 Fonctions de deux variables
Fonctions de deux variables
Exo 3. Calculez fx (xy) pour f := (x
 FONCTION EXPONENTIELLE
FONCTION EXPONENTIELLE
f (0). = 1. 1. = 1 k(x) = 1 f (x) = g(x) f ' = f f (0) = 1 exp(0) = 1 3. III. Propriété de la fonction exponentielle. 1) Relation fonctionnelle.
 f(x)= 2x ? 3x +5x ?1 f (x)= 3×2x ?2× 3x +5
f(x)= 2x ? 3x +5x ?1 f (x)= 3×2x ?2× 3x +5
+5x ?1 f '(x)= 3×2x. 2. ?2× 3x +5. Définition : Soit f une fonction polynôme du troisième degré définie sur ? par f(x) = ax3 +bx2 + cx + d .
 2.2 Quelques propriétés des intégrales définies
2.2 Quelques propriétés des intégrales définies
f(x)dx a et b sont les bornes d'intégration
 FONCTION DERIVÉE
FONCTION DERIVÉE
1+ 2a + h = 1+ 2a alors f est dérivable sur R et on a pour tout x de R f '(x) = 1+ 2x . Page 3. 3. Yvan Monka – Académie de Strasbourg – www.maths-et-tiques
 1.6 Graphs of Functions
1.6 Graphs of Functions
use the formula f(x) = x ? 3 so the point on the graph (1
 SECOND DEGRÉ (Partie 1)
SECOND DEGRÉ (Partie 1)
f (x) = 3x2 ? 7x + 3. - g(x) = 1. 2 x2 ? 5x +. 5. 3.
 Tableaux des dérivées
Tableaux des dérivées
%20primitives
 IV. Applications linéaires
IV. Applications linéaires
Ici x = y ? 3 et ??1(y) = y ? 3. Définition. Soit EF deux espaces vectoriels. Un isomorphisme de E sur F est une application linéaire f:E ?
 Transformations of Functions
Transformations of Functions
Step 4: Thus we have obtained the graph of g (x) =
 SECTION 33: TECHNIQUES OF DIFFERENTIATION
SECTION 33: TECHNIQUES OF DIFFERENTIATION
(Section 3 3: Techniques of Differentiation) 3 3 12 FOOTNOTES 1 Proof of the Sum Rule of Differentiation Throughout the Footnotes we assume that f and g are functions that are differentiable “where we care ” Let p = f + g (We will use h for “run” in the Limit Definition of the Derivative ) px ()= lim h 0 px()+h px() h = lim h 0
 PDF - Forex Trading for Beginners (2021) - Finance Illustrated
PDF - Forex Trading for Beginners (2021) - Finance Illustrated
FX(3) = = 1 (d)x>3: = 3 FX(x) = = 1 x > 3 Therefore FX(x) 0 x2 2 x < 0 0 ? x < 1 = 12 1 1 ? x < 3 x ? 3 Retrieving PDF from CDF Theorem Theprobability density function(PDF) is the derivative of thecumulative distribution function (CDF): dFX(x)dZxfX(x) ==fX(x?)dx? (6)dxdx??
 Solutions to HW5 Problem 31 - IUPUI
Solutions to HW5 Problem 31 - IUPUI
Use the PDF to ?nd (a) the constant c (b) P[0 ? X ? 1] (c) P[?1/2 ? X ? 1/2] (d) the CDF FX(x) Problem 3 2 1 Solution fX (x) = ˆ cx 0 ? x ? 2 0 otherwise (1) (a) From the above PDF we can determine the value of c by integrating the PDF and setting it equal to 1 Z 2 0 cxdx = 2c = 1 (2) Therefore c = 1/2 (b) P[0 ? X ? 1
What Is A PDF/X-3 file?
PDF/X-3 files are regular PDF 1.3 or PDF 1.4 files. There are a number of restrictions that apply to PDF/X-3 files: 1. All fonts must be embedded in the file. 2. All color data can be grayscale, CMYK, or named spot colors. RGB, LAB or ICC based color spaces are also allowed. If such device-independent colors are used, both the embedded ICC profiles...
Which Other PDF/X Flavors Exist?
Below are other PDF/X flavors that are either actively used in the market or may become popular in the future. 1. PDF/X-1a 1.1. The first standard, created for black&white, CMYK or spot color jobs. 1.2. This is a standard that originated in the USA but is also popular in Europe. 2. PDF/X-4 2.1. An updated version of PDF/X-3 which adds among others ...
PDF/X Is Just The Starting Point
If you think all of the above restrictions make sure that you get perfectly printable PDF files, think again. There are no rules in PDF/X that state that images need to have a certain resolution. A file with 50 dpi images in it can be a valid PDF/X-3 file yet the printed result will be horrible. PDF/X is meant to be a standard that is independent f...
Is this forex trading PDF for beginners?
This Forex Trading PDF is written in such a way that even complete beginners can understand it and learn from it. In other words, we have read tons of Forex books, opened and closed thousands of trades; have filtered out all the needed basics for beginner traders, and simplified them.
