 OER Math 1060 – Trigonometry
OER Math 1060 – Trigonometry
CHAPTER 4 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES AND FORMULAS. 166. 4.1 The Even/Odd answers. For example when fitting a sine function to the data
 Sections 4.1-4.4
Sections 4.1-4.4
. Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC. -4-. Evaluate the trigonometric function using Chapter 4: Trigonometric. Functions. Sections 4.5-4.7. Page 38. © P2w0y1o9G ...
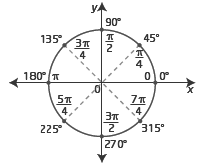 Chapter 4 Trigonometry and the Unit Circle
Chapter 4 Trigonometry and the Unit Circle
Chapter 4. Page 7 of 85. Section 4.1 Page 176. Question 12 a) Use a proportion with r = 9.5 and central angle 1.4 radians. arc length central angle.
 Worked Examples from Introductory Physics (Algebra–Based) Vol. I
Worked Examples from Introductory Physics (Algebra–Based) Vol. I
၂၀၁၂၊ အောက် ၃ 4.1.4 Units and Stuff . ... CHAPTER 4. FORCES I. F. F. Rearth. Figure 4.3: Earth exerts force F on ...
 Untitled
Untitled
Trigonometry (4.1-4.4). Name. Key. Chapter 4 Review Problems: Non-calculator. Find the exact value of each of the trigonometric functions given. Watch signs! 5π.
 CHAPTER 4 Trigonometric Functions
CHAPTER 4 Trigonometric Functions
Section 4.1. Radian and Degree Measure. 273. 9. (a). (b) x y π. 3. 2. 2. 3 x. 11. 6 π Answers will vary. (Make a Decision). □ You should be able to graph: □ ...
 tangent – the slope ratio (trigonometry) 4.1.1
tangent – the slope ratio (trigonometry) 4.1.1
In the first section of Chapter 4 students consider different slope triangles for a given line or segment and notice that for each line
 Lesson 4.1.1 - 4-6.
Lesson 4.1.1 - 4-6.
The slope ratio for 68°≈ 2.5 so. BC≈ 4 feet. Thus
 Chapter 4 Trigonometry
Chapter 4 Trigonometry
Chapter 4. Trigonometry. Section 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure. Objective: In this lesson you learned how to describe an angle and to convert between radian
 NEW GENERAL MATHEMATICS
NEW GENERAL MATHEMATICS
• Chapter revision test answers: the answers for all the chapter revision tests are Assign questions 1 3 and 4 from Worksheet 4 as homework. Assessment.
 CHAPTER 4 Trigonometry
CHAPTER 4 Trigonometry
306 Chapter 4 Trigonometry. © 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. Sample answers: ... Section 4.1 Radian and Degree Measure 307.
 Untitled
Untitled
160 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions. Chapter 4 Section 4.1 Angles and Their Measures ... (This would be the answer for any two adjacent lanes.).
 Chapter 4 Trigonometry and the Unit Circle
Chapter 4 Trigonometry and the Unit Circle
MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Section 4.1 Page 175 ... Joran's answer includes the given angle obtained when n = 0.
 4 Trigonometric Functions
4 Trigonometric Functions
shown in FIGURE 4.1.4 CHAPTER 4 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS ... Exercises 4.1 Answers to selected odd-numbered problems begin on page ANS–14.
 Chapter 4
Chapter 4
Precalculus with Limits Answers to Section 4.1. 1. Chapter 4. Section 4.1 (page 290) 4. radians. 5. 1 radian. 6. 6.5 radians. 7. (a) Quadrant I.
 164 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
164 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions
4. ? radians. Quick Review 4.1. 1. C=2? 2.5=5? in. 2. C=2? 4.6=9.2? m. 3. 4. (This would be the answer for any two adjacent lanes.).
 Chapter 4- Trigonometry
Chapter 4- Trigonometry
Chapter 4- Trigonometry 4.1 – Special Angles 1 - Worksheet ... 4. Solve the following equations for 0° ? ? 360°. Round answers to the nearest ...
 OER Math 1060 – Trigonometry
OER Math 1060 – Trigonometry
CHAPTER 4 TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES AND FORMULAS. 166. 4.1 The Even/Odd Identities Use your answer from part (1) to determine the radian measure for ...
 Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric Functions
CHAPTER 4 Trigonometric Functions. 4.1. Angles and Their Measures You may use a graphing calculator when answering these questions.
 4 Trigonometry - 4.1 Squares and Triangles
4 Trigonometry - 4.1 Squares and Triangles
Find the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle shown in the diagram. Give your answer correct to. 2 decimal places. Solution. As this is a right angled
 Trigonometry worksheets and PowerPoints - DoingMaths
Trigonometry worksheets and PowerPoints - DoingMaths
Chapter 4 8 Glencoe Precalculus Word Problem Practice Right Triangle Trigonometry 1 MONUMENTS The Leaning Tower of Pisa in Italy is about 55 9 meters tall and is leaning so it is only about 55 meters above the ground At what angle is the tower leaning? about 10 3° 2 SUBMARINES A submarine that is 250 meters below the surface of the ocean
 C H A P T E R 4 Trigonometric Functions - Fraser HS Math
C H A P T E R 4 Trigonometric Functions - Fraser HS Math
274 Chapter 4 Trigonometric Functions 12 (a) Coterminal angles for (b) Coterminal angles for 5p 4 2 2p5 2 3p 4 5p 4 1 2p5 13 p 4 5p 4: 7p 6 2 2p5 2 5p 6 7p 6 1 2p5 19 p 6 7p 6: 13 (a) Coterminal angles for
 Trigonometry Worksheet T1 – Labelling Triangles
Trigonometry Worksheet T1 – Labelling Triangles
Trigonometry Worksheet T4 – Calculating Angles - ANSWERS 1 23 58o sin 0 4 sin 0 4 10 4 sin 1 = = = = ? s s s s 6 38 68o sin 0 625 sin 0 625 8 5 sin 1 = = = = ? b b b b 2 60o cos 0 5 cos 0 5 12 6 cos 1 = = = = ? c c c c 7 73 74o tan 3 428571429 tan 3 428571429 7 24 tan 1 = = = = ? z z z z 3 63 43o tan 2 tan 2 9 18 tan 1
What is a trigonometry worksheet?
A worksheet with various right-angles and isosceles triangles where trigonometry is needed to find the missing side lengths. This worksheet uses cos, sin and tan. A worksheet containing various right-angles triangles with missing angles, requiring the use of trigonometry to find them. This worksheet use sin, cos and tan.
What is Chapter 8 Introduction to trigonometry?
Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry is included under Unit 5 Trigonometry of class 10 maths syllabus. Chapter 8 exercise 8.2 covers important questions based on trigonometric ratios of some specific angles. Download PDF: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Exercise 8.2
What is trigonometry Unit 4?
The topics in this unit serve as the underpinning for trigonometry studied in Unit 4 and provide the first insight into geometry as a modeling tool for contextual situations. This unit begins with Topic A, Dilations off the Coordinate Plane. Students identify properties of dilations by performing dilations using constructions.
