 9-2 Study Guide and Intervention - Solving Quadratic Equations by
9-2 Study Guide and Intervention - Solving Quadratic Equations by
The roots of a quadratic equation can be found by graphing the related quadratic function f(x) = a 2. + bx + c and finding the x-intercepts or zeros of the
 9-3 - Study Guide and Intervention
9-3 - Study Guide and Intervention
Study Guide and Intervention. Transformations of Quadratic Functions. Describe how the graph of each function is related to the graph of f(1) = 12. Example.
 Chapter 9 Resource Masters
Chapter 9 Resource Masters
Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing. Study The graph of a quadratic function opening upward has no ... 9-3 Study Guide and Intervention (continued).
 LT 3.1-3.4 Study Guide and Intervention
LT 3.1-3.4 Study Guide and Intervention
Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing. Solve Quadratic Equations 5. 2 + 4 + 6 = 0. 6. ? 2 ? 6 ? 9 = 0 x = 3 7 no solution x = -3 ...
 5-1 Study Guide and Intervention
5-1 Study Guide and Intervention
Basic Trigonometric Identities An equation is an identity if the left side is 9. cos x + sin x tan x ... 5-3 Study Guide and Intervention(continued).
 Untitled
Untitled
4-1 Study Guide and Intervention. Graphing Quadratic The equation of the axis of symmetry is x = 0. 1. 3 ... Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing.
 9-4 Study Guide and Intervention - Solving Quadratic Equations by
9-4 Study Guide and Intervention - Solving Quadratic Equations by
Solve each equation. The solution set is {–3 13}. Since (?3 ? 5). 2.
 9-3 Study Guide and Intervention - Transformations of Quadratic
9-3 Study Guide and Intervention - Transformations of Quadratic
Adding or subtracting constants in the equations of functions translates the graphs of the functions. The graph of g(x) = . . + k is the graph of
 Untitled
Untitled
Study Guide and InterventionEVENS. Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing (Both sides). The zeros of a quadratic 37. 1
 Untitled
Untitled
P2A.3.3 Quadratic Functions Vocabulary A technique used to solve quadratic equations graph quadratic ... Study Guide and Intervention (continued).
 Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Compan ies, Inc.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Compan ies, Inc. NAME DATE PERIOD
Lesson 9-3
Chapter 9 17 Glencoe Algebra 1
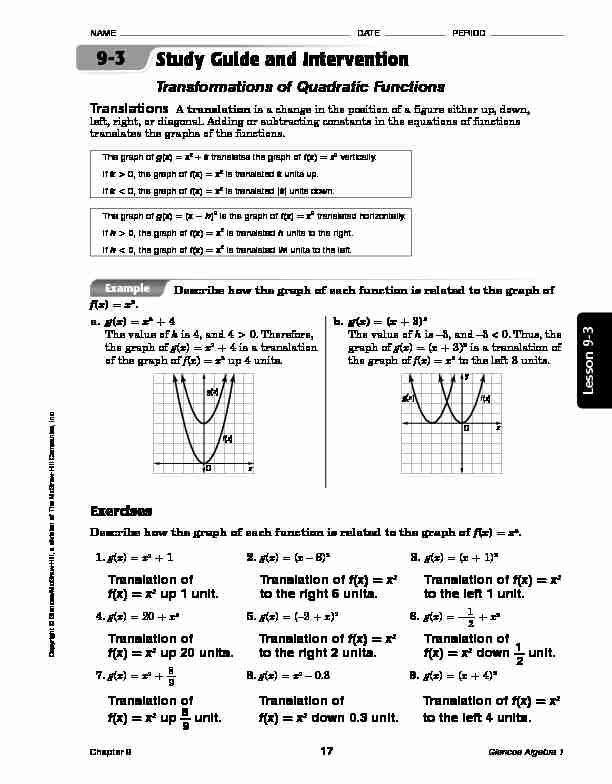
9-3 Translations A translation is a change in the position of a figure either up, down, left, right, or diagonal. Adding or subtracting constants in the equations of functions translates the graphs of the functions.The graph of
g x ) = x 2 k translates the graph of f x ) = x2 vertically.
If k > 0, the graph of f(x) = x
2 is translated k units up.If k < 0, the graph of f(x) = x
2 is translated k | units down.The graph of
g x ) = (x - h) 2 is the graph of f(x) = x 2 translated horizontally.If h > 0, the graph of f(x) = x
2 is translated h units to the right.If h < 0, the graph of f(x) = x
2 is translated | h | units to the left.Study Guide and InterventionTransformations of Quadratic Functions
Describe how the graph of each function is related to the graph of f x ) = x 2Example
a. g(x) = x 2 + 4The value of
k is 4, and 40. Therefore,
the graph of g x ) = x 2 + 4 is a translation of the graph of f x ) = x 2 up 4 units. g(x) f x x b. g(x) = (x + 3) 2The value of
h is3, and
3 < 0. Thus, the
graph of g x ) = (x + 3) 2 is a translation of the graph of f x ) = x 2 to the left 3 units. y x O f(x) g xExercises
Describe how the graph of each function is related to the graph of f(x) = x 21. g(x) = x
2 + 1 2. g(x) = (x - 6) 23. g(x) = (x + 1)
2Translation of Translation of
f x ) = x 2Translation of f(x
) = x2 f x ) = x 2 up 1 unit. to the right 6 units. to the left 1 unit.4. g(x) = 20 + x
25. g(x) = (-2 + x)
26. g(x) = -
1 2 + x 2Translation of Translation of f(x) = x
2Translation of
f x ) = x 2 up 20 units. to the right 2 units. f(x) = x 2 down 1 2 unit.7. g(x) = x
2 8 98. g(x) = x
2 - 0.3 9. g(x) = (x + 4) 2 Translation of Translation of Translation of f x ) = x 2 f x ) = x 2 up 8 9 unit. f(x) = x 2 down 0.3 unit. to the left 4 units. Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Compan ies, Inc.NAME DATE PERIOD
Chapter 9 18 Glencoe Algebra 1
Dilations and Reflections A dilation is a transformation that makes the graph narrower or wider than the parent graph. A reflection flips a figure over the x - or y -axis.The graph of
f x ) = ax 2 stretches or compresses the graph of f x ) = x 2If |a| > 1, the graph of f(x) = x
2 is stretched vertically. If 0 |a| < 1, the graph of f(x) = x 2quotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_3[PDF] 9 3 study guide and intervention transformations of quadratic functions answers
[PDF] 9 3 study guide and intervention trigonometric functions of general angles
[PDF] 9 4 practice factoring trinomials ax2+bx+c
[PDF] 9 4 skills practice factoring trinomials ax2+bx+c
[PDF] 9 4 skills practice solving quadratic equations by factoring answer key
[PDF] 9 4 study guide and intervention
[PDF] 9 4 study guide and intervention compositions of transformations
[PDF] 9 4 study guide and intervention compositions of transformations answers
[PDF] 9 4 study guide and intervention ellipses answers
[PDF] 9 4 study guide and intervention ellipses answers
[PDF] 9 4 study guide and intervention inscribed angles
[PDF] 9 4 study guide and intervention inscribed angles answer key
[PDF] 9 4 study guide and intervention solving quadratic equations by factoring
[PDF] 9 5 study guide and intervention hyperbolas