What is PDF X 3?
This set of rules is called PDF/X, a series of well defined subsets of the PDF standard that promise predictable and consistent PDF files. PDF/X-3 used to be one of the more popular PDF/X flavors but it has largely been replaced by the more modern PDF/X-4 standard. This page covers: What are PDF/x-3 files? Which other PDF/X flavors exist?
What is the PDF of Y?
From De?nition 3.6, the PDF of Y is fY(y) = ˆ (1/5)e?y/5y ? 0 0 otherwise (1) (a) The event A has probability P [A] = P [Y < 2] = Z2 0 (1/5)e?y/5dy = ?e?y/5 2 0
What is d f x(x) d x?
d F X ( x) d x = F X ? ( x), if F X ( x) is differentiable at x. Consider a continuous random variable X with an absolutely continuous CDF F X ( x). The function f X ( x) defined by is called the probability density function (PDF) of X .
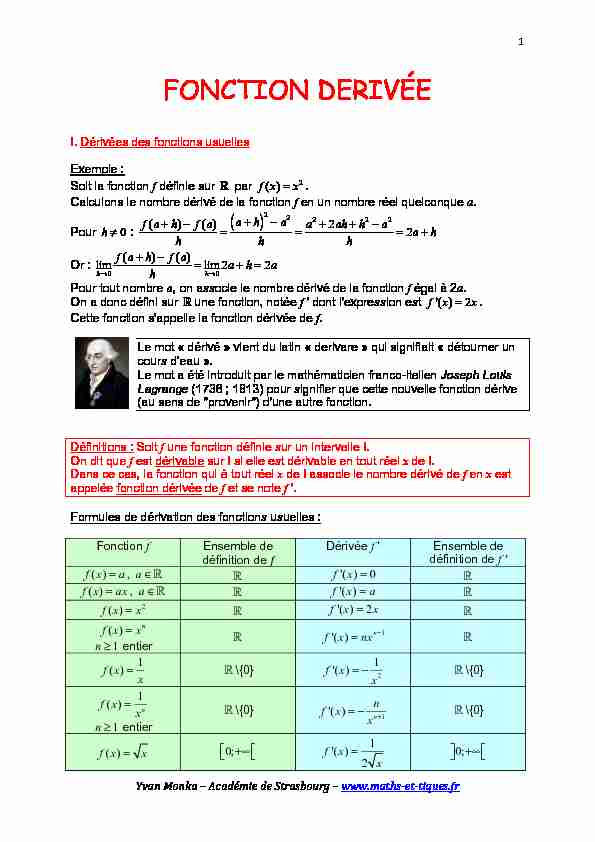
1YvanMonka-AcadémiedeStrasbourg-www.maths-et-tiques.frFONCTION DERIVÉE I. Dérivées des fonctions usuelles Exemple : Soit la fonction f définie sur
par f(x)=x 2 . Calculons le nombre dérivé de la fonction f en un nombre réel quelconque a. Pour h≠0 f(a+h)-f(a) h a+h 2 -a 2 h a 2 +2ah+h 2 -a 2 h =2a+h Or : lim h→0 f(a+h)-f(a) h =lim h→02a+h=2a
Pour tout nombre a, on associe le nombre dérivé de la fonction f égal à 2a. On a donc défini sur
une fonction, notée f ' dont l'expression est f'(x)=2x. Cette fonction s'appelle la fonction dérivée de f. Le mot " dérivé » vient du latin " derivare » qui signifiait " détourner un cours d'eau ». Le mot a été introduit par le mathématicien franco-italien Joseph Louis Lagrange (1736 ; 1813) pour signifier que cette nouvelle fonction dérive (au sens de "provenir") d'une autre fonction. Définitions : Soit f une fonction définie sur un intervalle I. On dit que f est dérivable sur I si elle est dérivable en tout réel x de I. Dans ce cas, la fonction qui à tout réel x de I associe le nombre dérivé de f en x est appelée fonction dérivée de f et se note f '. Formules de dérivation des fonctions usuelles : Fonction f Ensemble de définition de f Dérivée f ' Ensemble de définition de f '
f(x)=a a∈! f'(x)=0 f(x)=ax a∈! f'(x)=a f(x)=x 2 f'(x)=2x f(x)=x n n≥1 entier f'(x)=nx n-1 f(x)= 1 x \{0} f'(x)=- 1 x 2 \{0} f(x)= 1 x n n≥1 entier \{0} f'(x)=- n x n+1 \{0} f(x)=x0;+∞
f'(x)= 1 2x0;+∞
2YvanMonka-AcadémiedeStrasbourg-www.maths-et-tiques.frExemples : Vidéo https://youtu.be/9Mann4wOGJA 1) Soit la fonction f définie sur
par f(x)=x 4 alors f est dérivable sur et on a pour tout x de f'(x)=4x 3 . 2) Soit la fonction f définie sur \{0} par f(x)= 1 x 5 alors f est dérivable sur -∞;0 et sur0;+∞
