 Untitled
Untitled
⚫ Grammar Explanations in Korean ..... 360. 293. Grammar Index. 375. ① A/V-(으)ㄴ/는지. 296. ② V-는 데 걸리다/들다. 299. 03 A/V-XIQ? 301. Unit 21.
 BASIC KOREAN: A GRAMMAR AND WORKBOOK
BASIC KOREAN: A GRAMMAR AND WORKBOOK
Basic Korean : a grammar & workbook / Andrew Sangpil Byon. – 1st ed. p. cm. – (Grammar workbook series). 1. Korean language – Grammar – Problems exercises
 Using a Meta-Grammar for LTAG Korean Grammar
Using a Meta-Grammar for LTAG Korean Grammar
Generating elementary trees for wide-coverage. Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammars (LTAG) is one of the great concerns in the TAG project.
 KEIPI です
KEIPI です
considerably different to the Korean grammar and sentence order. [2]. 한글 is a phonetic writing system which means that the words correspond to pronunciation.
 Korean Grammar
Korean Grammar
Professor of. Phonetics and. Linguistics Seoul National University
 Untitled
Untitled
May 30 2001 the title Korean Grammar I
 Towards standardizing Korean Grammatical Error Correction
Towards standardizing Korean Grammatical Error Correction
Jul 9 2023 sidering the nature of Korean grammar
 Essential Grammar
Essential Grammar
Korean_Grammar_Textbook
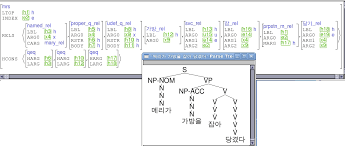 A Computational Treatment of Korean Serial Verb Constructions⋆
A Computational Treatment of Korean Serial Verb Constructions⋆
preexisting computational grammar KRG (Korean Resource Grammar). 2 Grammatical Properties of the SVCs. 2.1 Syntactic Headedness and Types of the SVC. As
 Two Types of Korean Light Verb Constructions in a Typed Feature
Two Types of Korean Light Verb Constructions in a Typed Feature
Jun 23 2011 Adopting and adapting the idea of qualia structure (Pustejovsky
 Untitled
Untitled
Korean. Grammar in Use. Beginning to. Early Intermediate. Ahn Jean-myung Lee Kyung-ah
 BASIC KOREAN: A GRAMMAR AND WORKBOOK
BASIC KOREAN: A GRAMMAR AND WORKBOOK
expect to encounter in their first year of learning Korean. Grammar points are followed by examples and exercises which allow students to reinforce.
 ?????????? ?????????? ????? ??? ????????
?????????? ?????????? ????? ??? ????????
??? ?????? ??????? ???????? ??????????? «Korean Grammar in Use: Beginning» ?? ??????? ?????. ?????? ??????? ???????? 112 ??????? ?????????? ?????????? ????? ??
 Ramstedt A Korean Grammar.pdf
Ramstedt A Korean Grammar.pdf
%20A%20Korean%20Grammar.pdf
 BEGINNING KOREAN: A GRAMMAR GUIDE
BEGINNING KOREAN: A GRAMMAR GUIDE
18 ????. 2004 ?. Beginning Korean: A Grammar Guide ... Don't worry about grammar. ... it may be tough going at first try your hardest to learn Korean using ...
 Korean Grammar
Korean Grammar
Korean Grammar. HANSOL H. B. LEE. Professor of Phonetics and Linguistics; and. Director of Language Research Institute. Seoul National University.
 KEIPI ??
KEIPI ??
considerably different to the Korean grammar and sentence order. [2]. ?? is a phonetic writing system which means that the words correspond to pronunciation.
 Zero-shot North Korean to English Neural Machine Translation by
Zero-shot North Korean to English Neural Machine Translation by
10 ???. 2020 ?. However since “” is a formal noun
 A Local Grammar-based Approach to Recognizing of Proper Names
A Local Grammar-based Approach to Recognizing of Proper Names
We present an LO-based approach to recognizing of Proper Names in Korean texts. Local grammars (LGs) are constructed by examining specific syntactic
 Mapping Scrambled Korean Sentences into English Using
Mapping Scrambled Korean Sentences into English Using
machine translation and were applied to Korean-. English machine translation in a STAGs was necessary to translate Korean scrambled ... source grammar.
