 Drug Calculations
Drug Calculations
It's OK to use a calculator! 1. A patient requires 4 mg of Morphine IVI. Morphine is available as. 10mg/ml. How many mls will you draw up
 Drug Dosage & IV Rates Calculations
Drug Dosage & IV Rates Calculations
formula and simplify. x 1 = 2 tablets. Therefore the nurse should give 2 tablets. The same formula can be used for dosage calculations where the medication is.
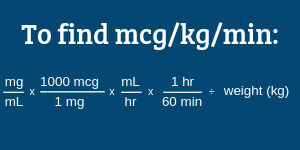 Common Drug Calculations
Common Drug Calculations
2 Feb 2023 Two dosage calculation techniques are presented below: traditional formulas and dimensional analysis. Nurses should select one formula and ...
 PRACTICE DRUG CALCULATIONS
PRACTICE DRUG CALCULATIONS
How many mLs should you draw up to give this dose? 6. A patient weighing 60 kg is prescribed intravenous dopamine 4 micrograms/kg/minute. Calculate
 DRUG CALCULATIONS FOR NURSES
DRUG CALCULATIONS FOR NURSES
Drug calculations part 1: a critique of the formula used by nurses. Nursing paediatric-formulary-9th-edition.pdf. Your local hospital pharmacy department ...
 how to solve drug calculations
how to solve drug calculations
• Identify what type of drug calculation and as a first step use common sense to estimate a rough • After applying the formula (if relevant)
 Drug Calculations Workbook
Drug Calculations Workbook
The formula to calculate the concentrations of drug per ml. Amount of Drug (2005) 'Paediatric Nursing Calculation Skills'(online): http://hy.health.gov.il ...
 LET - Maths Stats & Numeracy
LET - Maths Stats & Numeracy
2) A male patient weighs 90 kg and has been prescribed 1.5 mg/kg/dose of drug. X To calculate the time an infusion will run for
 LET - Maths Stats & Numeracy
LET - Maths Stats & Numeracy
This site has nursing calculation quizzes with answers that you can access Drug Calculations Practice 2 - Answers. 1) 0.27 mg. 2) 7600 mg. 3). 3 ml. 4). 0.8 ...
 drug calculations for Registered Nurses
drug calculations for Registered Nurses
Calculations for these drugs are carried out in the same way as for mg per ml. Just make sure all units in the same equation match! Now try these examples:.
 Drug Dosage & IV Rates Calculations
Drug Dosage & IV Rates Calculations
formula and simplify. x 1 = 2 tablets. Therefore the nurse should give 2 tablets. The same formula can be used for dosage calculations where the medication
 Drug Calculations
Drug Calculations
Prepared by: Janet Tweedy and Deb Mason Nurse Educators
 drug-calculations-for-nurses-4th-ed-2016.pdf
drug-calculations-for-nurses-4th-ed-2016.pdf
In current nursing practice the need to calculate drug dosages is not uncommon. These calculations have to be performed competently and.
 Students
Students
Remember that for intravenous infusion sometimes you are asked to calculate volume
 Dosage Calculations Formulas for Calculating Medication Dosage
Dosage Calculations Formulas for Calculating Medication Dosage
ADN 841: Nursing Seminar II. Learning Unit 3: Handout. Page 1 of 6. Dosage Calculations. This unit looks at drug calculations. It's important to remember
 Drug Calculations Workbook
Drug Calculations Workbook
Drug Calculations Workbook. Registered nurses & Operating department practitioners The formula to calculate the concentrations of drug per ml.
 Medication Calculations - Nursing
Medication Calculations - Nursing
dose as well as working with paediatric doses. When medication is injected. The formula to calculate the volume required for an injection is:.
 Study Guide with Sample Questions: Dosage Calculation Competency
Study Guide with Sample Questions: Dosage Calculation Competency
Applicants to the LPN-to-Associate Degree "Bridge"Nursing Program must document competency indosage calculation that is equivalent to the content covered in
 Drug calculation competencies ot graduate nurses
Drug calculation competencies ot graduate nurses
Introduction. The ability to accurately calculate a drug dosage is a fundamental clinical skill required of all registered nurses. There is.
