2.3 Newtons Method and Its Extension
2.3 Newtons Method and Its Extension
Taylor expansion. Remark: In order for Newton's method to converge we need a good starting guess. 6. Page 7. Relation to fixed-point iteration. Newton's method
 2.29 Numerical Fluid Mechanics Lecture 4 Slides
2.29 Numerical Fluid Mechanics Lecture 4 Slides
– Use of Taylor series to derive finite difference schemes (first-order Euler scheme Newton-Raphson Method: Example. Example – Square Root. Newton-Raphson.
 application of the newton-raphson method to vibration problems
application of the newton-raphson method to vibration problems
28-Jul-2010 Derivation. The Newton-Raphson method is derived from the Taylor series. Page 2. 2. The Taylor series equation is taken from Reference 1.
 6.2 THE NEWTON-RAPHSON METHOD
6.2 THE NEWTON-RAPHSON METHOD
Thus we have derived the Newton-. Raphson formula using a Taylor series. Aside from the derivation
 Accurate benchmark results of Blasius boundary layer problem
Accurate benchmark results of Blasius boundary layer problem
06-Apr-2022 Figure 1: Taylor series expansions about leaping ... series solutions for boundary value problems using Newton-Raphson method in this work.
 NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
03-Apr-2020 of Picard's method or Taylor's series method or Euler's method or ... In the derivation of the fourth order Runge-Kutta formula it is called.
 Accurate benchmark results of Blasius boundary layer problem
Accurate benchmark results of Blasius boundary layer problem
18-Jun-2022 Keywords and phrases: Blasius function leaping Taylor's series
 Modified Newton-Raphson Method to Achieve Variable Step Hill
Modified Newton-Raphson Method to Achieve Variable Step Hill
Abstract—This work presents a derivation of the Newton-. Raphson method different manipulation of the Taylor series expansion the method becomes a ...
 Solution of the Nonlinear Finite Element Equations in Static Analysis
Solution of the Nonlinear Finite Element Equations in Static Analysis
• Derivation of governing equations by Taylor series expansion. • Initial The procedures used are based on the. Newton-Raphson method (commonly used to ...
 Chapter 03.04 Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear
Chapter 03.04 Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear
methods. Derivation. The Newton-Raphson method is based on the principle that if the Appendix B. Derivation of Newton-Raphson method from Taylor series.
 The Newton-Raphson Method
The Newton-Raphson Method
for solving equations numerically. Like so much of the differential calculus it is based on the simple idea of linear approximation. The Newton Method
 Solutions of Equations in One Variable [0.125in]3.375in0.02in
Solutions of Equations in One Variable [0.125in]3.375in0.02in
Newton's (or the Newton-Raphson) method is one of the most powerful The Taylor series derivation of Newton's method points out the.
 Appendix C - Analytic derivation of the Newton-Raphson method
Appendix C - Analytic derivation of the Newton-Raphson method
Analytic derivation of the. Newton-Raphson method If p0 is su ciently close to p the expansion of f(p) as a Taylor series in powers of (p ? p0) is.
 CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS Newton-Raphson Method
CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS Newton-Raphson Method
ENCE 203 œ CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS. Newton-Raphson Method. ? Derivation of Newton-Raphson Method œ Derivation using Taylor Series.
 3 Approximating a function by a Taylor series
3 Approximating a function by a Taylor series
The algorithm stops when f(a) and f(b) are sufficiently close to each other. 4.2 Newton's method. This method is also known as the Newton-Raphson method and is
 Generalized Newton Raphsons method free from second derivative
Generalized Newton Raphsons method free from second derivative
Let f : X ? R X ? R is a scalar function then by using Taylor series Using the above idea
 NUMERICAL HYBRID ITERATIVE TECHNIQUE FOR SOLVING
NUMERICAL HYBRID ITERATIVE TECHNIQUE FOR SOLVING
The proposed NHIT is developed by combining the Taylor Series method. (TSM) and Newton Raphson's iterative method (NRIM). MATLAB and Excel software.
 Deprived of Second Derivative Iterated Method for Solving Non
Deprived of Second Derivative Iterated Method for Solving Non
by modified the Newton Raphson Method [9 10]
 A simple algorithm for high order Newton iteration formulae and
A simple algorithm for high order Newton iteration formulae and
convergent Newton-Raphson method of frequently at the disposal of the scientific However this constraint helps us derive the Taylor expansion of F near.