Chapter 4 Trigonometry and the Unit Circle
Section 4.1 Angles and Angle Measure
Section 4.1 Page 175 Question 1
a) -4ʌ is a clockwise rotation b) 750° is a counterclockwise rotation c) -38.7° is a clockwise rotation d) 1 radian is a counterclockwise rotationSection 4.1 Page 175 Question 2
a) 30°ʌ30180
ʌ 6
b) 45°ʌ45180
ʌ 4
c) -330°ʌ330180
11ʌ 6
d) 520°ʌ520180
26ʌ 9
MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Page 2 of 85 e) 90°ʌ90180
ʌ 2
f)21°
ʌ21180
7ʌ 60
Section 4.1 Page 175 Question 3
a) 60°ʌ60180
ʌ 3
1.05 b) 150°ʌ150180
5ʌ 6
2.62 c) -270°ʌ270180
3ʌ 2
4.71 d) 72°ʌ72180
2ʌ 5
1.26 e) -14.8°ʌ14.8180
1481800
37
450
0.26 f) 540°
ʌ540180
3 9.42Section 4.1 Page 175 Question 4
a)ʌ180
6630
b) 2
ʌ2(180 )
33120
c) 3
ʌ3(180 )
8867.5
d) 5
ʌ5(180 )
22450
e)
18011ʌ
18057.3
f)
1802.75 2.75ʌ
495157.6
MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Page 3 of 85
Section 4.1 Page 175 Question 5
a) 2ʌ2(180 )
77360
7
51.429
b) 7ʌ7(180 )
13 13 126013
96.923
c)2 2 180
33ʌ
12038.197
d)1803.66 3.66ʌ
658.8209.703
e)1806.14 6.14ʌ
1105.2
351.796
f)18020 20ʌ
36001145.916
Section 4.1 Page 175 Question 6
a) An angle that measures 1 radian is in quadrant I. b) An angle that measures 225° is in quadrant II. c) An angle that measures17ʌ
6 is in
quadrant II. d) An angle that measures 650° is in quadrant IV. e) An angle that measures 2ʌ3 is in
quadrant III. MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Page 4 of 85 f) An angle that measures -42° is in quadrant IV.Section 4.1 Page 176 Question 7
a)72° + 360° = 432° 72° - 360° = -288°
For an angle of 72°, one positive coterminal angle is 432° and one negative coterminal angle is -288°. b)3ʌ11ʌ2ʌ44 3ʌ5ʌ 2ʌ44
For an angle of
34, one positive coterminal angle is 11ʌ
4 and one negative coterminal
angle is - 5ʌ 4. c) -120° + 360° = 240° -120° - 360° = -480° For an angle of -120°, one positive coterminal angle is 240° and one negative coterminal angle is -480°. d)11ʌ7ʌ2ʌ22
11ʌʌ6ʌ 22
For an angle of
11ʌ
2, one positive coterminal angle is 7ʌ
2 and one negative coterminal
angle is 2. e) -205° + 360° = 155° -205° - 360° = -565° For an angle of -205°, one positive coterminal angle is 155° and one negative coterminal angle is -565°. f) 7.8 - 2ʌ 1.5 7.8 - 4ʌ -4.8 For an angle of -7.8, one positive coterminal angle is 1.5 and one negative coterminal angle is -4.8. MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Page 5 of 85Section 4.1 Page 176 Question 8
a)The angles
56 and 17ʌ
6 are coterminal because
5ʌ5ʌ12ʌ2ʌ666
17ʌ
6 b) The angles 52 and 17ʌ
6 are not coterminal because 5ʌ
2 is coterminal with ʌ
2 which
falls on the positive y-axis, while17ʌ
6 is coterminal with 5ʌ
6, which is in quadrant II.
c) The angles 410° and -410° are not coterminal because 410° is coterminal with 50° and so is in quadrant I, while -410° is coterminal with 310° and is in quadrant IV. d) The angles 227° and -493° are coterminal because -493° is coterminal with -493° + 2(360°) which is 227°.Section 4.1 Page 176 Question 9
a) The coterminal angles for 135° are 135° ± (360°)n, where n is any natural number. b) The coterminal angles for2 are ʌ2ʌ2
n, where n is any natural number. c) The coterminal angles for -200° are -200° ± (360°)n, where n is any natural number. d) The coterminal angles for 10 radians are 10 ± 2ʌn, where n is any natural number.Section 4.1 Page 176 Question 10
Example: Choose -45°.
