 statics.pdf
statics.pdf
17 Oct 2023 At its core Engi- neering Statics provides the tools to solve static equilibrium problems ... possible solutions to the problem
 Chapter 3 Static Equilibrium
Chapter 3 Static Equilibrium
Summarizing we have found: T1 = 48.8N. T2 = 28.0N. T3 = 57.3N θ = 29.3◦. This answers all the parts of the problem. 2. The system in Fig. 3.3 is in
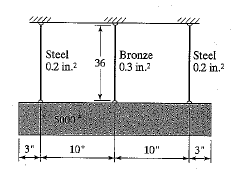 Example Problems on Static Equilibrium.pdf
Example Problems on Static Equilibrium.pdf
Example Problems on Static Equilibrium. Example 1. Suppose one truck is parked on a bridge as shown in Figure 1. The truck weighs. 1000 lb which is acting
 PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS
PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS
Fluid statics deals with problems associated with fluids at rest. The fluid Problems with the icon are solved using EES and complete solutions together with ...
 Solutions for Chapter 3 Problems for Sections 3.1 and 3.2 3.1 A 20
Solutions for Chapter 3 Problems for Sections 3.1 and 3.2 3.1 A 20
3.17 In both statics and dynamics the calculation of multiplying three vectors together using both the dot and cross products
 Statics – Formulas and Problems
Statics – Formulas and Problems
With the present collection “Engineering Mechanics 1 - Formulas and. Problems Statics” we provide more additional exercise material. For the solutions of the ...
 Engineering Mechanics (Statics) Stage
Engineering Mechanics (Statics) Stage
Mechanics (Statics). Instructor: Haider K. Sakban. First Year. Types of Friction Problems Solution: Free-Body Diagrams. The free-body diagram of the beam is ...
 Problems for Chapter 5 Statics PROBLEMS FOR SECTION 5.2-5.3
Problems for Chapter 5 Statics PROBLEMS FOR SECTION 5.2-5.3
Solution: This is a good time to point out that the exact location of the normal force N is not known until the equation of equilibrium determines it. x y /font
 Basic Fluid Statics Solved Problems
Basic Fluid Statics Solved Problems
SOLUTIONS. P.1CSolution. The system is illustrated below. The gage pressure is related to the vertical distance h between the two fluid levels by gage p gh ρ.
 STATICS
STATICS
SOLUTION: • Create a free-body diagram for the crane. • Determine B by solving the equation for the sum of the moments of all forces about A. Note there will be
 4 Solving Statics problems
4 Solving Statics problems
SAQ 49.) 4 Solving Statics problems. 4.1 Procedure me reiterate the steps in solving a Statics problem. Which of the above answers for the forces in the.
 Statics – Formulas and Problems
Statics – Formulas and Problems
Neither does it improve the problem solving skills. Using this collection wisely one has to try to solve the problems independently. The proposed solution
 statics.pdf
statics.pdf
provides the tools to solve static equilibrium problems for rigid bodies. The additional Apply the strategy to solve for unknowns and check solutions.
 Statics – Formulas and Problems
Statics – Formulas and Problems
Neither does it improve the problem solving skills. Using this collection wisely one has to try to solve the problems independently. The proposed solution
 Chapter 3 Static Equilibrium
Chapter 3 Static Equilibrium
forces and torques on rigid objects in statics problems we can treat the mass of the entire This answers all the parts of the problem.
 Example Problems on Static Equilibrium
Example Problems on Static Equilibrium
Example Problems on Static Equilibrium. Example 1. Suppose one truck is parked on a bridge as shown in Figure 1. The truck weighs.
 Access Free Fluid Statics Problems And Solutions File Type Pdf
Access Free Fluid Statics Problems And Solutions File Type Pdf
see guide Fluid Statics Problems And Solutions File Type Pdf as you such as. By searching the title publisher
 PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS
PRESSURE AND FLUID STATICS
SOLUTION The gage pressure of a vacuum chamber is given. The absolute Fluid statics deals with problems associated with fluids at rest. The fluid.
 Problems for Chapter 5 Statics PROBLEMS FOR SECTION 5.2-5.3
Problems for Chapter 5 Statics PROBLEMS FOR SECTION 5.2-5.3
Solution: This is a good time to point out that the exact location of the normal force N is not known until the equation of equilibrium determines it. x y /font
 “Dynamics” Review Problems and Solutions Downloaded from the
“Dynamics” Review Problems and Solutions Downloaded from the
“Dynamics” Review Problems and Solutions Downloaded from the Beer and Johnston Statics/Dynamics Website. Prepared by. Stephen F. Felszeghy.