KoreanGrammar
H.B.LEE
Thisbookisareferencegrammarcoveringmany
aspectsofmodernstandardKoreanrangingfrom phoneticstosyntax,andeveryefforthasbeen madetodescribeassimplyandconciselyas possiblethelinguisticfactsofKoreanasitis spokeninSeoul.Korea.Thelanguageissetoutinamethodological
andorderlymanner,withmanyexamples,and whiletheauthorhastakenadvantageofcurrent manyofhistechnicaltermsareintroducedwith explanationsandillustrationsfromEnglish detailsofpresent-daylinguistics.Thebookwillbeusefulnotonlytolinguistsin
generalandspecialistsinKoreanbutalsoto inanyaspectoftheKoreanlanguage,now spokenbynearly64millionpeople.H.B.LeeisProfessorofPhoneticsand
SCHOOLOFORIENTALANDAFRICANSTUDIES
KoreanGrammar
KoreanGrammar
HANSOLH.B.LEE
ProfessorofPhoneticsandLinguistics;and
DirectorofLanguageResearchInstitute,
SeoulNationalUniversity
OXFORDUNIVERSITYPRESS
1989OxfordNewYorkToronto
DelhiBombayCalcuttaMadrasKarachi
PetalingJavaSingaporeHongKongTokyo
NairobiDaresSalaamCapeTown
MelbourneAuckland
andassociatedcompaniesinBeirutBerlinIbadanNicosia
PublishedintheUnitedStates
byOxfordUniversityPress,NewYorkCcHansolH.B.Lee1989
Lee,HansolH.B.
Koreangrammar.
I.Koreanlanguage-Grammar
1.Title
495.782PL9I3
ISBN0-19-713606-0
Yi,Hyon-bok,1936-
Koreangrammar.
'SchoolofOrientalandAfricanStudies'-Bibliography:p.195Includesindex.
I.Koreanlanguage-Grammar.I.Universityof
II.Title.
PL91LY461988495.7587-25027
ISBN0-19-713606-0
SetbyMoonycKoreaPublications
PrintedandboundinGreatBritainby
BiddlesLtd,GuildfordandKing'sl.vnn
Preface
general. duringhisstudentdaysinLondon.LondonHansolHyunBokLee
July,1986
vContents
Prefacev
Abbreviationsxi
I.Introduction
1.1.TheKoreanLanguagepassim1
1.2.WritingSystem2
1.3.TheTypeofKoreandescribedinthisBook6
1.4.TheScopeandMethodofAnalysis7
II.PhoneticsandPhonology
2.1.PhoneticsandPhonology10
2.2.TheKoreanPhonemes10
2.4.TheSyllableStructure20
2.5.SyllableQuantityandStress21
2.6.StressGroup23
2.7.Juncture27
2.8.Intonation29
2.9.Intonemes32
2.10.Transcription33
ill.WordandWordClasses3.1.DefinitionofWord37
3.2.TypesofWords38
3.3.WordClasses39
3.3.1.Verb39
3.3.2.Noun40
3.3.3.Adjective40
3.3.4.Adverb41
3.3.5.Particle41
3.3.6.Interjection41
3.4.Sub-classesofWordClasses42
3.4.1.Sub-classesofVerbs42
3.4.2.Sub-classesofNouns50
3.4.3.Sub-classesofAdjectives59
3.4.4.Sub-classesofAdverbs61
3.4.5.Sub-classesofParticles65
3.4.6.Sub-classesofInterjections75
KJ tO viiiContentsIV.StructureoftheVerb
4.1.ElementswithintheVerb76
4.2.Stem77
4.2.1.StructureoftheVerbStem77
4.2.2.StemClasses78
4.3.VerbSuffixesandInflectionalEndings83
4.3.1.VoiceSuffix84
4.3.2.HonorificSuffix87
4.3.3.TenseSuffixes87
4.3.4.HumbleSuffix96
4.3.5.InflectionalEndings98
4.3.5.1.FinalEndings98
4.3.5.2.Non-FinalEndings105
4.3.5.3.ConcatenatingEndings11
1V.Phrase
1 1 5.1.NominalPhrase112
5.1.2.NominalHead113
5.1.3.NominalExpansion118
5.2.VerbalPhrase122
5.2.1.1.HeadofVerbalPhrase124
5.2.1.1.1.NucleusofVerbalHead125
5.2.1.1.2.SatelliteofVerbalHead126
Restrictions128
VerbalHead129
5.2.1.