-45° = -45° + 360° = 315°In general, all angles coterminal with -45°
are given by -45° ± (360°) n, where n is any natural number. MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Page 6 of 85Section 4.1 Page 176 Question 11
a)65° + 360° = 425°
In the domain 0°
ș < 720°, the angle 425° is coterminal with 65°. b) -40° + 360° = 320° In the domain -180° ș < 360°, the angle 320° is coterminal with -40°. c) -40° + 360° = 320° -40° - 360° = -400° -40° + 2(360°) = 680° In the domain -720° ș < 720°, the angles -400°, 320°, and 680° are coterminal with -40°. d) 3ʌ5ʌ2ʌ44
In the domain -2
ș < 2ʌ, the angle
5ʌ4 is coterminal with 3ʌ
4. e) 11ʌ23ʌ2ʌ66 11ʌʌ2ʌ66
11ʌ13ʌ4ʌ66
In the domain -4
ș < 4ʌ, the angles
236 6 and
13ʌ
6 are coterminal with 11ʌ
6. f) 7ʌʌ2ʌ33 7ʌ5ʌ4ʌ33
In the domain, -2
ș < 4ʌ, the angles
3 and 5ʌ
3 are coterminal with 7ʌ
3. g) 2.4 - 2ʌ -3.9In the domain -2
ș < 2ʌ, the angle -3.9 is coterminal with 2.4. h) -7.2 + 2ʌ -0.9 -7.2 + 4ʌ 5.4 -7.2 - 2ʌ -13.5 (outside specified domain)In the domain -4
ș < 2ʌ, the angles -0.9 and 5.4 are coterminal with -7.2. MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Page 7 of 85Section 4.1 Page 176 Question 12
a) Use a proportion with r = 9.5 and central angle 1.4 radians. arc length central angle=circumference complete rotation arc length 2ʌ() 2ʌ
arc length 1.4(9.1.4 9.5 5) 13.3The arc length is 13.3 cm.
b) Use the formula a = șr, with r = 1.37 and ș = 3.5. a = 3.5(1.37) = 4.795 The arc length is 4.80 m, to the nearest hundredth of a metre. c) Use a proportion with r = 7 and central angle 130°. arc length central angle=circumference complete rotation arc length 2ʌ( ) 360
13(14ʌ)ar13
c le0 7 ngth 3615.88 The arc length is 15.88 cm, to the nearest hundredth of a centimetre. d) Use a proportion with r = 6.25 and central angle 282°. arc length central angle=circumference complete rotation arc length 2
ʌ( ) 360
282(12.5ʌ)arc l282
6.2 ength 3560
30.76
The arc length is 30.76 in., to the nearest hundredth of an inch. MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Page 8 of 85
Section 4.1 Page 176 Question 13
a) Use the formula a = șr, with a = 9 and r = 4. 9ș(4)
94= ș
2.25 =
The central angle is 2.25 radians.
b) Use the formula a = șr, with ș = 1.22 and r = 9. a = 1.22(9) = 10.98The arc length is 10.98 ft.
c) Use the formula a = șr, with a = 15 and ș = 3.93. 15 3.93 r 153.93 =
r 3.82 r The radius is 3.82 cm, to the nearest hundredth of a centimetre. d) Use a proportion with r = 7 and central angle 140°. arc length central angle=circumference complete rotation arc length 2ʌ( ) 360
14(14ʌ)ar14
c le0 7 ngth 3617.10 The arc length is 17.10 m, to the nearest hundredth of a metre.
Section 4.1 Page 176 Question 14
a) Use the formula a = șr, with r = 5 and ș = 5ʌ 3.5ʌ5
25ʌ
326. 83
1 a MHR • 978-0-07-0738850 Pre-Calculus 12 Solutions Chapter 4 Page 9 of 85The arc length of the sector watered is
25ʌ
3 m or 26.18 m, to the nearest tenth of a metre.
b) Use a proportion with r = 5 and central angle 5ʌ 3. 2 area of sector central angle=area of circle complete rot 5ʌ3ation
area of sectorʌ() 2ʌ
5(25ʌ)area of sector 65
The area of the sector watered is
125ʌ
6, or approximately 65.45 m
2 c) The sprinkler makes one revolution every 15 s, so in 2 min it will make 8 revolutions. In 2 min the sprinkler will rotate through 8(2ʌ) radians, which is 16ʌ radians, or 8(360°) which is 2880°.Section 4.1 Page 177 Question 15
a) One revolution in 24 h is the same as:quotesdbs_dbs5.pdfusesText_9[PDF] trilateration gps pdf
[PDF] trimble 4d monitoring
[PDF] trimethoprim
[PDF] tripomatic new york
[PDF] trivia about british culture
[PDF] trizetto payer list
[PDF] trois cent
[PDF] trophic level
[PDF] troubleshooting computer hardware problems and solutions
[PDF] troubleshooting pfaff sewing machine
[PDF] troubleshooting powerpoint narration
[PDF] trouver un bureau de poste ouvert pendant le confinement
[PDF] trouver une adresse en france avec un numéro de téléphone
[PDF] trove
