 Structures in C++
Structures in C++
13 янв. 2017 г. The next example gives an idea of how this could be done using a structure. This program will show how two measurements of type Distance can be ...
 Structures
Structures
Example: Write a C++ program that computes the area of rectangle using the structure Rectangle. #include<iostream.h> struct Rectangle. { float length; float
 Object Oriented Programming Using C++
Object Oriented Programming Using C++
STRUCTURE OF C++ PROGRAM. • Include files. • Class declaration. • Class functions definition. • Main function program. Example :- # include<iostream.h> class
 Programming TMS320x28xx and TMS320x28xxx Peripherals in C/C++
Programming TMS320x28xx and TMS320x28xxx Peripherals in C/C++
In the C/C++ Header Files and Peripheral Examples the register-file structures and bit fields have been implemented for all peripherals on the C28x cores
 C xor C++ Programming
C xor C++ Programming
5 дек. 2022 г. particular instance of incompatibility contrived code examples ... N.B. implementations frequently allow the declaration of an anonymous struct ...
 C++ Programming
C++ Programming
– Infinite!!! Page 19. Structure inside a structure. ○ Thankfully the previous example does not compile.
 Object-Oriented Programming in C++ Fourth Edition
Object-Oriented Programming in C++ Fourth Edition
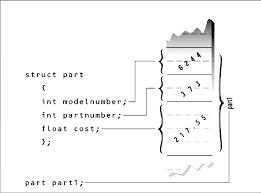
structure for the widget parts inventory last seen in such examples as PARTS in Chapter 4
 writing statistical algorithms for general model structures with
writing statistical algorithms for general model structures with
12 апр. 2016 г. For example the compiler resolves nodes in model objects at compile time so that the C++ code can find the right object by simple pointer ...
 Data Structure G S Baluja - web.mei.edu
Data Structure G S Baluja - web.mei.edu
Malik brings his proven approach to C++ programming to the CS2 course. Clearly written with the student in mind this text focuses on Data Structures and
 Using generic programming for designing a data structure for
Using generic programming for designing a data structure for
structure the responsibilities of the layers
 Structures in C++
Structures in C++
13 ene 2017 The next example gives an idea of how this could be done using a structure. This program will show how two measurements of type Distance can be ...
 C++ Programming
C++ Programming
An example. ? C does not have a type for complex numbers. ? Recall: a complex number is z = a + ib struct complex { double a; double b;. };.
 Programming TMS320x28xx and TMS320x28xxx Peripherals in C/C++
Programming TMS320x28xx and TMS320x28xxx Peripherals in C/C++
In the C/C++ Header Files and Peripheral Examples the register-file structures and bit fields have been implemented for all peripherals on the C28x cores of
 Where To Download Discrete Mathematical Structures 6 Editions
Where To Download Discrete Mathematical Structures 6 Editions
The sample programs along with a Microsoft Visual C++ .NET project for each is included with the book. The samples are of increasing sophistication and
 C and C++ Structure of this course Text books Past Exam Questions
C and C++ Structure of this course Text books Past Exam Questions
15 ene 2010 pointers structures. ? extended examples
 Download File PDF Mark Allen Weiss Solutions Manual (PDF
Download File PDF Mark Allen Weiss Solutions Manual (PDF
case analysis of heapsort * Offers source code from example programs via anonymous FTP 0201498405B04062001. Data Structures Using C++ D. S. Malik 2009-07-31
 Object-Oriented Programming in C++ Fourth Edition
Object-Oriented Programming in C++ Fourth Edition
C++ Programming Basics 29 Returning Structure Variables . ... Virtual Functions in a Graphics Example ......................................514.
 Structures
Structures
Example: Write a C++ program that computes the area of rectangle using the structure Rectangle. #include<iostream.h> struct Rectangle. { float length;.
 Practical C++ Programming
Practical C++ Programming
be used in the construction of advanced types such as structures unions
 Access Free Discrete Mathematical Structures Kolman Solutions
Access Free Discrete Mathematical Structures Kolman Solutions
continuous examples the student is shown that the optimum way to write a program is to design before you begin the actual coding into the. C++ language.
