 Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
most important functional groups in organic chemistry. In aldehydes the carbonyl group is bonded to a 12.1 Nomenclature and Structure of Carbonyl Group.
 Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared Spectroscopy
May 15 2013 compound's structure
 INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
What functional groups exist in the molecule? • If we have a specific stereoisomer? The field of organic structure determination attempts.
 Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Nomenclature of Molecules Containing Substituents and Functional Groups hydroxy- amino-. Structure. Family of Compound. Carboxylic Acid. Aldehyde.
 An Introduction to Organic Chemistry Biochemistry
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry Biochemistry
https://www.webassign.net/question_assets/prepchem1/prepchemaf1/Bishop_eBook_AF15-1.pdf
 testsforfunctionalgroups - inorganiccompounds
testsforfunctionalgroups - inorganiccompounds
To identify the functional groups present in an organic compound. I. TESTS FOR UNSATURATION These two carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) are.
 1. Identify the functional groups on the following organic molecules.
1. Identify the functional groups on the following organic molecules.
Apr 12 2018 H-C-C-0-C-C-H. H H. H H. Which type of compound is represented by the structural formula shown? A. a ketone. B. an aldehyde. C. an ester.
 Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes
most important functional groups in organic chemistry. In aldehydes the carbonyl group is bonded to a 12.1 Nomenclature and Structure of Carbonyl Group.
 Identification of an Unknown – Alcohols Aldehydes
Identification of an Unknown – Alcohols Aldehydes
https://people.chem.umass.edu/mcdaniel/chem269/experiments/aak/procedure.pdf
 A Ru(II) Polypyridyl Complex Bearing Aldehyde Functions as a
A Ru(II) Polypyridyl Complex Bearing Aldehyde Functions as a
May 10 2019 two aldehyde functional groups (complex 3
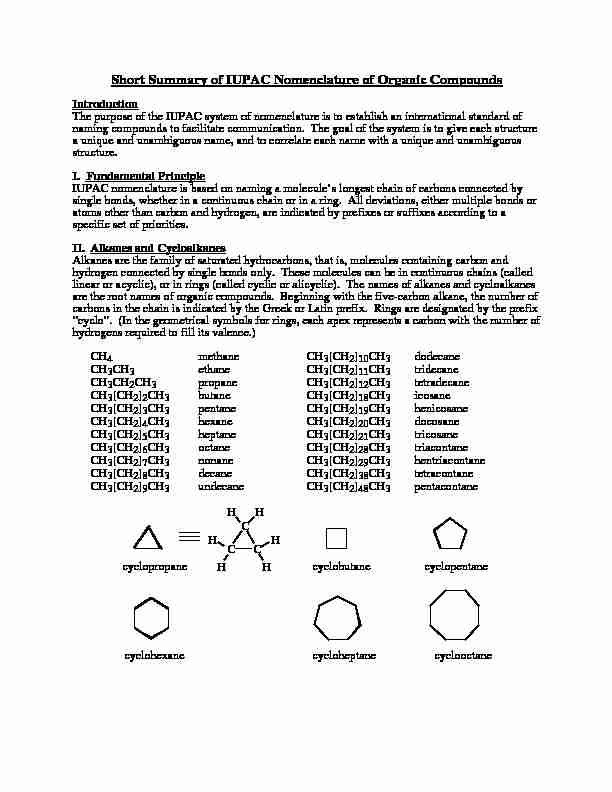 Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds IntroductionThe purpose of the IUPAC system of nomenclature is to establish an international standard ofnaming compounds to facilitate communication. The goal of the system is to give each structurea unique and unambiguous name, and to correlate each name with a unique and unambiguousstructure.
I. Fundamental Principle IUPAC nomenclature is based on naming a molecule's longest chain of carbons connected bysingle bonds, whether in a continuous chain or in a ring. All deviations, either multiple bonds oratoms other than carbon and hydrogen, are indicated by prefixes or suffixes according to aspecific set of priorities.
II. Alkanes and CycloalkanesAlkanes are the family of saturated hydrocarbons, that is, molecules containing carbon andhydrogen connected by single bonds only. These molecules can be in continuous chains (calledlinear or acyclic), or in rings (called cyclic or alicyclic). The names of alkanes and cycloalkanesare the root names of organic compounds. Beginning with the five-carbon alkane, the number ofcarbons in the chain is indicated by the Greek or Latin prefix. Rings are designated by the prefix"cyclo". (In the geometrical symbols for rings, each apex represents a carbon with the number ofhydrogens required to fill its valence.)
CH4methaneCH3[CH2]10CH3dodecaneCH
3CH3ethaneCH3[CH2]11CH3tridecaneCH
3CH2CH3propaneCH3[CH2]12CH3tetradecaneCH
3[CH2]2CH3butaneCH3[CH2]18CH3icosaneCH
3[CH2]3CH3 pentaneCH3[CH2]19CH3henicosaneCH
3[CH2]4CH3hexaneCH3[CH2]20CH3docosaneCH
CHH H HHHShort Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature, p. 2
III. Nomenclature of Molecules Containing Substituents and Functional GroupsA. Priorities of Substituents and Functional GroupsLISTED HERE FROM HIGHEST TO LOWEST PRIORITY, except that the substituents withinGroup C have equivalent priority.
Family of Compound
Alkene
AlkyneStructurePrefix
----Suffix -ene -yneSuffix -oic acid (-carboxylic acid) -al(carbaldehyde) -one -ol -aminePrefix carboxy- oxo- (formyl) oxo- hydroxy- amino-StructureFamily of CompoundCarboxylic Acid
Aldehyde
Ketone
Alcohol
AmineRCO
OH CHO R RCO R OH NR R CC CCGroup A - Functional Groups Indicated By Prefix Or Suffix Group B - Functional Groups Indicated By Suffix Only Group C - Substituents Indicated by Prefix Only Substituent Structure Prefix SuffixAlkyl (see list below)R - alkyl-------AlkoxyR - O - alkoxy-------HalogenF - fluoro---------Cl - chloro---------Br - bromo---------I - iodo---------Group C continued on next page
Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature, p. 3
Group C - Substituents, continued
Miscellaneous substituents and their prefixes NO 2CHCH 2CHCH 2CH2nitrovinylallylphenyl
Common alkyl groups - replace "ane" ending of alkane name with "yl". Alternate names forcomplex substituents are given in brackets.
methyl ethyl propyl (n-propyl)butyl (n-butyl)isopropyl [1-methylethyl]isobutyl [2-methylpropyl]sec-butyl[1-methylpropyl]tert-butyl or t-butyl[1,1-dimethylethyl]CH 3CH2CH3CH
2CH2CH3CH
2CH2CH2CH3CH
CH 3CH 3CHCH 3CH 3CH 2CH CH2CH3CH
quotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2[PDF] aldehyde functional group ir spectrum
[PDF] aldehyde functional group name
[PDF] aldehyde functional group properties
[PDF] aldehyde functional group suffix
[PDF] aldehyde hydrolysis
[PDF] aldehyde ir spectrum
[PDF] aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid mcq pdf
[PDF] aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid notes for neet pdf
[PDF] aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid notes in hindi
[PDF] aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid notes pdf download
[PDF] aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid pdf target
[PDF] aldehyde ketone and carboxylic acid questions pdf
[PDF] aldehyde to ketone
[PDF] aldehyde vs ketone
