 Chapter 7: Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
Chapter 7: Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
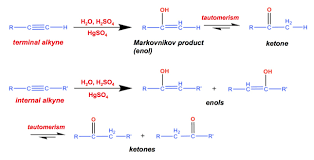
Reagent: HgSO4/H2SO4/H2O. • You need a Hg catalyst for terminal alkyne hydration. • This reaction adds an OH with Markovnikov regioselectivity to form an enol.
 Summary of Alkene Reactions Ch. 8. Memorize Reaction
Summary of Alkene Reactions Ch. 8. Memorize Reaction
Alcohols can function in the same way that water does resulting in an ether OR rather than alcohol OH. Page 6. Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 8 Handouts. 6. 10.
 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
H2SO4. Page 22. CHAPTER 5 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes. 150. Because hydrogen Yet when treated with H2O H2SO4
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Alkene reactions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Alkene reactions
35) Which of the following is the best reaction sequence to accomplish a Markovnikov addition of water to H2SO4. (acid-cat. E1). 1) Hg(OAc)2 / H2O. 2) NaBH4.
 Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/index_2353/Chapter_03_2SPP.pdf
 A hypothesis for growth of fresh atmospheric nuclei
A hypothesis for growth of fresh atmospheric nuclei
the reaction of alkenes and sulfuric acid–addition of water and addition of J. H. Seinfeld Ternary nucleation of H2SO4
 Pre-Lab: #5 Title: Dehydration of 2-methylcyclohexanol. Introduction
Pre-Lab: #5 Title: Dehydration of 2-methylcyclohexanol. Introduction
Heading: Alkenes: Preparation Reactions and Properties. Name: Susan W. Mburu H +H2O. (cis / trans) 2-methylcyclohexanol acid. 3-methylcyclohexene water. CH3.
 Identifying an Unknown Compound by Solubility Functional Group
Identifying an Unknown Compound by Solubility Functional Group
Water-insoluble compounds that are insoluble in 5% HCl are tested with concentrated sulfuric acid. (H2SO4). Virtually all organic compounds containing alkene
 Reactions of Amines
Reactions of Amines
50. NH2. H3C. 1. NaNO2 HCl. 2. H2O
 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
+H2O. H2SO4. 3. CH3. OH. See problems 5.19 5.20
 Summary of Alkene Reactions Ch. 8. Memorize Reaction
Summary of Alkene Reactions Ch. 8. Memorize Reaction
Summary of Alkene Reactions Ch. 8. Alkene Synthesis and Reactions. ... -H2O. HSO4. + H2SO4. Protonation. Elimination. Deprotonation.
 PRACTICE EXERCISE – ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I Alkynes
PRACTICE EXERCISE – ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I Alkynes
19) Provide the structure of the major organic product(s) in the reaction below. C CH. HgSO4. H2SO4 H2O. 20) Provide the structure of the major organic
 Practice Set Answer Keys Organic Chemistry I Table of Contents
Practice Set Answer Keys Organic Chemistry I Table of Contents
Test 3 PS3: Test 3 Alkene Reactions Practice H-Cl H2SO4. 102. 2. Hydronium. H3O+
 CHEM 109A CLAS Alkenes and Reactions of Alkenes - KEY 1
CHEM 109A CLAS Alkenes and Reactions of Alkenes - KEY 1
trans-3-methyl-pent-2-ene. H. I d. 1-methylcyclopentene. H. Cl. 1-methylcyclopentene. H. Cl. H. Cl-. H. Cl e. 2-butene. H2O. H2SO4. Page 1 of 6
 Chapter 7: Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
Chapter 7: Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
Reagent: HgSO4/H2SO4/H2O. • You need a Hg catalyst for terminal alkyne hydration. • This reaction adds an OH with Markovnikov regioselectivity to form an enol.
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Elimination
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Elimination
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE. Elimination Reactions and Alkene Synthesis or H2O. 4). + H3O. + or H2SO4. 26). 27). 28) Triethylamine.
 Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes: Addition Reactions 6.1
Chapter 6: Reactions of Alkenes: Addition Reactions 6.1
6.1: Hydrogenation of Alkenes – addition of H-H (H2) to the ?-bond of alkenes to afford + H2O. H2SO4. How is the position of the equilibrium controlled?
 Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/index_2353/Chapter_03_2SPP.pdf
 Acid catalyzed reactions you should be able to write arrow-pushing
Acid catalyzed reactions you should be able to write arrow-pushing
(-H2O). OH. OH. OTs. H. (-H2O). O. O. O. OH. O. OTs. H. O. O. H2SO4 / H2O (A Lewis or Bronsted acid = E+ = strong the acidity drives the reaction).
[PDF] alkyl halide functional group
[PDF] all 2d shapes and 3d shapes
[PDF] all 2d shapes and their properties
[PDF] all 2d shapes formulas
[PDF] all 2d shapes images
[PDF] all 2d shapes list
[PDF] all 2d shapes names
[PDF] all 2d shapes names and pictures
[PDF] all 2d shapes with 4 sides
[PDF] all 3d shapes names and pictures
[PDF] all 3d shapes names list
[PDF] all 5 parts of the 5th amendment
[PDF] all 50 adobe apps explained
[PDF] all 7th chords guitar pdf
