 Le Châteliers Principle
Le Châteliers Principle
Le Châtelier's Principle. “If a chemical system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration temperature
 Section 13.7 Le Chateliers Principle Workshop – Chem 201
Section 13.7 Le Chateliers Principle Workshop – Chem 201
So why do I have to know the Le Chatelier's Principle? Because it's really useful and helps to predict the effects of changes in concentration
 4.0 Le Chateliers Principle 4.1 Le Chateliers Principle Le
4.0 Le Chateliers Principle 4.1 Le Chateliers Principle Le
4.1 Le Chatelier's Principle. Le Châtelier's principle states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to an external stress the equilibrium will shift
 Green Chemistry - Equilibrium/Le Chateliers Principle
Green Chemistry - Equilibrium/Le Chateliers Principle
Provide students with an understanding of the concept of chemical equilibrium and to demonstrate. Le Chatelier's Principle i.e. if a stress is applied to a
 EQUILIBRIUM
EQUILIBRIUM
In accordance with the Le Chatelier's principle the concentration stress of removed Fe3+ is relieved by dissociation of [Fe(SCN)]2+ to replenish the Fe3+ ions.
 Le Chateliers Principle – NO2/N2O4 tubes
Le Chateliers Principle – NO2/N2O4 tubes
Description: Le Chatelier's principle is demonstrated by invoking a color change inside a sealed tube containing NO2 (brown) and N2O4 (colorless) gases at.
 Le Chateliers Principle
Le Chateliers Principle
Le Chatelier-Braun principle states that various secondary processes induced by the fluctuation also tend to restore a homogeneous state of the system.
 Applications of Le-Chateliers Principle.
Applications of Le-Chateliers Principle.
The Le-Chateliers principle has a great significance for the chemical (2) Applications to the physical equilibrium: Le-Chatelier's principle is ...
 Section 19.1. Acid-Base Buffer Solutions
Section 19.1. Acid-Base Buffer Solutions
(example of Le Chatelier's Principle). = the shift in an equilibrium caused by the addition (or removal) of one of the species participating in the equilibrium.
 Chapter 14. CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
Chapter 14. CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
Le Chatelier's Principle: If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by an external stress the system adjusts to partially offset the stress as the system
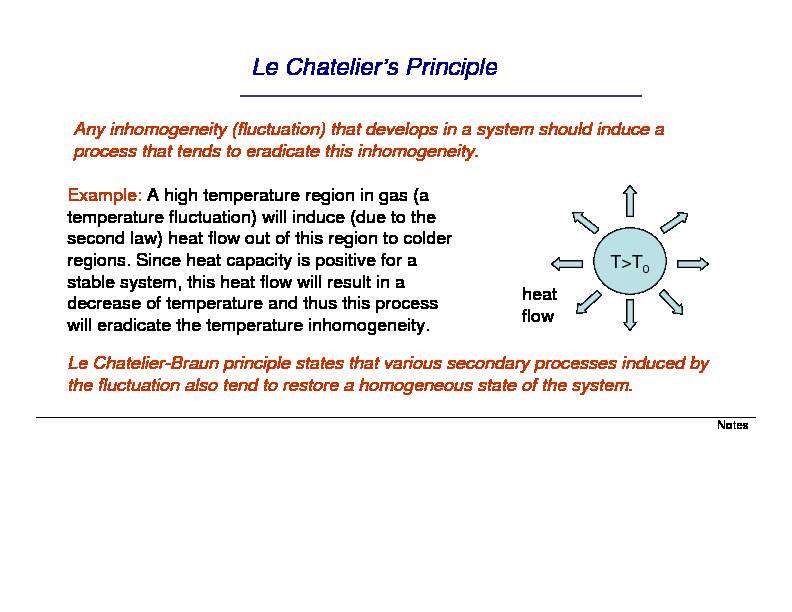
Le Chatelier's Principle
Any inhomogeneity (fluctuation) that develops in a system should induce a process that tends to eradicate this inhomogeneity.Example:
A high temperature region in gas (a
temperature fluctuation) will induce (due to the second law) heat flow out of this region to colder regions. Since heat capacity is positive for a stable system, this heat flow will result in a decrease of temperature and thus this process will eradicate the temperature inhomogeneity. Le Chatelier-Braun principle states that various secondary processes induced by the fluctuation also tend to restore a homogeneous state of the system. T>T0 heat flow NotesLe Chatelier - Brown Principle: Example
gasenvironment diathermal wall movable pistonConsider a fluctuation of the piston positionPrimary effect
: change of pressure, restores equilibriumSecondary effect
: change of temperature: dVNcTdVVTdT TvS dT induces heat flowδQ ~ sign(
α), that tends to change the pressure:
QcNTQSP
TdPTvVδκαδ
21=)∂∂=0 dP
Volume fluctuation
decreasing pressure NotesFirst Order Phase Transitions
A phase transition
is an abrupt or a qualitative change of some macroscopic property of a thermodynamic system as a function of a thermodynamic coordinate. For example, in a liquid-gas phase transition, density of the material undergoes an abrupt change. The qualitatively different states of the system are called phases. Mechanical Model of a First Order Phase Transition T sphere radius RL RR Tc Thermal reservoirSpheres made from materials with different coefficients of thermal expansion. pipeOne mole of gas
in each partition massive freely sliding piston Notes Mechanical Model of a First Order Phase TransitionIn the absence of spheres
and at low enough temperature , the position of the piston at the apex of the pipe is unstable equilibrium due to the gravitational energy cost. There are two equivalent stable equilibrium states.Unstable equilibrium
x Notes Mechanical Model of a First Order Phase TransitionThe total energy of the system as
a function of position of the piston has two equivalent minima: X FThe system is best described by
the Helmholtz free energy F(in contact withT but not
Preservoir).
Notes Mechanical Model of a First Order Phase TransitionIn the presence of spheres
and at low enough temperature , the position of the piston at the apex of the pipe is still unstable but the two minima are not equivalent at any temperature other then T c.Unstable equilibrium
x NotesUnstable equilibriumx
The total energy of the system as
a function of position of the piston has two non-equivalent minima X FT>TCT Mechanical Model of a First Order Phase Transition Notes Mechanical Model of a First Order Phase Transition As the temperature of the system is lowered through the transition temperature Tc, the global energy minimum shifts from right to left. This change is discontinuous, a macroscopic coordinate of the system, x, changes by a discontinuous jump. X F T>TCT Notes Role of fluctuations
As the temperature is lowered through
Tc, the system initially finds itself in
a localquotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2
T>TCT Notes Role of fluctuations
As the temperature is lowered through
Tc, the system initially finds itself in
a localquotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2
Role of fluctuations
As the temperature is lowered through
Tc, the system initially finds itself in
a localquotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2[PDF] Le Chatelier#exercices 1
[PDF] Le Chatelier#exercices2
[PDF] Le Chatelier#question
[PDF] le chatelier's principle example problems
[PDF] le chatelier's principle khan academy
[PDF] le chatelier's principle temperature
[PDF] le chatelier's principle volume
[PDF] le chatelier's principle worksheet
[PDF] Le chauffage à l'epoque Moderne
[PDF] le chauffage electrique
[PDF] Le chauffe électrique et le compresseur
[PDF] le chef d'oeuvre inconnu analyse des personnages
[PDF] le chef d'oeuvre inconnu mouvement littéraire
[PDF] le chef d'oeuvre inconnu questionnaire de lecture
