] star academy 2 paris latino live