03.04.1
Chapter 03.04
Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear
Equation
After reading this chapter, you should be able to: 1. derive the Newton-Raphson method formula, 2. develop the algorithm of the Newton-Raphson method, 3. use the Newton-Raphson method to solve a nonlinear equation, and 4. discuss the drawbacks of the Newton-Raphson method.Introduction
Methods such as the bisection m
ethod and the false position method of finding roots of a nonlinear equation0)(xf require bracketing of the root by two guesses. Such methods
are called bracketing methods. These methods are always convergent since they are based on reducing the interval between the two guesses so as to zero in on the root of the equation. In the Newton-Raphson method, the root is not bracketed. In fact, only one initial guess of the root is needed to get the iterative process started to find the root of an equation. The method hence falls in the category of open methods. Convergence in open methods is not guaranteed but if the method does converge, it does so much faster than the bracketing methods.Derivation
The Newton-Raphson method is based on the principle that if the initial guess of the root of0)(xf is at
i x, then if one draws the tangent to the curve at )( i xf, the point 1i x where the tangent crosses the x-axis is an improved estimate of the root (Figure 1). Using the definition of the slope of a function, at i xxș = xf
i tan 1 0 iii xxxf = , which gives ii ii xfxf = xx 1 (1)03.04.2 Chapter 03.04
Equation (1) is called the Newton-Raphson formula for solving nonlinear equations of the form0xf. So starting with an initial guess,
i x, one can find the next guess, 1i x, by using Equation (1). One can repeat this process until one finds the root within a desirable tolerance.Algorithm
The steps of the Newton-Raphson method to find the root of an equation 0xf are 1.Evaluate xf symbolically
2.Use an initial guess of the root,
i x, to estimate the new value of the root, 1i x, as ii ii xfxf = xx 1 3.Find the absolute relative approximate error
a as 010 11 iii a x xx = 4. Compare the absolute relative approximate error with the pre-specified relative error tolerance, s . If a s , then go to Step 2, else stop the algorithm. Also, check if the number of iterations has exceeded the maximum number of iterations allowed. If so, one needs to terminate the algorithm and notify the user. Figure 1 Geometrical illustration of the Newton-Raphson method. f (x) f (x i f (x i+1 x i+2 x i+1 x i x ș [x i , f (x iNewton-Raphson Method
03.04.3
Example 1
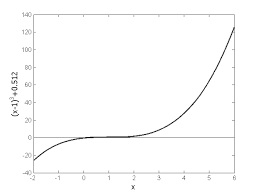
You are working for 'DOWN THE TOILET COMPANY' that makes floats for ABC commodes. The floating ball has a specific gravity of 0.6 and has a radius of 5.5 cm. You are asked to find the depth to which the ball is submerged when floating in water.Figure 2 Floating ball problem.
The equation that gives the depth
x in meters to which the ball is submerged under water is given by010993.3165.0
423xx Use the Newton-Raphson method of finding roots of equations to find a) the depth x to which the ball is submerged under water. Conduct three iterations to estimate the root of the above equation. b) the absolute relative approximate error at the end of each iteration, and c) the number of significant digits at least correct at the end of each iteration.
Solution
42310993.31650
x.xxf x.xxf3303 2Let us assume the initial guess of the root of
0xf is ..xm 050
0This is a reasonable
guess (discuss why0x and m 11.0x are not good choices) as the extreme values of the
depth x would be 0 and the diameter (0.11 m) of the ball.Iteration 1
The estimate of the root is
00 01 xfxfxx050330050310993.30501650050050
2423
34
10910118.1050
01242.0050.
062420.
03.04.4 Chapter 03.04
The absolute relative approximate error
a at the end of Iteration 1 is 100101
xxx a
19.90% 100
062420050062420
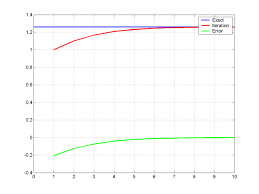
The number of significant digits at least correct is 0, as you need an absolute relative approximate error of 5% or less for at least one significant digit to be correct in your result.Iteration 2
The estimate of the root is
11 12 xfxfxx 2423
quotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2
[PDF] dérivée en ligne
[PDF] dérivée fonction exponentielle
[PDF] dérivée fonction exponentielle terminale es
[PDF] dérivée fonction exponentielle terminale es exercices
[PDF] dérivée fonction exponentielle terminale es exercices corrigés
[PDF] dériver une fonction exponentielle terminale es
[PDF] des examen d analyse mathématique s1 economie
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de chimie en solution
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de controle de gestion
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de l'algorithme pdf
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de nombres complexes
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de probabilité
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de thermodynamique pdf
[PDF] des exercices corrigés sur les bascules pdf