2.ExpansionofVerbalPhrase142
5.3.RelationalPhrase145
VI.Clause
j4j6.1.FinalandNon-FinalClause148
6.2.ElementsofClause149
.1.Predicate149 .2.Subject1526.2.3.Object152
6.2.4.Complement152
6.2.5.Agent153
6.2.6.Adjunct153
6.3.TypesofFinalClause155
6.3.1.TransitiveClause155
6.3.2.IntransitiveClause157
6.3.3.DescriptiveClause157
6.3.4.EquationalClause160
ContentsIX
6.3.5.PassiveClause161
6.3.6.CausativeClause163
6.4.TypesofNon-FinalClause169
6.4.2.NominalClause170
6.4.3.AdjectivalClause173
6.4.4.AdverbialClause177
VII.Sentence186
7.1.DefinitionoftheSentence186
7.2.MajorandMinorSentence186
7.3.MajorSentence187
7.3.1.StructureofMajorSentence187
7.3.2.MajorSentenceCategories189
7.3.2.1.DeclarativeSentence189
7.3.2.2.InterrogativeSentence189
7.3.2.3.ImperativeSentence191
7.3.2.4.PropositiveSentence191
7.4.SimpleandCompoundSentences192
7.4.1.SimpleSentences192
7.4.2.CompoundSentences192
7.5.MinorSentences193
7.5.1.EllipticalType193
7.5.2.InitiatingType194
Bibliography
PartI:KoreanLinguistics195
PartII:GeneralLinguistics203
Index213
Abbreviations
A act.Adj./adj.
adj.cl. adj.(rei.)ph.Adv./adv.
adv.cl. adv.ph. Ag. aux. ani. C c. caus. cl. comp. concat. conj. d. decl. deic. deriv. end. Exp. f.cl./nf.cl. fmtv. fut. H hon. impcr. ina. infix.Interj./interj.
intr. md. mdf.Adjunct
activeAdjective/adjectival
adjectivalclause adjectivalrelationalphraseAdverb/adverbial
adverbialclause adverbialphrase Agent auxiliary animate (ii)Complement coordinator causative clause compound concatenating conjunctive descriptive declarative deictic derived/derivational endingExpansion
finalclause/non-finalclause formative future Head honorific imperative inanimate inflectionalInterjection/interjectival
intransitive mood modifying xiAbbreviationsxii
N/nN.ani.
N.ina.
N.hon.
N.num.
N.n.ind.
N.pl.N.Cl./n.cl.
NPNuc./nuc.
num. O P- pasv.Pcl./pcl.
ph. pres. prfx. presump. progr. prop.Rel/rel.
retros. SSat./sat.
sfx.St./st.
sub. t. tr. V/v.V.aux.
V.c. V.d. V.p. V.pl.V.hon.
V.intr.
V.tr. VP vc. Z/zNoun/nominal
Animatenoun
Inanimatenoun
Honorificnoun
Numeralnoun
Non-independentnoun
Plainnoun
NominalClause
NominalPhrase
Nucleus
numeralObject
processive passiveParticle
phrase present prefix presumptive progressive propositive relational retrospectiveSubject
Satellite
suffix stem subordinate tense transitive (ii)Verb/verbalAuxiliaryVerb
CopulaVerb
DescriptiveVerb
ProcessiveVerb
PlainVerb
HonorificVerb
IntransitiveVerb
TransitiveVerb
VerbalPhrase
voiceSentence
AbbreviationsXlll
Symbolsandnotations
//phonemictranscription (i)phonetictranscription (ii)translationfill-in optional,e.g.(S)P->PorSP rewrite *hypotheticalorunrealformquotesdbs_dbs12.pdfusesText_18[PDF] korean vocabulary pdf
[PDF] kotler principles of marketing pdf
[PDF] kounouz bac economie
[PDF] kounouz bac gestion
[PDF] kounouz bac physique
[PDF] kounta kinte films complets en francais 2014
[PDF] kpmg algerie 2016
[PDF] kpmg algerie 2016 pdf
[PDF] kpmg algerie 2017
[PDF] kpmg algerie pdf
[PDF] kpsc exam 2015 questions and answers
[PDF] kqxs truc tiep m bac
[PDF] krayti bac libre
[PDF] kristina si x
