 144 SOUDURE EXOTHERMIQUE at3w.com
144 SOUDURE EXOTHERMIQUE at3w.com
Ces connexions seront établies de manière fiable et sûre par soudure aluminothermique ou autogène”. AVEC TOUS LES AVANTAGES DE LA SOUDURE EXOTHERMIQUE. La
 Etude dune réaction exothermique en vue de sa mise en œuvre
Etude dune réaction exothermique en vue de sa mise en œuvre
dans le cas d'une réaction fortement exothermique présentant un risque d'emballement thermique. La réaction d'estérification de l'anhydride propionique par
 I. Réaction endothermique II. Réaction exothermique III. Le bris et la
I. Réaction endothermique II. Réaction exothermique III. Le bris et la
en dégagent. Comme l'énergie thermique est généralement l'énergie associée aux réactions chimiques on parlera alors de réaction endothermique et exothermique.
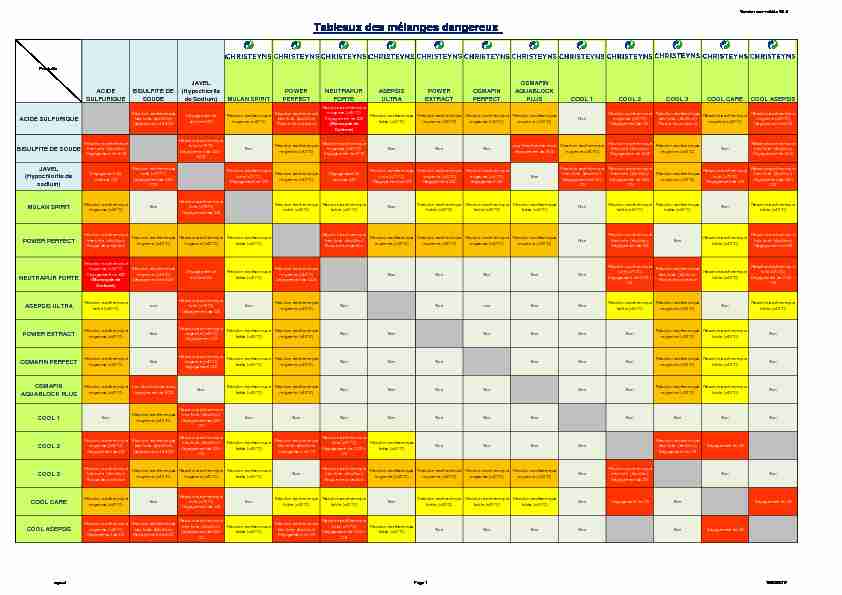
 Tableau Melanges Dangereux _xls
Tableau Melanges Dangereux _xls
16 mars 2017 OSMAFIN. AQUABLOCK. PLUS. COOL 1. COOL 2. COOL 3. COOL CARE. COOL ASEPSIS. ACIDE SULFURIQUE. Réaction exothermique très forte (ébulliton).
 Chimie BI – réactions endothermiques et exothermiques – exercices
Chimie BI – réactions endothermiques et exothermiques – exercices
Soit le diagramme d'énergie potentielle suivant. S'agit-il d'une réaction endothermique ou exothermique ? endothermique. Quelle est la variation d'enthalpie de
 EXFOLIATION EXOTHERMIQUE DES COMPOSb DINSERTION DU
EXFOLIATION EXOTHERMIQUE DES COMPOSb DINSERTION DU
EXFOLIATION EXOTHERMIQUE DES COMPOSb. D'INSERTION DU CARBONE CONTENANT. DE L'ACIDE PERCHLORIQUE. D. PETITJEAN M. KLATT
 EXFOLIATION EXOTHERMIQUE DES COMPOSb DINSERTION DU
EXFOLIATION EXOTHERMIQUE DES COMPOSb DINSERTION DU
EXFOLIATION EXOTHERMIQUE DES COMPOSb. D'INSERTION DU CARBONE CONTENANT. DE L'ACIDE PERCHLORIQUE. D. PETITJEAN M. KLATT
 Chapitre 1 Echange dénergie : Thermodynamique.
Chapitre 1 Echange dénergie : Thermodynamique.
?H ? 0 Réaction EXOTHERMIQUE. Le système cède de l'énergie au milieu extérieur. ?H ? 0 Réaction ENDOTHERMIQUE. Le système reçoit de l'énergie du.
 Transformations endothermiques ou exothermiques
Transformations endothermiques ou exothermiques
Observer et conclure. Transformation endothermique. Lors d'une transformation endothermique la température du système diminue. Transformation exothermique.
 Etude dune réaction exothermique en vue de sa mise en oeuvre
Etude dune réaction exothermique en vue de sa mise en oeuvre
3 avr. 2014 dans le cas d'une réaction fortement exothermique présentant un risque ... Cette synthèse est exothermique : son enthalpie de réaction a.
