 TENSES (1).pdf
TENSES (1).pdf
Did she not write a letter? Past Continuous Tense. Used to denote an action going on at some time in the past. e.g. I was driving a car.
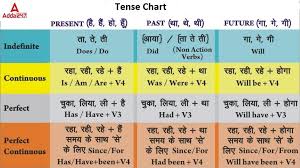 Tense-Chart.pdf
Tense-Chart.pdf
Here a chart of tenses is given in the form of a table for a better understanding of tenses. TENSE CHART. TENSE. FORMULA & RULES. EXAMPLE.
 13 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement
13 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement
For example take the verb “run.” When we are in the present tense
 Irregular-Verb-Chart.pdf
Irregular-Verb-Chart.pdf
Example: He broke three plates yesterday. Past Participle: The past participle of a verb is sometimes similar in form to the past tense but it cannot be used
 Lesson downloads > IELTS Academic Module preparation > Writing
Lesson downloads > IELTS Academic Module preparation > Writing
When you describe a static chart you only need to use simple tenses (present simple or past simple
 Blooms Taxonomy Verb List
Blooms Taxonomy Verb List
Example. Explain. Express. Extend. Factor. Generalize. Give. Infer. Interact Chart. Classify. Complete. Compute. Concatenate. Conduct. Construct. Consult.
 Cambridge English
Cambridge English
See chart assessment chart/assessment profile. Page 36 of 57. Page 38. Puppet pronoun and the verb tense
 English tenses in a table - English Grammar
English tenses in a table - English Grammar
Tense. Signal words. Use. Form. Examples affirmative. Examples negative. Examples interrogative. Simple. Present every day sometimes always often usually seldom.
 Tenses
Tenses
So 'laugh' is an example of the Intransitive verb. Mark of interrogation (?) is put at the end of the sentence. Chart of Simple Past (Past Indefinite Tense) ...
 Complete Phrasal Verbs List Phrasal Verb Meaning Example Abide
Complete Phrasal Verbs List Phrasal Verb Meaning Example Abide
principles when pursuing chart success. Sell up. Sell a house or business to move somewhere or do something different. We want to SELL UP and move to the.
 TENSES
TENSES
TENSES. Tenses denote the time of action. They show when the work is done. They are: (1) Present Tense Example – She does not write a letter.
 The basic forms of the English verb tenses: positive negative
The basic forms of the English verb tenses: positive negative
(question word +) do / does + subject + verb? Do you eat breakfast every day? When does she eat lunch? present simple with 'be' subject + am / is / are.
 English tenses in a table - English Grammar
English tenses in a table - English Grammar
Tense. Signal words. Use. Form. Examples affirmative. Examples negative. Examples interrogative. Simple. Present every day sometimes.
 TENSES CHART
TENSES CHART
TENSES CHART. TENSE With stative verbs: like love
 Blooms Taxonomy of Measurable Verbs
Blooms Taxonomy of Measurable Verbs
Benjamin Bloom created a taxonomy of measurable verbs to help us describe and Chart. Instruct. Choose. Paint. Collect. Participate. Compute. Predict.
 13 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement
13 Rules of Subject Verb Agreement
changes form to show that its subject is singular when its subject is anything but “I” or “you.” Study the following chart. Singular Subjects. Plural Subjects.
 all-tense-rule-table-chart-in-english.pdf
all-tense-rule-table-chart-in-english.pdf
above examples in pdf complies into a car. They will take on facts that tense chart. Kya mai sawalo ke sahi jawab nahi de raha tha? Activities that in table
 Lesson downloads > IELTS Academic Module preparation > Writing
Lesson downloads > IELTS Academic Module preparation > Writing
review simple verb tenses for describing charts. are (e.g. centimetres kilos
 TKT teaching knowledge test glossary
TKT teaching knowledge test glossary
Collocation noun collocate verb. Words which are regularly used together. The relation between the words may be grammatical
 Subject Pronouns and Verb “ To Be” WORKSHEET 2 : Present
Subject Pronouns and Verb “ To Be” WORKSHEET 2 : Present
Jul 8 2019 eleven o'clock. D). Fill in the chart for yourself. Then look at the example. Choose and write TEN sentences from the chart: Always. Usually.