et on a pour tout x de \{0}, f'(x)=- 5 x 6 . Démonstration pour la fonction inverse : Soit la fonction f définie sur \{0} par f(x)= 1 x . Pour h≠0 et h≠-a f(a+h)-f(a) h 1 a+h 1 a h a-a-h a(a+h) h 1 a(a+h) Or : lim h→0 f(a+h)-f(a) h =lim h→0 1 a(a+h) 1 a 2 Pour tout nombre a, on associe le nombre dérivé de la fonction f égal à 1 a 2 . Ainsi, pour tout x de \{0}, on a : f'(x)=- 1 x 2 . II. Opérations sur les fonctions dérivées Exemple : Soit la fonction f définie sur par f(x)=x+x 2 . Pour h≠0 f(a+h)-f(a) h a+h+a+h 2 -a-a 2 h a+h+a 2 +2ah+h 2 -a-a 2 h h+2ah+h 2 h =1+2a+h donc lim h→0 f(a+h)-f(a) h =lim h→01+2a+h=1+2a
alors f est dérivable sur et on a pour tout x de f'(x)=1+2x3YvanMonka-AcadémiedeStrasbourg-www.maths-et-tiques.frOn pose pour tout x de
u(x)=x et v(x)=x 2 . On a ainsi : f(x)=u(x)+v(x) . Pour tout x de u'(x)=1 et v'(x)=2x . On constate sur cet exemple que : f'(x)=u'(x)+v'(x) . Soit encore : u+v '(x)=u'(x)+v'(x)Formules d'opération sur les fonctions dérivées : u et v sont deux fonctions dérivables sur un intervalle I. Démonstration pour la somme et l'inverse : - On veut démontrer que :
lim h→0 u+v (a+h)-u+v (a) h =u'(a)+v'(a) u+v (a+h)-u+v (a) h u(a+h)+v(a+h)-u(a)-v(a) h u(a+h)-u(a) h v(a+h)-v(a) hComme u et v sont dérivables sur I, on a :
lim h→0 u(a+h)-u(a) h =u'(a) et lim h→0 v(a+h)-v(a) h =v'(a) donc : lim h→0 u+v (a+h)-u+v (a) h =u'(a)+v'(a) 1 u (a+h)- 1 u (a) h 1 u(a+h) 1 u(a) h u(a)-u(a+h) hu(a)u(a+h) u(a+h)-u(a) h 1 u(a)u(a+h) u+v est dérivable sur I u+v '=u'+v' ku est dérivable sur I, où k est une constante ku '=ku' uv est dérivable sur I uv '=u'v+uv' 1 u est dérivable sur I, où u ne s'annule pas sur I 1 u u' u 2 u v est dérivable sur I, où v ne s'annule pas sur I u v u'v-uv' v 24YvanMonka-AcadémiedeStrasbourg-www.maths-et-tiques.frdonc :
lim h→0 1 u (a+h)- 1 u (a) h =-u'(a)× 1 u(a)u(a) u'(a) u(a) 2. Méthode : Calculer les dérivées de sommes, produits et quotients de fonctions Vidéo https://youtu.be/ehHoLK98Ht0 Vidéo https://youtu.be/1fOGueiO_zk Vidéo https://youtu.be/OMsZNNIIdrw Vidéo https://youtu.be/jOuC7aq3YkM Vidéo https://youtu.be/-MfEczGz_6Y Calculer les fonctions dérivées des fonctions suivantes : 1)
f 1 (x)=5x 3 2) f 2 (x)=3x 2 +4x 3) f 3 (x)= 1 2x 2 +5x 4) f 4 (x)=3x 2 +4x 5x-1 5) f 5 (x)= 6x-5 x 3 -2x 2 -1 . 1) f 1 (x)=5u(x) avec u(x)=x 3 u'(x)=3x 2Donc :
f 1 '(x)=5u'(x)=5×3x 2 =15x 2 . 2) f 2 (x)=u(x)+v(x) avec u(x)=3x 2 u'(x)=6x v(x)=4x v'(x)=4 1 2x 2 xDonc :
f 2 '(x)=u'(x)+v'(x)=6x+ 2 x . 3) f 3 (x)= 1 u(x) avec u(x)=2x 2 +5x u'(x)=4x+5Donc :
f 3 '(x)=- u'(x) u(x) 2 4x+5 2x 2 +5x 2 . 4) f 4 (x)=u(x)v(x) avec u(x)=3x 2quotesdbs_dbs31.pdfusesText_37[PDF] mécanique appliquée définition
[PDF] mécanique appliquée cours et exercices corrigés pdf
[PDF] mecanique appliquée bac pro
[PDF] pdf mecanique general
[PDF] mécanique appliquée et construction
[PDF] z+1/z-1 imaginaire pur
[PDF] z+1/z-1=2i
[PDF] questions ? poser lors dun audit interne
[PDF] questions posées lors dun audit
[PDF] questionnaire audit interne pdf
[PDF] questionnaire d'audit interne gratuit
[PDF] audit interne questionnaire exemple
[PDF] integrale t^n/(1 t)
[PDF] intégrale de exp(-t)ln(t)
