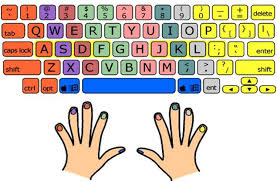
 Lesson 1: English Typing Basics
Lesson 1: English Typing Basics
After loading online typing tutor lesson you have to type the highlighted character in 'pink' color see on the keyboard the target character that has to be
 Typing/Keyboarding Lessons asdfg hjkl; asdfg hjkl; ;lkjh gfdsa asdfg
Typing/Keyboarding Lessons asdfg hjkl; asdfg hjkl; ;lkjh gfdsa asdfg
Don't let your mistakes cause you to lose heart typing is a skill that can be learned by practice. Lesson 1 Exercises: Exercise 1: Please type asdfg hjkl
 jktLFkku jktLFkku deZpkjh p;u deZpkjh p;u deZpkjh p;u cksMZsZsZsZ
jktLFkku jktLFkku deZpkjh p;u deZpkjh p;u deZpkjh p;u cksMZsZsZsZ
27-Sept-2018 Download the practice test zip from the http://103.253.70.13:8280 ... test exe from Practice Test->Typing6.6->Typing.exe am roll number will ...
 Typing speed spelling accuracy
Typing speed spelling accuracy
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1149999.pdf
 Data Entry and Keyboarding Skills
Data Entry and Keyboarding Skills
09-Nov-2018 Many websites and software products (e.g. Rapid. Typing Tutor) are available to learn touch typing and many of these are free. There are ...
 ABO grouping and Rh typing
ABO grouping and Rh typing
transfusion practice. • It is the ONLY system that the reciprocal antibodies are consistently and predictably present in the sera of people who have had no
 Typewriting and Computer Operation
Typewriting and Computer Operation
EIGHTH EXERCISE. -. LESSON VIII: PRACTICING IN SENTENCE FORM. 3. FINGERING CHART. 1st TYPING PRACTICE : LESSON IX. 10. Page 19. TYPING PRACTICE : LESSON X. 11.
 REVISED GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATION OF TYPING TEST/DEST
REVISED GUIDELINES FOR EVALUATION OF TYPING TEST/DEST
Paragraphic Errors : Half mistake shall be treated for each irrational para where the space given before starting of any paragraph is not uniform
 Gender stereotypes and Stereotyping and womens rights
Gender stereotypes and Stereotyping and womens rights
Gender stereotypes can be both positive and negative for example “women are nurturing” or. “women are weak”. Gender stereotyping is the practice of ascribing
 CENTRAL RESERVE POLICE FORCE
CENTRAL RESERVE POLICE FORCE
04-Jan-2023 process and download of Admit Cards for each stage of Test. Each stage of ... actual typing speed (For HC(M) only). They will be tested in ...
 ENG-XI-2010 cdr final
ENG-XI-2010 cdr final
3 Fingering Chart & Budget Book (Lessons I to VII). 2. 4 Typing Practice: When we learn Typewriting/Computer Operation more attention.
 GCC–TBC
GCC–TBC
1.1.1 Practice Of Typing Words Drill for 40 W.P.M.. 07 Marks. 1.1.2 Sentence Writing /Typing Practice FOR 40. W.P.M.. 07 Marks 6) Working with PDF Files.
 GCC–TBC
GCC–TBC
1.1.1 Practice Of Typing Words Drill for Lesson 8. Sentences Paragraph. 1 day. 12. Paragraph Typing Practice ... 6) Working with PDF Files.
 Lesson 1: English Typing Basics
Lesson 1: English Typing Basics
Lesson 1: English Typing Basics. Instructions :- The home row of the keyboard is the most important to the touch- typist. When at rest the typist's fingers
 jktLFkku jktLFkku deZpkjh p;u deZpkjh p;u deZpkjh p;u cksMZsZsZsZ
jktLFkku jktLFkku deZpkjh p;u deZpkjh p;u deZpkjh p;u cksMZsZsZsZ
27-Sept-2018 Download the practice test zip from the ... document IA 2018: Instructions For Typing Test of Informatics Assi.
 Data Entry and Keyboarding Skills
Data Entry and Keyboarding Skills
09-Nov-2018 Many websites and software products (e.g. Rapid. Typing Tutor) are available to learn touch typing and many of these are free. There are many ...
 Typing speed spelling accuracy
Typing speed spelling accuracy
https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1149999.pdf
 Domestic Data Entry Operator
Domestic Data Entry Operator
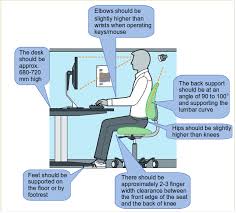
26-Sept-2018 Unit 2 will help students to learn typing skills using a typing tutor. It also covers the ergonomics and sitting posture to put the.