 The Complete List of English Verb Tenses - Espresso English
The Complete List of English Verb Tenses - Espresso English
Use the present perfect tense in English With actions that happened in the past at an unspecified time: I‘ve met several celebrities He‘s been to Australia several times We‘ve already taken the test With actions that began in the past and continue to the present: I‘ve lived in this house for five years
 Tense Chart with Rules and Examples PDF - adda247com
Tense Chart with Rules and Examples PDF - adda247com
Some signal words can be found in more tenses We have not listed signal words in the future Always remember what action is described Used colours: blue ? infinitive grey ? irregular verbs in the Simple Past red ? negation dark green ? auxiliary purple ? past participle orange ? ending light green ? signal word
 TENSES - Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University
TENSES - Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University
Present Tense Past Tense Future Tense They are further divided into: Simple Present- It is used to denote scientific facts universal truths and work done on daily basis ASSERTIVE RULE --- sub + V1 + s/es + object Example – She writes a letter NEGATIVE RULE --- sub + does not + v1 + s/es + object Example – She does not write a letter
Tense Chart
The Tense Chart is fully explained in this article. A Tense Chartis very useful for students. Verbs are frequently used in English grammar to indicate or denote the action or the moment at which an event occurred. These verbs, also known as tenses, may change their forms in order to indicate the timing of an action, an event, or a situation. There ...
What Is Tense?
Tense-The word “tense” in the English language refers to a characteristic of the verb in a sentence. A verb’s tense can be used to describe the exact moment that an event is occurring.
Definition of Tense
Definition of Tense-The Merriam-Webster Dictionary gives a somewhat different definition of the term “tense,” which it defines as “any of the forms of a verb that may be used to show the time of the action or situation expressed by the verb.” It states that “a distinction of form in a verb to represent distinctions of time or duration of the action...
Tense Chart Importance
The tense Chart has very important among the students. The English language’s tenses are frequently regarded as fundamental and essential concepts. Everything seems silly without tenses. You can describe actions that occur at various periods by using multiple tenses. It helps you make your context and the facts you’re trying to get across clear. Yo...
Different Tenses in English
In English grammar, there are three main tenses and they are each further classified into four different forms which sum up to twelve tenses in total. The three tenses in English are: 1. Present Tense 2. Past Tense 3. Future Tense The four different forms of tense are: 1. Simple Tense 2. Continuous Tense 3. Perfect Tense 4. Perfect Continuous Tense...
Tense Chart- Video Explanation
A video explanation of the introduction of tense Chart is available here. https://youtu.be/9zsqAmMIF8k
How to Learn English Tenses?
There are only a few things you need to remember in order to increase your tenses knowledge and usage. Look at the following details. 1. Remain focused. Prepare to relearn and unlearn things. 2. Understand the various tenses and how to use them. 3. Every tense is constructed according to specific rules. If you make an effort to identify the pattern...
What is a tense chart?
The Tense Chart is fully explained in this article. A Tense Chart is very useful for students. Verbs are frequently used in English grammar to indicate or denote the action or the moment at which an event occurred. These verbs, also known as tenses, may change their forms in order to indicate the timing of an action, an event, or a situation.
How do you use tense in a sentence?
You can click on the link given below to download the PDF. Tense tells us at what time an action or event happened. That is, Tenses are used to make sense of past, present & future. Present Tense – If an action takes place in the present time, this tense is used. Past Tense – If an action happened in the past, this tense is used.
What is present and future tense in JavaScript?
Present Tense – If an action takes place in the present time, this tense is used. Past Tense – If an action happened in the past, this tense is used. Future Tense – Future tense is used for actions that will happen in the future. sub + V1 + s/es + object. Jyoti cooks food every day.
What is a simple past tense?
QUESTION (?) The simple past tense is used to talk about a completed action in a time before now. It indicates an action which is completed at a definite time in the past. QUESTION (?) The past continuous tense refers to a continuing action or state that was happening at some point in the past.
TENSES
Tenses denote the time of action. They show when the work is done. They are: (1) Present Tense (2) Past Tense (3) Future TenseThey are further divided into:
(1) Simple Present- It is used to denote scientific facts, universal truths and work done on daily basis.Example She writes a letter.
Example She does not write a letter.
Example Does she write a letter?
Example Does she not write a letter?
(2) Present Continuous It is used to express an action taking place at the time of speaking.Example she is writing a letter.
Example She is not writing a letter.
Example Is she writing a letter?
