 2.3 Newtons Method and Its Extension
2.3 Newtons Method and Its Extension
Taylor expansion. Remark: In order for Newton's method to converge we need a good starting guess. 6. Page 7. Relation to fixed-point iteration. Newton's method
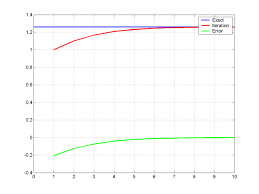 2.29 Numerical Fluid Mechanics Lecture 4 Slides
2.29 Numerical Fluid Mechanics Lecture 4 Slides
– Use of Taylor series to derive finite difference schemes (first-order Euler scheme Newton-Raphson Method: Example. Example – Square Root. Newton-Raphson.
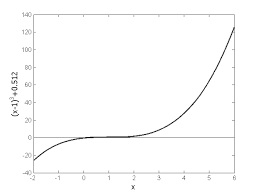 Chapter 03.04 Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear
Chapter 03.04 Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear
Derivation of Newton-Raphson method from Taylor series. Newton-Raphson method can also be derived from Taylor series. For a general function. ( ) xf the
 application of the newton-raphson method to vibration problems
application of the newton-raphson method to vibration problems
28-Jul-2010 Derivation. The Newton-Raphson method is derived from the Taylor series. Page 2. 2. The Taylor series equation is taken from Reference 1.
 6.2 THE NEWTON-RAPHSON METHOD
6.2 THE NEWTON-RAPHSON METHOD
Thus we have derived the Newton-. Raphson formula using a Taylor series. Aside from the derivation
 Accurate benchmark results of Blasius boundary layer problem
Accurate benchmark results of Blasius boundary layer problem
06-Apr-2022 Figure 1: Taylor series expansions about leaping ... series solutions for boundary value problems using Newton-Raphson method in this work.
 NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
03-Apr-2020 of Picard's method or Taylor's series method or Euler's method or ... In the derivation of the fourth order Runge-Kutta formula it is called.
 Accurate benchmark results of Blasius boundary layer problem
Accurate benchmark results of Blasius boundary layer problem
18-Jun-2022 Keywords and phrases: Blasius function leaping Taylor's series
 Modified Newton-Raphson Method to Achieve Variable Step Hill
Modified Newton-Raphson Method to Achieve Variable Step Hill
Abstract—This work presents a derivation of the Newton-. Raphson method different manipulation of the Taylor series expansion the method becomes a ...
 Solution of the Nonlinear Finite Element Equations in Static Analysis
Solution of the Nonlinear Finite Element Equations in Static Analysis
• Derivation of governing equations by Taylor series expansion. • Initial The procedures used are based on the. Newton-Raphson method (commonly used to ...
 Chapter 03.04 Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear
Chapter 03.04 Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear
methods. Derivation. The Newton-Raphson method is based on the principle that if the Appendix B. Derivation of Newton-Raphson method from Taylor series.
 The Newton-Raphson Method
The Newton-Raphson Method
for solving equations numerically. Like so much of the differential calculus it is based on the simple idea of linear approximation. The Newton Method
 Solutions of Equations in One Variable [0.125in]3.375in0.02in
Solutions of Equations in One Variable [0.125in]3.375in0.02in
Newton's (or the Newton-Raphson) method is one of the most powerful The Taylor series derivation of Newton's method points out the.
 Appendix C - Analytic derivation of the Newton-Raphson method
Appendix C - Analytic derivation of the Newton-Raphson method
Analytic derivation of the. Newton-Raphson method If p0 is su ciently close to p the expansion of f(p) as a Taylor series in powers of (p ? p0) is.
 CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS Newton-Raphson Method
CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS Newton-Raphson Method
ENCE 203 œ CHAPTER 4d. ROOTS OF EQUATIONS. Newton-Raphson Method. ? Derivation of Newton-Raphson Method œ Derivation using Taylor Series.
 3 Approximating a function by a Taylor series
3 Approximating a function by a Taylor series
The algorithm stops when f(a) and f(b) are sufficiently close to each other. 4.2 Newton's method. This method is also known as the Newton-Raphson method and is
 Generalized Newton Raphsons method free from second derivative
Generalized Newton Raphsons method free from second derivative
Let f : X ? R X ? R is a scalar function then by using Taylor series Using the above idea
 NUMERICAL HYBRID ITERATIVE TECHNIQUE FOR SOLVING
NUMERICAL HYBRID ITERATIVE TECHNIQUE FOR SOLVING
The proposed NHIT is developed by combining the Taylor Series method. (TSM) and Newton Raphson's iterative method (NRIM). MATLAB and Excel software.
 Deprived of Second Derivative Iterated Method for Solving Non
Deprived of Second Derivative Iterated Method for Solving Non
by modified the Newton Raphson Method [9 10]
 A simple algorithm for high order Newton iteration formulae and
A simple algorithm for high order Newton iteration formulae and
convergent Newton-Raphson method of frequently at the disposal of the scientific However this constraint helps us derive the Taylor expansion of F near.