 Typing/Keyboarding Lessons asdfg hjkl; asdfg hjkl; ;lkjh gfdsa asdfg
Typing/Keyboarding Lessons asdfg hjkl; asdfg hjkl; ;lkjh gfdsa asdfg
Don't let your mistakes cause you to lose heart typing is a skill that can be learned by practice. Lesson 1 Exercises: Exercise 1: Please type asdfg hjkl;
 Typing Textbook.pdf
Typing Textbook.pdf
Index to Lessons: 1 2-3 4-9 10 11-14 15. 16 17 18 19 20 21 22. 23 24 25 26 27 28 29. 30 31 32. FINAL TEST. DOWNLOAD the TYPING PROGRAM.
 Pg1 Pg2 ii Pg3 Pg4 iiiiiiiiiiiiiii Pg5 iiiiiiiiiiiiii Pg6 iiii Pg7 1.1 Pg8
Pg1 Pg2 ii Pg3 Pg4 iiiiiiiiiiiiiii Pg5 iiiiiiiiiiiiii Pg6 iiii Pg7 1.1 Pg8 LESSON NO. 1LESSON NO.2
Pg9LESSON NO. 3q
Pg10LESSON NO.4LESSON NO.5ak
Pg11LESSON NO.6qiak
Pg12LESSON NO.7LESSON NO.8
Pg13 Pg14 Pg15 Pg16 Pg17 Pg18 Pg19 Pg20 Pg21 Pg22 iPage24
Page25
Page26
Page27
Page28
Page29
Page30
Page31
Page32
Page33
iPage34
1.2Page35
1.3Page36
1.4Page37
INTRODUCTIONA computer is an electronic device which can perform Arithmetic and logicaloperations at very high speed. It can also store large amount of data almostpermanently. The stored data can be recalled or retrieved as and whenrequired.HISTORY OF COMPUTERSThe history of computers is a story of stage by stage development of thiswonderful tool offered by electronics to the human being.GENERATIONSOF COMPUTERThe digital computer has evolved through a series of technical innovationsand developments. These are so clearly defined that the computers are said tobelong to different generations.Presently the computers are supposed to be in fourth fifth and sixthgenerations. The typical characteristics and salient features of each generation ofcomputers are summarized in following paragraphs.FIRST GENERATION COMPUTERS : (1949 to 1959)Second Generation computers : (1959-1965)Third Generation Computers : (1965-1970)Fourth Generation Computers :(1970-1985)Fifth Generation Computers : (1985-1990)Sixth Generation Computers :(1990 onwards)TYPES OF COMPUTERS :Analog Computers:Digital Computers :Mainframe Computers :Mini Computers:MicroComputers :COMPUTER:-Computer is an electronic device which takes some input, stores it, process itto give some meaningful result.Inputmeans different characters, figures, numbers, information, charts, etc.which we are providing to computer. Along with this we have to provide instructionto the computer because computer do not have own brain. It is just like an obedientservant. So it will work according to our instruction.
Page38
PROCESSIn process, computer performs arithmetic and logical operations.OUTPUTOutput means result which we will get after the processingUSES OF COMPUTER1. Entertainment 2. Calculations 3. Account 4. Advertisements5. Industry 6. Banking 7. Printing technology 8. Hospitals9. Hotels 10.Movies 11. Agriculture 12. Research, etc.CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERSa)SPEEDb)STORAGEc)ACCURACYd)AUTOMATIONe)VERSATILITYf)DILIGENCECOMPUTER SYSTEM ORGANISATIONMainly Computer System consists of 3 units :-1) Input Unit2) Central Processing Unit ( CPU )3) Output Unit
a)MemoryThisis used to store the data. The given input data is first stored in thememory is BIT (BInary DigiT). When we collect 8 BITS, it is called as 1 Byte.8Bits = 1 Byte1024 Bytes =1 Kilo Byte (KB)1024 KB = 1 Mega Byte (MB)1024 MB = 1 Giga Byte (GB)1024 GB = 1 Tera Byte (TB)
Page38
PROCESSIn process, computer performs arithmetic and logical operations.OUTPUTOutput means result which we will get after the processingUSES OF COMPUTER1. Entertainment 2. Calculations 3. Account 4. Advertisements5. Industry 6. Banking 7. Printing technology 8. Hospitals9. Hotels 10.Movies 11. Agriculture 12. Research, etc.CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERSa)SPEEDb)STORAGEc)ACCURACYd)AUTOMATIONe)VERSATILITYf)DILIGENCECOMPUTER SYSTEM ORGANISATIONMainly Computer System consists of 3 units :-1) Input Unit2) Central Processing Unit ( CPU )3) Output Unit
a)MemoryThisis used to store the data. The given input data is first stored in thememory is BIT (BInary DigiT). When we collect 8 BITS, it is called as 1 Byte.8Bits = 1 Byte1024 Bytes =1 Kilo Byte (KB)1024 KB = 1 Mega Byte (MB)1024 MB = 1 Giga Byte (GB)1024 GB = 1 Tera Byte (TB)