 (PDF) Statics practice questions with solutions - Academiaedu
(PDF) Statics practice questions with solutions - Academiaedu
Statics practice questions with solutions
 [PDF] staticspdf
[PDF] staticspdf
neering Statics provides the tools to solve static equilibrium problems for rigid bodies The PDF is searchable and easy to navigate using embedded
 [PDF] Statics – Formulas and Problems
[PDF] Statics – Formulas and Problems
This collection of problems results from the demand of students for sup- plementary problems and support in the preparation for examinations
 (PDF) Statics Practice Problems - DOKUMENTIPS
(PDF) Statics Practice Problems - DOKUMENTIPS
DESCRIPTION Practice problems for a mechanical engineering statics class Text of Statics Practice Problems Page 1 Page 1: Statics Practice Problems
 [PDF] Engineering Mechanics Statics
[PDF] Engineering Mechanics Statics
This course covers: principles of statics Resultant of a force system Equilibrium of a force system Moment of a force Friction centroid and center of
 Statics Solved Problems - Engineer4Free
Statics Solved Problems - Engineer4Free
By choosing the $10 tier on Patreon you can immediately unlock all solutions 2 1 - Calculate the tension in each cable 2D Statics Solved Problem
 [PDF] Engineering Mechanics Statics Solved Problems Pdf
[PDF] Engineering Mechanics Statics Solved Problems Pdf
Recognizing the showing off ways to acquire this book Engineering Mechanics Statics Solved Problems Pdf is additionally useful You have remained in right site
 [PDF] Fluid Statics Problems And Solutions Pdf
[PDF] Fluid Statics Problems And Solutions Pdf
Thank you unconditionally much for downloading Fluid Statics Problems And Solutions Pdf Most likely you have knowledge that people have look numerous times
 [PDF] Solving Practical Engineering Mechanics Problems: Statics
[PDF] Solving Practical Engineering Mechanics Problems: Statics
In order to absorb the materials of engineering mechanics it is not enough to A solution of one similar sample problem from each topic is provided
How do you solve static problems?
In Physics, a static issue is one in which we must determine the force or torque operating on an object in static equilibrium. Static equilibrium is a sort of equilibrium in which the body remains immobile and the total of its forces and torques are equal to zero.What are 10 examples of static?
Some examples of static equilibrium could include a book at rest on top of a table and a balanced seesaw. Both situations satisfy the two conditions for static equilibrium. For a book at rest, the gravitational force and the normal force are balanced and no torque might cause the book to rotate.
Dietmar Gross · Wolfgang Ehlers
Ralf MüllerEngineering Mechanics 1
Statics ... Formulas and Problems
123Statics-Formulas and Problems
Dietmar Gross
Wolfgang Ehlers
Peter Wriggers
Ralf Müller
Statics-Formulas
and ProblemsEngineering Mechanics 1
123Dietmar Gross
Division of Solid Mechanics
TU Darmstadt
Darmstadt
Germany
Wolfgang Ehlers
Institute of Applied Mechanics
Stuttgart
Germany
Peter Wriggers
Institute of Continuum Mechanics
Hannover
Institute of Mechanics
EssenGermany
Ralf Müller
Institute of Applied Mechanics
TU Kaiserslautern
Kaiserslautern
Germany
ISBN 978-3-662-53853-1 ISBN 978-3-662-53854-8 (eBook)DOI 10.1007/978-3-662-53854-8
Library of Congress Control Number: 2016956635
©Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany 2017
This work is subject to copyright. All rights are reserved by the Publisher, whether the whole or part of the material is concerned, specically the rights of translation, reprinting, reuse of illustrations, recitation, broadcasting, reproduction on microlms or in any other physical way, and transmission or information storage and retrieval, electronic adaptation, computer software, or by similar or dissimilar methodology now known or hereafter developed. The use of general descriptive names, registered names, trademarks, service marks, etc. in this publication does not imply, even in the absence of a specic statement, that such names are exempt from the relevant protective laws and regulations and therefore free for general use. The publisher, the authors and the editors are safe to assume that the advice and information in this book are believed to be true and accurate at the date of publication. Neither the publisher nor the authors or the editors give a warranty, express or implied, with respect to the material contained herein or for any errors or omissions that may have been made.Printed on acid-free paper
This Springer imprint is published by Springer Nature The registered company is Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany The registered company address is: Heidelberger Platz 3, 14197 Berlin, GermanyPreface
This collection of problems results from the demand of students for sup- plementary problems and support in the preparation for examinations. With the present collection Engineering Mechanics 1 - Formulas and Problems, Statics we provide more additional exercise material. The subject Statics is commonly taught in the basic course of EngineeringMechanics classes at universities.