 [PDF] Structures in C++
[PDF] Structures in C++
13 jan 2017 · Structures in C++ similar to records in Pascal Here's an example program DAYENUM that uses an enumeration for the days of the week:
 (PDF) Structures in C++ - ResearchGate
(PDF) Structures in C++ - ResearchGate
2 fév 2021 · PDF This presentation is about Structures in C++ The presentation starts with explaining what the structure is
 [PDF] Chapter 14 Structures - Calgary
[PDF] Chapter 14 Structures - Calgary
14 1 2 Examples of Structures 14 1 3 Accessing Structure Members 14 1 4 Arrays of Structures 14 2 Structures and Pointers 14 2 1 Assigning Structures
 [PDF] Structures - C++ Programming
[PDF] Structures - C++ Programming
Structures are a general way to store more structures/objects is different in C++ and Java Thankfully the previous example does not compile
 [PDF] Structures
[PDF] Structures
In order to use a structure in our C++ programs we need the following: Example: Write a C++ program that computes the area of rectangle using
 [PDF] Introduction to Programming (in C++) Data structures
[PDF] Introduction to Programming (in C++) Data structures
Data structure design • Up to now designing a program (or a procedure or a function) has meant designing an algorithm The structure of the data on which
 [PDF] C++ Data Structures
[PDF] C++ Data Structures
C/C++ arrays allow you to define variables that combine several data items of the same kind but structure is another user defined data type which allows you to
 [PDF] Programmation C++ (débutant)/Les structures
[PDF] Programmation C++ (débutant)/Les structures
D'autres comporteront du code et porteront l'extension cpp Chaque programme sera constitué de modules : chaque module sera défini par un fichier h et un
 Structure of C++ Program: Layout of C++ Program Simple C++
Structure of C++ Program: Layout of C++ Program Simple C++
Instances of these data types are known as objects and can contain member variables constants member functions and overloaded operators defined by the
 [PDF] Practical C++ Programming - MIMUW
[PDF] Practical C++ Programming - MIMUW
This book is devoted to practical C++ programming It teaches you not only the mechanics of the language but also style and debugging
What are the basic structure of a C++ program?
In C++, a program is divided into the following three sections: Standard Libraries Section. Main Function Section. Function Body Section.What are structures in programming with examples?
A structure is used to represent information about something more complicated than a single number, character, or boolean can do (and more complicated than an array of the above data types can do). For example, a Student can be defined by his or her name, gpa, age, uid, etc.What is the structure of class in C++ program?
A class is defined in C++ using keyword class followed by the name of the class. The body of the class is defined inside the curly brackets and terminated by a semicolon at the end. class className { // some data // some functions };- Structure is a collection of variables of different data types under a single name. It is similar to a class in that, both holds a collecion of data of different data types. For example: You want to store some information about a person: his/her name, citizenship number and salary.
C++ Programming
Structures, Classes, Linked Lists
M1 Math
Michail Lampis
michail.lampis@dauphine.frStructures
Structures are a general way to store more
complicated objects in C/C++General syntax:
struct generalName { declare member1; declare member2;... struct generalName obj1, obj2;An example
C does not have a type for complex numbers
Recall: a complex number is z = a + ib
struct complex { double a; double b; struct complex z1,z2;Struct = a new type
The idea here is that when we define a
structure we define a new type of objectHence, we can define variables that have this
typeAt declaration, enough memory is allocated to
store all member properties of the structure objectAccessing inside members
Data stored inside a struct can be accessed
using the . operator struct Complex z1; z1.a = 7.2; z1.b = 5;The = operator
The = operator is automatically defined for all
structures struct Complex z1,z2; z1.a = 7.2; z1.b = 5.3; z2 = z1; //This is OK, will copy value-by-valueThe = operator
Be careful!
-The meaning of the = operator when applied to structures/objects is different in C++ and Java -Recall: in Java = copies a reference when dealing with objects -In C++, = copies field-by-field -This may or may not be what you want...Hidden =s
Consider the following program
struct Complex add(struct Complex z1, struct Complex a2) struct Complex res; res.a = z1.a + z2.a; res.b = z1.b + z2.b; return res;Hidden =s
The previous program is correct
However, it performs a number of = operations
-For each parameter, a new copy is allocated and data copied field-by-field -For the return value, a new copy is allocated and res is copied to it -Note: This is desirable, since res is deleted when the function terminates!Performance
The fact that so many copies are generally
performed means that performance degrades when passing/returning structsGenerally: we NEVER pass/return a struct
-We prefer to pass/return a pointer/reference to a struct -This is better because only a pointer (~8bytes) must be copied, independent of the complexity of the structPassing pointers
Consider the following program
struct Complex* add(struct Complex* z1, struct Complex* a2) struct Complex res; res.a = (*z1).a + (*z2).a; res.b = (*z1).b + (*z2).b; return &res;Wait a minute
The previous program contains a serious
mistake...What is the problem with the previous
program?Pointers to struct
The mistake was the res will be deleted, so its
address should not be returned...But the syntax is correct:
-(*z1) is an expression that dereferences the pointer z1 -Its type is struct Complex -Therefore, we can apply . to it.Fixed (?)