Page38
PROCESSIn process, computer performs arithmetic and logical operations.OUTPUTOutput means result which we will get after the processingUSES OF COMPUTER1. Entertainment 2. Calculations 3. Account 4. Advertisements5. Industry 6. Banking 7. Printing technology 8. Hospitals9. Hotels 10.Movies 11. Agriculture 12. Research, etc.CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERSa)SPEEDb)STORAGEc)ACCURACYd)AUTOMATIONe)VERSATILITYf)DILIGENCECOMPUTER SYSTEM ORGANISATIONMainly Computer System consists of 3 units :-1) Input Unit2) Central Processing Unit ( CPU )3) Output Unit
a)MemoryThisis used to store the data. The given input data is first stored in thememory is BIT (BInary DigiT). When we collect 8 BITS, it is called as 1 Byte.8Bits = 1 Byte1024 Bytes =1 Kilo Byte (KB)1024 KB = 1 Mega Byte (MB)1024 MB = 1 Giga Byte (GB)1024 GB = 1 Tera Byte (TB)
Page39
Arithmetic Logic Unit(ALU)It is used for arithmetic and logical calculations.This has 3 subunits.1) Register(2) Adder(3) Accumulator1)Register:-It is used for temporary storage of the data.2)Adder:-It is used for exact calculations.3)Accumulator:-It is used to store the intermediate results.Control UnitOutput UnitSECONDARY STORAGE DEVICESiHard DiskiOptical DiskiFlashMemory CardsiPen DriveHARDWARE AND SOFTWAREHardwareSoftwareTypes of System SoftwareApplication SoftwareSystem SoftwareProgramming LanguageTYPES OF MEMORYRAM(RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY)ROM(READ ONLY MEMORY)INPUT DEVICESKEYBOARD :MOUSE :SCANNEROUTPUT DEVICESVDU(VISUAL DISPLAY UNIT)PRINTERSINK-JET PRINTERSLASER PRINTERSPLOTTERCompilerInterpreter
Page40
COMPUTERVIRUSESWhat is a virus?Origin of VirusFull form of VirusV-vitalI-informationR-resourcesU-underS-seizeTwo types of viruses:A) File VirusesB) Boot File VirusesThe virus can infect a system by two ways:By infecting a boot sector (Boot Sector Virus)By infecting other files.(File Virus)Activities of VirusHow do viruses spread?Symptoms ofvirusPrevention of virusDetecting virusesA number of programs are available which can detect the virus and clean theinfected disk or program. Such programs are calledAntiviruses.One such set of programs that is widely used isViruscanViruscan:Removing the virusWatchdog programsE.g.Nashmen.comThe Antivirus
Page41
MICROSOFT WORD(More detailingthan GCC-TBC 30 w.p.m.)MS-Word is the application software whichis normally used for wordprocessing. It is under the software MS Office. It is useful for words processing theword editing, formatting and other processing works and printing. There are certaincommands that have great control over word processing which are the basicfeatures of word.INTRODUCTIONMicrosoft word for windows is a powerful and features-rich word processor itcan practically do everything that one desires from a word processor. It can userfriendly interface, simple techniques andmore often intuitive ways of getting yourwork done.THE TITLE BARThis is the top most bar on the screen.THE MENU BARMenu Bar provides access to the Word commands.THE TOOLBARSToolbars are strips of buttons, each button representing acommand. Theyprovide quick access to commonly used commands.THE RULERSA ruler allows you to adjust your text the way you want.THE SCROLL BARSThere are two Scroll bars-a vertical scroll bar on the right edge of the screenand horizontal one at the bottom of the screen.THE PAGE VIEW BUTTONSOn the left end of the horizontal bar you will see a set of four buttons. Theseare page view buttons.Normal ViewOnline Layout ViewPage Layout ViewOutline View
Page42