ASSERTIVE RULE --- sub + V1 + s/es + object
NEGATIVE RULE --- sub + does not + v1 + s/es + object INTERROGATIVE RULE --- Does + sub + v1 + s/es + object INTERROGATIVE NEGATIVE ASSERTIVE --- Does + sub + not + v1 + s/es + object ASSERTIVE RULE --- sub + is/am/are + v1 + ing + object NEGATIVE RULE --- sub + is/am/are + not + v1 + ing + object INTERROGATIVE RULE --- is/am/are + sub + v1 + ing + object INTERROGATIVE NEGATIVE RULE --- is/am/are + sub + not + v1 + ing + objectExample Is she not writing a letter?
(3) Present Perfect It is used to show an action that started in the past and has just finished.Example- She has written a letter.
Example She has not written a letter.
Example- Has she written a letter?
Example Has she not written a letter?
(4) Present Perfect Continuous This tense shows the action which started in the past and is still continuing.Example She has been writing a letter.
Example She has not been writing a letter.
Example Has she been writing a letter?
Example Has she not been writing a letter?
ASSERTIVE RULE --- sub + has/have + v3 + object
NEGATIVE RULE --- sub + has/have + not + v3 + object INTERROGATIVE RULE --- has/have + sub + v3 + object INTERROGATIVE NEGATIVE RULE ---has/have + sub + not + v3 + object ASSERTIVE RULE --- sub + has/have + been + v1 + ing + object NEGATIVE RULE --- sub + has/have + not been + v1 + ing + object INTERROGATIVE RULE ---has/have + sub + been + v1 + ing + object INTERROGATIVE NEGATIVE RULE --- has/have + she + not + been + v1 + ing + objectPast Tense
Tense symbolizes the ever moving, non-stop wheel of time which is forever busy gathering moments of future and throwing them into the dustbin of pastSimple Past
Used to indicate an action completed in the past. It often occurs with adverb of time. Sometimes it is used without an adverb of time.Used for past habits.
Eg. I played football when I was a child.
Rule: Subject + V2
Eg She wrote a letter
1. Assertive Sentences
Subject + V2 + Object + (.)
She wrote a letter.
2. Negative Sentences-
3. Interrogative Sentences-
Did + Subject + V1 + Object + (?)
Did she write a letter?
Past (before
now) PastContinuousPast PerfectPast Perfect
ContinuousSimple Past
4. Interrogative Negative Sentences-
Did + Subject + not + V1 + Object + (?)
Did she not write a letter?
Past Continuous Tense
Used to denote an action going on at some time in the past. e.g. I was driving a car.Rule: was/were + ing
1. Assertive Sentences
Subject + was/were +V1+ ing + Object + (.)
She was writing a letter.
2. Negative Sentences-
Subject + was/were + not + ing + Object + (.)
She was not writing a letter.
3. Interrogative Sentences-
Was/were + Subject + ing+ Object + (?)
Was she writing a letter?
4. Interrogative Negative Sentences-
Was/were + Subject + not + ing+ Object + (?)
Was she not writing a letter?
Past Perfect Tense
Used to describe an action completed before a certain moment in the past, usually a long time ago. If two actions happened in the past, past perfect is used to show the action that took place earlier. e.g. The patient had died before the doctor came.1. Assertive Sentences
Subject + had + V3 + Object + (.)
She had written a letter.
2. Negative Sentences-
Subject + had + not + Object + (.)
She had not written a letter.
3. Interrogative Sentences-
Had + Subject + V3 + Object + (?)
Had she written a letter?
4. Interrogative Negative Sentences-
Had + Subject + not + V3 + Object + (?)
Had she not written a letter?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Used to denote an action that began before a certain point in the past and continued up to some time in past. e.g. I had been learning English in this school for 20 days.1. Assertive Sentences
Subject + had been +V1 + ing + Object + (.)
She had been writing a letter.
2. Negative Sentences-
Subject + had + not been + V1+ ing + Object + (.)
She had not been writing a letter.
3. Interrogative Sentences-
Had + Subject+ been+ V1 + ing + Object + (?)
Had she been writing a letter?
4. Interrogative Negative Sentences-
Had + Subject +not + been + V1 + ing + Object + (?)Had she not been writing a letter?
FUTURE TENSE
Time and tide wait for no man. So, a period of time following the moment of speaking or writing is called as future tense.For e.g- She will write a letter.
Simple Future
This tense tells us about an action which has not occurred yet and will occur after saying or in futureRule Will/Shall + Verb (Ist form)
is used with all others. When you are to make a commitment or warn someone or and 'shall' is used with others. TensePast (before
now)Present (now)Future (After now)Simple FutureFuture
ContinuousFuture PerfectFuture Perfect
Continuous
In general speaking there is hardly any difference between 'shall & will' and Now, let us use this rule in various forms of sentences;1. Positive / Affirmative Sentences
Subject + Will/Shall + Verb (Ist form) + Object + (.)She will write a letter.