 I Réaction endothermique II Réaction exothermique III Le
I Réaction endothermique II Réaction exothermique III Le
Une réaction exothermique est une transformation qui dégage de l’énergie Dans une réaction exothermique les liaisons qui existent dans les réactifs sont plus faibles que celles présentes dans les produits Le système perd de la chaleur III Le bris et la formation de liaisons
When a chemical reaction is exothermic?
A chemical reaction is exothermic if heat is released by the system into the surroundings. Because the surroundings is gaining heat from the system, the temperature of the surroundings increases. See Figure 7.3. 1. Figure 7.3. 1: (A) Endothermic reaction. (B) Exothermic reaction.
What is exothermic transformation?
Exothermic refers to a transformation in which a closed system releases energy (heat) to the surroundings, expressed by When the transformation occurs at constant pressure and without exchange of electrical energy, heat Q is equal to the enthalpy change, i.e.
Who coined the term exothermic?
The term exothermic was first coined by 19th-century French chemist Marcellin Berthelot . The opposite of an exothermic process is an endothermic process, one that absorbs energy usually in the form of heat.
Why is energy downhill in an exothermic reaction?
In an exothermic reaction, the bonds in the product have higher bond energy (stronger bonds) than the reactants. In other words, the energy of the products is lower than the energy of the reactants, hence is energetically downhill, shown in Figure 7.3. 2 B. Energy is given off as reactants are converted to products.
Past day
Endothermic vs. exothermic reactions (article) | Khan Academy
An exothermic process releases heat, causing the temperature of the immediate surroundings to rise. An endothermic process absorbs heat and cools the surroundings.” Based on the above definition, let's pick a few examples from our daily lives and categorize them as endothermic or exothermic. Endothermic reactions: Heat is absorbed. lgo algo-sr relsrch lst richAlgo" data-08a="646175e37487d">www.khanacademy.org › test-prep › mcatEndothermic vs. exothermic reactions (article) | Khan Academy www.khanacademy.org › test-prep › mcat Cached
Version non-validée V0.2
Produits
ACIDESULFURIQUE
BISULFITE DE
SOUDE JAVEL (Hypochlorite de Sodium)MULAN SPIRIT POWERPERFECT
NEUTRAPUR
FORTEASEPSIS
ULTRA POWEREXTRACT
OSMAFIN
PERFECT
OSMAFIN
AQUABLOCK
PLUSCOOL 1 COOL 2COOL 3COOL CARECOOL ASEPSIS
ACIDE SULFURIQUE
Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de SO2
Dégagement de
dichlore Cl2Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Risque de projection
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement de CO
(Monoxyde deCarbone)
Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement de O2
Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Risque de projection
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement de O2
BISULFITE DE SOUDE
Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de SO2
Réaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de Cl2 +
SO2 NonRéaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement de SO2
NonNonNon
pas d'exothermie mais dégagement de SO2Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de SO2
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de SO2
JAVEL (Hypochlorite de sodium)Dégagement de
dichlore Cl2Réaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de Cl2+
SO2Réaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de Cl2
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement de
dichlore Cl2Réaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de Cl2
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement Cl2
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) dégagement Cl2 NonRéaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de O2+
Cl2Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de O2+
Cl2Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de Cl2
Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de O2+
Cl2MULAN SPIRIT
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de Cl2
Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)POWER PERFECT
Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Risque de projection
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Risque de projection
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de O2
NonRéaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Dégagement de O2
NEUTRAPUR FORTE
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement de CO
(Monoxyde deCarbone)
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement de SO2
Dégagement de
dichlore Cl2Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement de CO2
NonNonNonNonNon
Réaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de CO2 +
O2Réaction exothermique
très forte (ébulliton)Risque de projection
Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de CO2 +
O2ASEPSIS ULTRA
Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C) nonRéaction exothermique
forte (>70°C)Dégagement de Cl2
NonRéaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)NonNonnonNonNon
Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)POWER EXTRACT
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Dégagement Cl2
Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)NonNonNonNonNonNon
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C) NonOSMAFIN PERFECT
Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) NonRéaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C) dégagement Cl2Réaction exothermique
faible (<40°C)Réaction exothermique
moyenne (>40°C)NonNonNonNonNonNon
quotesdbs_dbs29.pdfusesText_35[PDF] combustion du butane exercice
[PDF] exercice sur la combustion des hydrocarbures
[PDF] on fait bruler du carbone dans du dioxygène
[PDF] équation combustion incomplète
[PDF] combustion du monoxyde de carbone
[PDF] cours combustion pdf
[PDF] cours combustion 4ème
[PDF] comedie classique regles
[PDF] la comédie classique définition
[PDF] comedie heroique
[PDF] comédie classique théâtre
[PDF] origine du mot grotesque
[PDF] comédie classique auteurs
[PDF] air caraibes film a bord aout 2017
