 Graphing Exponential Functions.ks-ia2
Graphing Exponential Functions.ks-ia2
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC. Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2. Name___________________________________. Period____. Date________________. Graphing
 7-1 Study Guide and Intervention
7-1 Study Guide and Intervention
Glencoe Algebra 2. 7-1 Study Guide and Intervention. Graphing Exponential Functions. Exponential Growth An exponential growth function has the form y = bx.
 Graphing Exponential Functions
Graphing Exponential Functions
27 мар. 2015 г. Include recognizing even and odd functions from their graphs and algebraic expressions for them. ... Graphing Exponential Functions (Day 2). Page ...
 Infinite Algebra 2 - Review: Graphing Exponential Functions
Infinite Algebra 2 - Review: Graphing Exponential Functions
a de with Infinite Algebra 2. Page 6. Answers to Review: Graphing Exponential Functions. 14. 12. 10. 10. 8. 6. 4. 2. ∞ 6 4 2. 8. 1). 2). 3). 4) y y. 20. 24. 20.
 Lesson 21-4
Lesson 21-4
You can use a graphing calculator to approximate the range 334 SpringBoard® Mathematics Algebra 2 Unit 4 Series
 Untitled
Untitled
Check the reasonableness of your answer by using a graphing calculator to graph the function and verify GRAPHING EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS. Let's quickly review ...
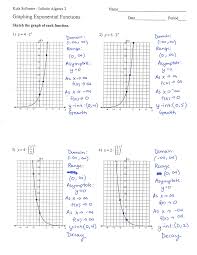 Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2 Graphing Exponential Functions
Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2 Graphing Exponential Functions
Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2. Graphing Exponential Functions. Sketch the graph of each function. 1) y = 4.2*. -6. T. 20 y. Domain: (∞ ∞). Name. Date.
 Exponential Functions with Base e
Exponential Functions with Base e
Since 2 < e < 3 the graph of the natural exponential function lies between the graphs of y = 2x and y = 3x
 Algebra 2 - Graphing Exponential Functions
Algebra 2 - Graphing Exponential Functions
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC. -4-. Answers to Graphing Exponential Functions. 1). −6 −4 −2 0. 2 4 6. 2. 4. 6. 8. 10. 12. 14. 16. 18. 20. 2). −6 −4 −2 0.
 Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2 Graphing Exponential Functions
Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2 Graphing Exponential Functions
Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2. Graphing Exponential Functions. Sketch the graph of each function. 1) y=4.2*. Name. 2) y=5.2*. -6. 4. 2. 16. 14. 12. 10. 3)
 Graphing Exponential Functions.ks-ia2
Graphing Exponential Functions.ks-ia2
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC. Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2 Graphing Exponential Functions. Sketch the graph of each function. 1) y = 4 ? 2x.
 Untitled
Untitled
Algebra 2. 10.2 Notes: Graphing Exponential Functions & Base e (Day 1) Algebra 2. Examples. Graph each exponential function. Describe the domain & range ...
 Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2 - Graphing Exponential Functions
Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2 - Graphing Exponential Functions
Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2. Graphing Exponential Functions. Sketch the graph of each function. 1) y = 4.2*. -6. T. 3) y=4. -6. ?. 15. (). 2.
 Untitled
Untitled
Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2. Graphing Exponential Functions. Sketch the graph of each function. 1) y = 4.2* y. ?2/14]. +. 3) y=4. 2. 2.
 A COURSE OUTLINE FOR ALGEBRA 2
A COURSE OUTLINE FOR ALGEBRA 2
Geometry. Algebra 2. A0 Introduction. G0 Introduction and Construction Graph exponential and logarithmic functions showing intercepts and end behavior
 10.1 Notes: Properties of Exponents & Base e
10.1 Notes: Properties of Exponents & Base e
Algebra 2. Unit 10 Notes 10.3 Worksheet. Graphing Exponential Functions (Day 2). Wednesday ... Graph each of the functions on the graphing calculator.
 Lesson Title: Graphing Exponential Equations Date: Stage 1
Lesson Title: Graphing Exponential Equations Date: Stage 1
Subject: Algebra I or Algebra II MATH.CONTENT.HSF.IF.C.7.E. Graph exponential and logarithmic functions ... ordered pairs in order to help graph.
 12.1 Exponential Functions
12.1 Exponential Functions
Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. 2. The graphs of all exponential functions of the form f x( )= bx pass ... Answers Section 12.1.
 7-1 Study Guide and Intervention
7-1 Study Guide and Intervention
Glencoe Algebra 2 Graphing Exponential Functions. Exponential Growth An ... The graphs of exponential equations can be transformed by changing the value.