 Reducing nurse medicine administration errors
Reducing nurse medicine administration errors
13 May 2015 medication error. 3Conceptual difficulties and poor numeracy skills can cause nurses to calculate dosages wrongly. 4Drug calculation.
DRUG-CALCS _20220927 Page 1 of 5
DRUG CALCULATIONS
© Student Learning Support Service, 2022
slss@flinders.edu.au students.flinders.edu.au/slss Identify what type of drug calculation and as a first step, use common sense to estimate a roughanswer. In many cases, drawing a picture that visually represents the problem is often a helpful strategy.
Remember that a formula often used for working out how many tablets to take or for a drug taken orally or injected is:VOLUME REQUIRED =
STRENGTH REQUIRED (SR)
xVOLUME OF STOCK
STOCK STRENGTH (SS) 1
Remember that a formula often used to work out the number of drops per minute delivered by an intravenous infusion is:DRIP RATE (DPM) =
VOLUME (mL) x DROPS/mL
TIME (h) x 60
Remember that for intravenous infusion, sometimes you are asked to calculate volume, time, or rate, and the following formulae can be useful:VOLUME (mL) =RATE (mL/h) x TIME (h)
RATEVOLUME (mL)
TIME =
VOLUME (mL)
TIME (h)
RATE (mL/h)
After applying the formula (if relevant), or calculating an exact answer using common sense, go back and check: is your final answer close to your initial estimate? If not, why not?EXAMPLE 1: DRUG MADE UP FROM STOCK SOLUTION
This example illustrates how to work out injections or orally taken drugs made up from stock solution
- for example, working out how many mLs to inject when the drug is in a stock solution.QUESTION: A patient is ordered 70 mg of pethidine. Find the volume required if the stock solution contains 10g
of pethidine per 200mL.TO SOLVE: We'll be using this formula:
VOLUME REQUIRED =
STRENGTH REQUIRED (SR)
x VOLUME OF STOCKSTOCK STRENGTH (SS) 1
1. Note down the strength of medication the patient needs and the stock strength:
Strength Required is 70 mg, Stock Strength is 10g in 200 mL At this point our rough answer is - More than 1 mL and a lot less than 200mL.2. Since you need units to be the same, convert 10 g to mg by multiplying by 1000.
e.g. 1000mg x 10 = 10,000mg (10,000mg = 10g)3. Now put the values into the above for.
Note that 70mg (what the patient needs) is a very small part of10,000mg - so expect your
answer in mL to be much less than 200mL ANSWER: Based on the above, your answer = 1.4mL VOLUME REQUIRED = 70x 200
mL = 14 14 mL = 1.4mL 10 1 10 10
HOW TO SOLVE DRUG CALCULATIONS
TIP: An easy way to
remember this formula isSUNRISE (SR)
SUNSET (SS)
NOTE: DPM stands for drops per minute CONVERSION TIP:X 1,000
g mg÷ 1,000
VISUAL
REPRESENTATION
10,000mg
PETHIDINE
200mLsolution
DRUG-CALCS _20220927 Page 2 of 5
DRUG CALCULATIONS
© Student Learning Support Service, 2022
slss@flinders.edu.au students.flinders.edu.au/slssEXAMPLE 2: INTRAVENOUS INFUSION
This example indicates how many mLs to give in a certain time, and how many drops per minute a patient will receive. QUESTION: A teenager who is badly dehydrated is to receive 1.5 L over10 hours of rehydration fluid by IV infusion. The giving set delivers 20
drops/mL. Calculate the drip rate. TO SOLVE: We'll be using this formula - remember that DPR stands for 'drops per minute'DRIP RATE (DPM)
VOLUME (mL) x DROPS/mL
TIME (h) x 60
quotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2[PDF] drystan bed assembly instructions
[PDF] ds chimie 1ere s oxydoréduction
[PDF] ds ondes et imagerie médicale seconde
[PDF] ds physique 1ere s oxydoréduction
[PDF] ds physique chimie 1ere s oxydoréduction
[PDF] dsc application form
[PDF] dsc application form 2019
[PDF] dsc application status
[PDF] dsc for government organization form
[PDF] dsc form 16 download
[PDF] dsc form amfi
[PDF] dsc form online
[PDF] dsc form sify
[PDF] dsc form vsign
