The exponential Fourier series for a periodic signal was developed in
The exponential Fourier series for a periodic signal was developed in
Example 6.3 A half-rectified sine wave. Passing a sine wave of angular frequency N through a half-wave rectifier produces the signal shown in Figure 6.10
 CHAPTER 4 FOURIER SERIES AND INTEGRALS
CHAPTER 4 FOURIER SERIES AND INTEGRALS
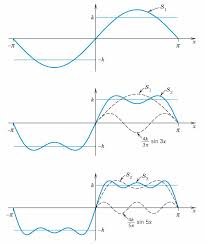
Example 1 Find the Fourier sine coefficients bk of the square wave SW(x). multiple of cosx is closest to f = cos3 x? 7. Sketch the 2π-periodic half wave ...
 Essential Mathematical Methods for Physicists - Weber and Arfken.1.1
Essential Mathematical Methods for Physicists - Weber and Arfken.1.1
This is our Fourier exponential series [Eq. (14.32)]. Separating real and This is the output of a simple half-wave rectifier. It is also an ap ...
 Table 15
Table 15
Half wave rectified sine wave: 0. 2. T π ω After some algebra the delay can be represented as a phase shift in the Fourier series of the voltage waveform.
 Fourier_Series_continuous_time_periodic_signal_and_ Fourier
Fourier_Series_continuous_time_periodic_signal_and_ Fourier
c = Fourier coefficients of exponential form of Fourier series. When a waveform has half wave symmetry the Fourier series will consist of odd harmonic terms.
 Unit 4 (Fourier Series & PDE with Constant Coefficient)
Unit 4 (Fourier Series & PDE with Constant Coefficient)
04-May-2020 n=1 n-1. So Half range sine series of f(x) on (0
 Untitled
Untitled
26-Apr-2007 Continuous-Time Complex-Exponential Fourier Series Complex exponential Fourier ... half-wave rectifier. Page 4. (b) Suppose the input sinusoid x ...
 CHAPTER 3. SPECTRUM REPRESENTATION 58 - 3-4 Fourier Series
CHAPTER 3. SPECTRUM REPRESENTATION 58 - 3-4 Fourier Series
08-Sept-2012 ... exponential signal—the integral of a complex exponential ... EXERCISE 3.15: Find the Fourier Series coefficients of the half-wave rectified sine ...
 Chapter 16 The Fourier Series
Chapter 16 The Fourier Series
It is also useful to know the values of the cosine sine
 Module 6 Introduction to Fourier series Objective:To understand
Module 6 Introduction to Fourier series Objective:To understand
exponential fourier series. Problem 1:Find the Fourier series expansion of the half wave rectified sine wave shown in fig below. Solution :.
 CHAPTER 3. SPECTRUM REPRESENTATION 58 - 3-4 Fourier Series
CHAPTER 3. SPECTRUM REPRESENTATION 58 - 3-4 Fourier Series
8 sept. 2012 half-wave rectified sine. Exploit complex exponential simplifications such as ej 2 k D 1 ej D 1
 The exponential Fourier series for a periodic signal was developed in
The exponential Fourier series for a periodic signal was developed in
Spectrum of a half-rectified sine wave. envelope of the amplitude lines - the dashed curve in the figure. Features to be noted here are: the uniform line
 Fourier Series
Fourier Series
Fourier Series: Half-wave Rectifier. • Ex. A sinusoidal voltage Esin?t is passed through a half-wave rectifier that clips the negative portion of the wave.
 Table 15
Table 15
Table 15.4-1 The Fourier Series of Selected Waveforms. Function. Trigonometric Fourier Series. Square wave: 0 Half wave rectified sine wave: 0.
 Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
Fourier Series and Fourier Transform
Fourier series is used to get frequency spectrum of a time-domain signal of the complex exponential Fourier series for a half wave rectified sine wave.
 Half-Wave Rectifiers
Half-Wave Rectifiers
wave rectifier circuit will enable the student to advance to the analysis of The Fourier series for the half-wave rectified sine wave for the voltage.
 Fourier series & transform Representation of Continuous Time
Fourier series & transform Representation of Continuous Time
Obtain the relation between trigonometric and exponential Fourier series The Fourier series expansion of half wave symmetry signal contains odd ...