Consider the following program
struct Complex add(struct Complex z1, struct Complex a2) struct Complex *res = new struct Complex; (*res).a = (*z1).a + (*z2).a; (*res).b = (*z1).b + (*z2).b; return res; This is correct, but someone has to eventually delete the new structPointers to structures
Because pointer are used heavily when
dealing with structures, we avoid the (*p).field notationInstead we can use the - > operator
struct Complex *z1 = new struct Complex; (*z1).a = 2.2; z1->a = 2.2; //These two are equivalent!Declaring a structure
The declaration struct Complex { ... }; describes the general form of the objects of type Complex, that is, their class. C allows variables to be declared in the same line: struct Complex {double a; double b;} z1,z2;C also allows anonymous structs!
struct {double a; double b;} z3,z4; Careful! z1,z3 don't have the same type (z1=z3 fails)Inside a structure
We can declare as many fields as we like, using
standard conventions for variable names.Members can be arrays (of predetermined size)
-The = operator will also copy array fields!Members can be structures
struct C2 { struct Complex z; } zz; zz.z.a = 5.2;Members can be pointers
Structure inside a structure
Consider the following declaration
struct myStruct { int a; struct myStruct s; } obj1;How much memory does such an object need?
-Infinite!!!Structure inside a structure
Thankfully, the previous example does not compile
-MyStruct has not been defined yet!But this does:
struct myStruct { int a; struct myStruct *s; } obj1;This is strange, but is used A LOT!
A linked list of structures
Consider the following declaration
struct Node { int data; struct Node * next; Each object contains a number and a pointer to the next objectWe can build a list of ints!
Its size is unlimited!
A simple linked list
struct Node *cur,*prev; cur = prev = NULL; for(int i=0; i<20; i++){ cur = new struct Node; cur - > data = i; cur - > next = prev; prev = cur;A simple linked list
At the end of the previous program
-What is cur pointing to? -What is cur->data? -What is cur->next? -What is cur->next->next->next->data? NULL (or 0) is a special value that signifies that a pointer points to NOTHING -NULL ->data is a run-time error (seg fault)Exercise
Write a simple loop that prints all the numbers
stored in a linked listGiven: a pointer to the first element
Solution
void print_list(struct Node *head) while(head){ cout << head->data; head = head->next;Classes
A class is a more sophisticated version of a
structAllows us to define "objects"
-Initially, C++ was called "C with objects"Defining a class uses similar syntax and has a
similar logic to defining a structExample
class Complex { double a; double b; class Complex z1,z2;What's the difference?
Let's start with some easy differences:
-In C++ you don't have to use the class keyword when defining instances of an object (i.e. variables).You only need it to define the general class;
-Complex z1; //this would be correct -In fact, this is also true for struct, in C++. However, it is not true in C. -Using the struct/class keyword is allowed in C++Access restrictions
A second easy difference is that classes protect
inside data from being accessed. class Complex { double a; double b;Complex z1,z2;
z1.a = 5.2; //Error!Public and Private
The fields of a class are divided into public and privateBy default, all fields are private
We can specify the public part using the public: label class Complex { public: double a; double b;Complex z1,z2;
z1.a = 5.2; //OKMethods
The most important difference is that classes
may also contain methods, that is, functionsquotesdbs_dbs14.pdfusesText_20[PDF] student accommodation leicester
[PDF] student assistance team checklist
[PDF] student attribute restriction
[PDF] student database management system project in sql
[PDF] student health forms
[PDF] student immunization form vcu
[PDF] student internship program
[PDF] student journals
[PDF] student record keeping system database project
[PDF] student research proposal example pdf
[PDF] student solutions manual to accompany complex variables and applications
[PDF] student visa france
[PDF] student writing samples with errors
[PDF] students can modify the documents in the class notebook content library