 Algebra 1 WORKBOOK Page #1
Algebra 1 WORKBOOK Page #1
Algebra 1. WORKBOOK Page #1 Concept 2: Graphing Linear Exponential
Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. 12.1 Exponential Functions Definition of the Exponential Function The exponential function f with base b is defined by
fx =b x or y=b xwhere b is a positive constant other than 1 and x is any real number. Example 1: The exponential function
fx =13.490.967 x -1describes the number of 0-rings expected to fail, f(x), when the temperature is x°F. On the morning the Challenger was launched, the temperature was 31°F, colder than any previous experience. Find the number of 0-rings expected to fail at this temperature. Graphing Exponential Functions Characteristics of Exponential Functions of the Form
fx =b x1. The domain of
fx =b xconsists of all real numbers. The range consists of all positive real numbers. 2. The graphs of all exponential functions of the form
fx =b x pass through the point (0,1) because f0 =b 0 = 1. The y-intercept is (0,1). 3. The graph of fx =b x may be either strictly increasing or strictly decreasing: • If b > 1, fx =b xhas a graph that goes up to the right and is an increasing function. The greater the value of b, the steeper the increase. • If b < 1,
fx =b xhas a graph that goes down to the right and is a decreasing function. The smaller the value of b, the steeper the decrease. 4. The graph of
fx =b x approaches, but does not cross, the x-axis. The x-axis, or y = 0, is a horizontal asymptote.Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. Example 2: Graph
fx =3 x1. The domain is all real numbers. The range is all positive real numbers. 2. The y-intercept is (0,1). 3. Since b > 1, the graph is increasing. 4. y = 0 is a horizontal asymptote Table of Coordinates x f(x) (x, f(x)) -2
f-2 =3 -2 1 3 2 1 9 -2, 1 9 -1 f-1 =3 -1 0 f0 =3 0 1 f1 2 fx =3 xNote: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. Example 3: Graph
fx 1 3 x1. The domain is all real numbers. The range is all positive real numbers. 2. The y-intercept is (0,1). 3. Since b < 1, the graph is decreasing. 4. y = 0 is a horizontal asymptote Table of Coordinates x f(x) (x, f(x)) -2
f-2 1 3 -2 1 3 -2 =9 -2,9 -1 f-1 1 3 -1 1 3 -1 0 f0 1 3 0 1 f1 2 fx 1 3 xNote: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. Example 4: Sketch the graph of
fx =2 x and gx =2 x+1 on the same coordinate axes. What is the relationship between the two graphs?Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. Example 5: Sketch the graph of
fx =2 x and gx =2 x - 3 on the same coordinate axes. What is the relationship between the two graphs?Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. In general, the graph of
gx =b x + d is simply the graph of fx =b x shifted d units up, if d > 0, or d units down, if d < 0. The horizontal asymptote of gx =b x + d is y = d. The graph of gx =b x+c is simply the graph of fx =b x shifted c units left, if c > 0, or c units right, if c < 0. The horizontal asymptote of gx =b x+cis y = 0. Example 6: For each of the following pairs of functions, tell how the graph of the second function can be obtained from the graph of the first function. Give the equation of the horizontal asymptote. a. fx
=4 x , gx =4 x-3 b. fx =4 x , gx =4 x+3 c. fx =4 x , gx =4 x + 2 d. fx =4 x , gx =4 x - 3 e. fx =4 x , gx =4 x+1 - 2Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. The Natural Base e An irrational number, symbolized by the letter e, appears as a base in many applied exponential functions. This irrational number is approximately equal to 2.72. The number e is called the natural base, and the function
fx =e x is called the natural exponential function. Example 7: The function fx =6e0.013x
describes world population, f(x), in billions, x years after 2000 subject to a growth rate of 1.3% annually. Use the function to find the world population in 2050.
Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. Compound Interest Formulas for Compound Interest After t years, the balance, A, in an account with principal P and annual interest rate r (in decimal form) is given by the following formulas: 1. For n compoundings per year:
A=P1+ r n nt2. For continuous compounding:
A=Pe rtExample 8: Find the accumulated value of an investment of $5000 for 10 years at an interest rate of 6.5% if the money is a. compounded semiannually b. compounded monthly c. compounded continuously.
Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. Answers Section 12.1 Example 1: f(31) ≅ 3.77. We would expect about 4 O-rings to fail. Example 2: The domain is all real numbers. The range is all positive real numbers. The y-intercept is (0,1). Since b > 1, the graph is increasing. y = 0 is a horizontal asymptote Example 3: The domain is all real numbers.The range is all positive real numbers.The y-intercept is (0,1). Since b < 1, the graph is decreasing. y = 0 is a horizontal asymptote
Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. Example 4: Note that the graph of
y=2 x (in purple) has been shifted one unit to the left to obtain the graph of y=2 x+1 (in red) Example 5: Note that the graph of y=2 x (in purple) has been shifted three units to the down to obtain the graph of y=2 x -3(in red) Example 6: a. c = -3, shift 3 units right. Equation of horizontal asymptote: y = 0. b. c = 3, shift 3 units left. Equation of horizontal asymptote: y = 0. c. d = 2, shift 2 units up. Equation of horizontal asymptote: y = 2. d. d = -3, shift 3 units down. Equation of horizontal asymptote: y = -3.
Note: Portions of this document are excerpted from the textbook Introductory and Intermediate Algebra for College Students by Robert Blitzer. e. c = 1 and d = -2, shift 1 unit left and 2 units down. Equation of horizontal asymptote: y = -2. Example 7: f(50) ≅ 11.49. The world population in 2050 is projected to be about 11.5 billion. Example 8: a. $9,479.19 b. $9,560.92 c. $9,577.70
quotesdbs_dbs17.pdfusesText_23[PDF] algebra calculator free
[PDF] algebra calculator mathway
[PDF] algebra calculator online
[PDF] algebra calculator simplify
[PDF] algebra calculator with exponents
[PDF] algebra calculator with fractions
[PDF] algebra calculator with steps free
[PDF] algebra factoring calculator with steps
[PDF] algebra help
[PDF] algebra solver
[PDF] algebra symbols pdf
[PDF] algebraic laws for regular expressions
[PDF] algèbre 7e année
[PDF] algeria after gaining independence