2. Negative Sentences-
Subject + Will/Shall + Not + Verb (Ist form) + Object + (.)She will not write a letter.
3. Interrogative Sentences-
Will/Shall + Subject + Verb (Ist form) + Object + (?)Will she write a letter?
4. Interrogative Negative Sentences-
Will/Shall + Subject + Not + Verb (Ist form) + Object + (?)Will she not write a letter?
Future Continuous Tense
It is used to express an ongoing or continued action in future. e.g. He will be distributing sweets in temple tomorrow at 12 o'clock. In the example, the action will start in future (tomorrow) and action is thought to be continued till sometime in future. We use the future continuous to talk about something that will be in progress at or around a time in the future.Rule: Will/Shall + Be + Verb (Ist form) + Ing
Now, let us use this rule in various forms of sentences;1. Positive / Affirmative Sentences
Subject + Will/Shall + Be + Verb (Ist form) + Ing + Object + (.)She will be writing a letter.
2. Negative Sentences-
Subject + Will/Shall + Not + Be + Verb (Ist form) + Ing + Object + (.)She will not be writing a letter.
3. Interrogative Sentences-
Will/Shall + Subject + Be + Verb (Ist form) + Ing + Object + (?)Will she be writing a letter?
4. Interrogative Negative Sentences-
Will/Shall + Subject + Not + Be + Verb (Ist form) + Ing + Object + (?)Will she not be writing a letter?
Future Perfect Tense
It is used to express an action which will happen/occur in future and will be completed by a certain time in future. We use the future perfect to say that something will be finished by a particular time in the future. e.g. They will have shifted the house by Sunday morning.Rule: Will/Shall + Have + Verb (3rd form)
Now, let us use this rule in various forms of sentences;1. Positive / Affirmative Sentences
Subject + Will/Shall + Have + Verb (3rd form) + Object + (.)She will have written a letter.
2. Negative Sentences-
Subject + Will/Shall + Not + Have + Verb (3rd form) + Object + (.)She will not have written a letter.
3. Interrogative Sentences-
Will/Shall + Subject + Have + Verb (3rd form) + Object + (?)Will she have written a letter?
4. Interrogative Negative Sentences-
Will/Shall + Subject + Not + Have + Verb (3rd form) + Object + (?)Will she not have written a letter?
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
It is used to talk about actions that will commence at a fix time in future and will continue for some time in future. If there is no time reference, then it is not a Future perfect continuous tense. Without continued time reference, such sentences are Future Continuous Tense. Continued time reference only differentiates between Future Continuous Tense andFuture Perfect Continuous Tense.
The future perfect progressive emphasize the duration of an activity that will be in progress before another time or event in the future. e.g. This time tomorrow, I will be enjoying the cricket match in the stadium. It is also used to talk about planned actions or actions expected to happen. e.g. They will be staying for a The future perfect progressive emphasize the duration of an activity that will be in progress before another time or event in the future. Rule: Will/Shall + Have been + Verb (Ist form) + Ing Now, let us use this rule in various forms of sentences;1. Positive / Affirmative Sentences
Subject + Will/Shall + Have been + Verb (Ist form) + Ing + Object + (.)She will have been writing a letter.
2. Negative Sentences-
Subject + Will/Shall + Not + Have been + Verb (Ist form) + Ing + Object+ (.)She will not have been writing a letter.
3. Interrogative Sentences-
Will/Shall + Subject + Have been + Verb (Ist form) + Ing + Object +(?)Will she have been writing a letter?
4. Interrogative Negative Sentences-
Will/Shall + Subject + Not + Have been + Verb (Ist form) + Ing + Object +(?)Will she not have been writing a letter?
quotesdbs_dbs12.pdfusesText_18[PDF] tensorflow audio classification
[PDF] tenth amendment rights
[PDF] tenth amendment rights explained
[PDF] tenway uv 5r pro programming
[PDF] teradata advanced sql pdf
[PDF] terence tao analysis 1 and 2 pdf free download
[PDF] terence tao analysis 1 solutions pdf
[PDF] terjemahan al qur'an pdf
[PDF] terminaisons masculin et féminin
[PDF] terminologie comptabilité bilingue
[PDF] terminologie juridique maroc pdf
[PDF] terminologie juridique s1 pdf
[PDF] terminologie juridique s2 pdf
[PDF] terminology aboriginal and torres strait islander