The problems analyzed within these courses use equilibrium condi- tions and the principle of virtual work to analyze static problems and to compute reaction forces and stress resultants. These concepts are the basic of many structural analyses of components used in civil and mechanical engineering. We would like to make the reader aware that pure reading and trying to comprehend the presented solutions will not provide a deeper under- standing of mechanics. Neither does it improve the problem solving skills. Using this collection wisely, one has to try to solve the problems independently. The proposed solution should only be considered when experiencing major problems in solving an exercise. Obviously this collection cannot substitute a full-scale textbook. If not familiar with the formulae, explanations, or technical terms the rea- der has to consider his or her course material or additional textbooks on mechanics of materials. An incomplete list is provided on page IX.Darmstadt, Stuttgart, Hannover,D. Gross
Essen and Kaiserslautern, Summer 2016W. Ehlers
P. Wriggers
J. Schr¨oder
R. M¨uller
Table of Contents
Bibliography, Nomenclature....................................IX2Center of Gravity, Center of Mass, Centroids...............29
3Support Reactions................................................45
5Beams, Frames, Arches..........................................97
7Work and Potential Energy.....................................169
8Static and Kinetic Friction......................................193
9Moments of Inertia...............................................217
Literature
Textbooks
Gross, D., Hauger, W., Schr¨oder, J., Wall, W., Rajapakse, N., Enginee- ring Mechanics 1: Statics, 2nd edition, Springer 2013 Hibbeler, R. C., Engineering Mechanics, Statics, Prentice Hall, 2012 Beer, F., Johnston, E.R., Mazurek, D., Vector Mechanics for Engineers:Statics, 11th edition, McGraw-Hill Education 2015
Beer, F., Johnston, E.R., Eisenberg, E., Cornwell, P., Mazurek, D., Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics, 11th edition,McGraw-Hill Education 2015
Collection of Problems
Hibbeler, R. C., Engineering Mechanics, Statics, Prentice Hall, 2012 Schaums Outlines of Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 6th Edition, McGraw-Hill Education 2010
Beer, F., Johnston, E.R., Mazurek, D., Vector Mechanics for Engineers:Statics, 11th edition, McGraw-Hill Education 2015
Notation
For the solutions of the problems we used the following symbols: α: Short notation forsum of all forces in direction of the arrow equal to zero. A: Short notation forsum of all moments with respect to reference pointA(with predetermined direction of rotation) equal to zero. ?Short notation forfrom this follows that. 1Chapter 1
Equilibrium
2Equilibrium
Forces with a common point of application in a
planeA system of forces with a common point
of application can be replaced by a statically equivalent force R= Fi.The system is inequilibrium, if
Fi=0 or in cartesian componentsFix=0?
Fiy=0?
Here we used the notation
Fi=Fixex+Fiyey?
Fix=Ficos?i?
Fiy=Fisin?i?
|Fi|=Fi= F 2 ix +F 2 iy i F iy F 1 F i F ix y x x y F i In agraphical solution, the equilibrium condition is expressed by aclo- sed force polygon. lines of actionforce polygon f i f F 1 F iForces with a common point of application in
spaceEquilibriumexists, if the resultantR=
Fivanishes, i.e. if
Fi=0 or in cartesian componentsFix=0?
Fiy=0?
Fiz=0?
Equilibrium3
Here, the following notation is used
Fi=Fixex+Fiyey+Fizez,
Fix=Ficosαi,
Fiy=Ficosβi,
Fiz=Ficosγi,
cos 2αi+ cos
2βi+ cos
2γi=1,
|Fi|=Fi= F 2 ix +F 2 iy +F 2 iz i i F ix i F iy F i F iz x z yGeneral systems of forces in a plane
A general system of forces can be re-
placed by a resultantR= Fiand a resulting momentM (A) R with re- spect to an arbitrary reference pointA. Equilibrium exists, if
Fix=0,
Fiy=0,
M (A) i =0. F 1 F i A y x Instead of using the two force conditions, two alternative moment con- ditions with dierent reference points (e.g.BandC) may be applied. Here the pointsA,BandCmust notlie on astraightline. Graphical solutions for the resultant force are obtained with the help of the link polygon and the force polygon. link polygon in layout diagramforce polygon f f f f 4 s ?s s s 4s r S S S S 4 S II Pol F 1 F 2 R F 3 F 44Equilibrium
The link linessiare parallel to the linesSiin the force polygon. The line of actionrof the resultantR(amplitude and direction follow from the force polygon) goes through the intersection of the outer link liness1ands5of the link polygon.quotesdbs_dbs4.pdfusesText_7[PDF] statistical measures of similarity
[PDF] statistics
[PDF] statistics 101 pdf
[PDF] statistics all formulas class 10
[PDF] statistics and machine learning in python pdf
[PDF] statistics austria building permits
[PDF] statistics austria immigration
[PDF] statistics austria migration
[PDF] statistics austria tourism
[PDF] statistics bootstrap methods and their application
[PDF] statistics formulas cheat sheet
[PDF] statistics formulas class 12
[PDF] statistics lecture notes pdf
[PDF] statistics of paramagnetism