 Lecture 4&5 MATLAB applications In Signal Processing
Lecture 4&5 MATLAB applications In Signal Processing
Using Fourier series expansion a square wave Exponential Fourier Series. The coefficient c ... For the full-wave rectifier waveform shown in Figure
© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Fourier Series
Ching-Han Hsu
© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Periodic Function
A function f(x)is called periodic, if it is
defined for every xin the domain of fand if there is some positive number psuch that f(x+p)= f(x)The number pis called a periodof f(x).
If a periodic function fhas a smallest
period p, this is often called the fundamental periodof f(x).© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Periodic Function
p f(x) x© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Periodic Function
For any integer n,
f(x+np) = f(x), for allxIf f(x)and g(x)have period p, then so does
h(x) = af(x) + bg(x), a and b are constants.© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Trigonometric Functions
Consider the following periodic functions
ʌ1, sin x, cos x, sin2x,
cos2xnx, cos nx© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Trigonometric Series
The trigonometric series is of the form
a0, a1, a2, a3b1, b2, b3are real constants and are called the coefficientsof the series.If the series converges, its sum will be a
1 0 22110sincos1
2sin2cossincos1
n nnnxbnxaa xbxaxbxaa3© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Fourier Series
Assume f(x)is a periodic function of
trigonometric series:That is, we assume that the series
converges and has f(x)as its sum.Question: how to compute the coefficients?
10sincos1
n nnnxbnxaaxf© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Properties of Trigonometric
Functions
Recall some basic properties of
trigonometric functions0sin1sin
0cos1cos
S S S S S S S S dxnxnxdx dxnxnxdx 0sin2 1sin2 1 sincos S S S S S S xdxmnxdxmn nxdxmx© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Properties of Trigonometric
Functions
z mn mnxdxmnxdxmn nxdxmx 0cos2 1cos2 1 sinsin S S S S S z mn mnxdxmnxdxmn nxdxmx 0cos2 1cos2 1 coscos S S S S S© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Determination of the Constant
Term a0
Integrating both sides from to :
0 1 0 2 sincos a dxnxbnxaadxxf n nn S S S fSdxxfa2
1 0© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Determination of the Coefficients anof the Cosine TermMultiply by cosmxwith fixed positive integer
and then integrate both sides from to : m n nn a mxdxnxbnxaa mxdxxf S S S f cossincos cos 1 0Smxdxxfamcos1
© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Determination of the Coefficients bnof the Sine TermMultiply by sinmxwith fixed positive integer
and then integrate both sides from to : m n nn b mxdxnxbnxaa mxdxxf S S S f sinsincos sin 1 0Smxdxxfbmsin1
© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Summary
10sincos
n nnnxbnxaaxfSdxxfa2
1 0Snxdxxfbnsin1
Snxdxxfancos1
© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Fourier Series: Square Wave
Ex. Find the Fourier coefficients of the
periodic function f(x) xfxfxk xkxf SS S2,0 0© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
Fourier Series: Square Wave
@02 1 2 1 2 1 0 0 0 SS SS S S S kk kdxkdxdxxfa0sinsin1
coscos1 cos1 0 0 0 0 S S S S S S S nxn knxn k nxdxknxdxk nxdxxfanQ: Is f(x)even or odd?!
© 2012, Ching-Han Hsu, Ph.D.
S SSS S S S S S S S S nn k nn knn k nxn knxn k nxdxknxdxk nxdxxfbn cos121coscos11
coscos1 sinsin1 sin1 0 0 0 0Snncoscosquotesdbs_dbs10.pdfusesText_16
[PDF] exponential function to log calculator
[PDF] exponential to log conversion calculator
[PDF] exponential to natural log calculator
[PDF] exponentielle de 0 7
[PDF] exponentielle de 0 valeur
[PDF] exponentielle de x u003d0
[PDF] exponentielle traduction en arabe
[PDF] exponents and logarithms worksheet
[PDF] exponents surds and logarithms pdf
[PDF] exposition art contemporain paris janvier 2019
[PDF] exposition art paris avril 2019
[PDF] exposition art paris mai 2019
[PDF] exposition art paris mars 2019
[PDF] exposition cite architecture paris