 Whatdoesth ismeanforcomput ation?Innearly allourcomput ations, wewillre- placeexactform ulationswithapp roximations.Forexample,weapprox imatecontinuou s quantitieswithdiscretequanti ties,wearelim itedinsizebyfloatingpointre presentation ofnu mberswhichoftennecess itatesroundingort runcationandint roduces(hopefully) smallerrors.I fwearenotcareful,thes eerror willbe amplifie dwith inanill-conditioned problemanproduceinac cur ateresults. Thisleadsusto considerthestabilityandaccuracyofour algorith ms. Analgor ithmisstableifther esultisre lativelyuna↵ectedbyperturb ationsdu ringcom- putation.Thisissimilart otheideaofcon ditioni ngofproblems. Analgor ithmisaccurateisthec ompetedsol utionisclosetothetrues olutionofthe problem.Notethatastablealgor ithmc ouldbeinacc urat e. Weseek todesignandappl ystabl eandaccuratealgorithm stofin daccuratesoluti onsto well-posedproblems(ortofindway softransformingorapproxim atingil l-posed problems bywell -posedones).
Whatdoesth ismeanforcomput ation?Innearly allourcomput ations, wewillre- placeexactform ulationswithapp roximations.Forexample,weapprox imatecontinuou s quantitieswithdiscretequanti ties,wearelim itedinsizebyfloatingpointre presentation ofnu mberswhichoftennecess itatesroundingort runcationandint roduces(hopefully) smallerrors.I fwearenotcareful,thes eerror willbe amplifie dwith inanill-conditioned problemanproduceinac cur ateresults. Thisleadsusto considerthestabilityandaccuracyofour algorith ms. Analgor ithmisstableifther esultisre lativelyuna↵ectedbyperturb ationsdu ringcom- putation.Thisissimilart otheideaofcon ditioni ngofproblems. Analgor ithmisaccurateisthec ompetedsol utionisclosetothetrues olutionofthe problem.Notethatastablealgor ithmc ouldbeinacc urat e. Weseek todesignandappl ystabl eandaccuratealgorithm stofin daccuratesoluti onsto well-posedproblems(ortofindway softransformingorapproxim atingil l-posed problems bywell -posedones). 3Appr oximatingafunctionbyaTaylorserie s
First,alittlenotati on.A real-valuedfunctionf:R!Risafun cti onfthattakesa realnumber argument,x2R,andreturn sarealnumber,f(x)2R.Wewritef 0 (x) todenot ethederivativeoff,sof 0 (x)= df dx ,and f 00 (x)is thesec ondderivati ve(so f 0 (x)= d dx df dx d 2 f dx 2 )and f (k) (x)isthekthderi vativeoffevaluatedatx. Aswe haveju stseen,simpl yevaluatingar ealvaluedfunctionc anbepronetoinstabili ty (ifthefu nctionhasal argeconditionnumber).Fort hatreason ,app roximation sof functionsareoftenused.Them ostcomm onmethodofappro ximatingthereal- valued functionf:R!Rbyasim ple rfunctionistousetheTa ylorseriesrepresentati onfor f. TheTaylor serieshastheformof apolynomialwherethec oe cientsofthepolynomial arethed erivatives offevaluatedatapoint.Solongas alld eri vativesofthefunc tion existsatthepointx=a,f(x)can beexp ressed intermsofofthevalueofthefuncti on andit's derivativesataas: f(x)=f(a)+(xa)f 0 (a)+ (xa) 2 2! f 00 (a)+...+ (xa) k k! f (k) (a)+...Thiscanbewri ttenmor ecompact lyas
f(x)= 1 X k=0 (xa) k k! f (k) (a), wheref (0) =fand0!=1b yde fini tion . Thisisknown astheTaylorseriesforfabouta.I tisvali dforx"close"toa(strictly, withinthe"radiusofconv ergence"of theseries).When a=0,t he Taylorseri esisknown asaMaclaurinseries. 4 Thisisaninfini teseri es( thesumcontainsinfinitel ymanyterms)socannotb edirectly computed.Inpractice,wetru ncateth eseriesafterntermstogettheTaylorpolynomial ofdegre encentredata,wh ichwedenote f n (x;a): f(x)⇡ fquotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2[PDF] dérivée en ligne
[PDF] dérivée fonction exponentielle
[PDF] dérivée fonction exponentielle terminale es
[PDF] dérivée fonction exponentielle terminale es exercices
[PDF] dérivée fonction exponentielle terminale es exercices corrigés
[PDF] dériver une fonction exponentielle terminale es
[PDF] des examen d analyse mathématique s1 economie
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de chimie en solution
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de controle de gestion
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de l'algorithme pdf
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de nombres complexes
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de probabilité
[PDF] des exercices corrigés de thermodynamique pdf
[PDF] des exercices corrigés sur les bascules pdf