RETRIEVING SAVED DOCUMENTDescriptionWhenever you create or modify your document, you should save it beforeclosing your document so that you can continue your work in the next session.Thus, the documents that are saved previously can be opened againEXITING WORDCREATING A NEW DOCUMENTSAVING THE DOCUMENTCLOSING THE DOCUMENT FILEINSERTING AND DELETING TEXTINSERTING TEXT IN A SENTENCEINSERTING TEXT AS A PARAGRAPHUNDO & REDOSELECTING TEXTSELECTING TEXT USING MOUSESELECTING FROM THE KEYBOARDCOPY, MOVE & DELETE TEXTCOPYING THE TEXT BY COPY AND PASTE METHOD.DELETING THE TEXTSPELLING & GRAMMAR CHECKINGREPLACING THE TEXTFORMATTING THE TEXTxCharacter formattingxParagraph formattingxPage formattingCHARACTER FORMATTINGCHANGING FONT & FONT SIZE :-Font is the term used to refer to the shape andstyle of characters in text.APPLYING BOLD,ITALIC AND UNDERLINE ATTRIBUTE[Usingkeyboard : Ctrl+B for Bold, Ctrl+I for Italic, Ctrl+U for underline]
Page43
CHANGING THE CASE OF CHARACTERSCase of text refers to the style of characters used, either lower case or Uppercase .Case options are asCase OptionSample TextSentence caseMycountry is great.lower casemy country is greatUPPER CASEMY COUNTRY IS GREATTitle CaseMy Country Is GreatToggle cASEmY cOUNTRY iS gREATPARAGRAPH FORMATTINGJUSTIFICATION OF TEXTKEYBOARD SHORTCUTSCtrl+L-Left AlignCtrl+R-Right AlignCtrl+E-Center AlignCtrl+J-JustifyCHANGING LINE SPACINGKEYBOARD SHORTCUTSCtrl + 1-Single Line Spacing.Ctrl + 2-Double Line Spacing.Ctrl + 5-One and a half line spacing.SETTING INDENTS (Left, Right, First Line)VIA RULER LINEALIGNING TEXT VERTICALLYNUMBERING OR BULLETING EXISTING TEXTCHANGINGTHE TYPE AND SHAPE OF BULLETSBORDERING AND SHADING TEXTSETTING PAGE BORDERSSHADING TEXTUSING TABSYOU CAN SET TAB STOPS VIA RULER LINE OR VIA FORMATrTABS OPTION
Page44
PAGE FORMATTINGPage formatting applies to whole pages and include, setting up of page, pagesize, page orientation, headers and footers, page numbering etc.SETTING PAGE MARGINSCHANGING FONT(USING FONT DIALOG BOX)(TO CHANGE FONT, FONT SIZE OR STYLE , FIRST OF ALL SELECT THE TEXTTO WHICH THE EFFECTS ARE TO BE APPLIED)CHANGING FONT SIZETo choose the font size click the down arrow key at the font size option andthen select the desired size or type it directly.CHANGING THE FONTSTYLEThere are different font styles as Regular, Bold, Italics etc. Choose it from thefont style option.USING DROP CAPIt is generally used for the first character of the beginning paragraph of yourdocument to give it an attractive look.HEADERS AND FOOTERSPAGE NUMBERINGSETTING PAGE SIZE AND ORIENTATIONINSERTING PAGE BREAKSCOLUMNS FORMATDIFFERENT VIEWSThere are different views with which you may view your document in different ways.1.NORMAL VIEW2.PAGE LAYOUT VIEW3.OUTLINE LAYOUT VIEW4.PRINT PREVIEWWORKING WITH TABLESMS Word Table:-Tables are made up of rows and columns or data enteredintercells. The cells contains are individual paragraphs and can be formatted. Atable consists of rows (no limit) and columns (maximum limit 63) of cells that you canfill with text and graphics.Cell expands vertically to fit the amount of text you type.You can create a new table and fill new empty cells or you can convert exiting theparagraph to a table. After you create a table you can modify it in a vertical ways bydeleting/editing rows and columns, adjusting columns width, sorting text and addingborders and shading. You can also set up simple data basics, perform calculations.
Page45
Tables are used to arrange information in rows and columns, that is in the tableformat.INSERTING A TABLEADDING OR INSERTING ROWSINSERTING OR ADDING COLUMNSDELETING COLUMNS AND ROWSMERGING OF THE CELLSFORMATTING TABLE WITH AUTOFORMATROTATING TEXT IN TABLESAUTOCORRECT FEATURETo make changes in the Auto Correct dictionary....AUTOTEXT FEATURETosee all the Auto Text entries follow steps....To delete an Auto Text entries, Follow steps...INSERTING SPECIAL SYMBOLS AND CHARACTERS.MAIL MERGEInsert a picture from the Clip Galleryiiii
Page46
MICROSOFT EXCEL(More detailingthan GCC-TBC 30 w.p.m.)INTRODUCTION TO MS EXCELExcel is a general purpose Application program software under MS OFFICEprogram group Excel is collection of Workbooks. Each workbook is the collection ofseveral spread-sheets or work-sheets.WORKSHEET (Excel sheet)WorkbooksROWS, COLUMNS & CELLSUNDERSTANDING EXCEL SCREEN ELEMENTTITLE BAR: This is the top most bar of the screen.THE MENU BAR: Menu bar provides access to excel commands.THE TOOL BAR:Toolbars are strips of buttons, each button representing acommand. They provide quick access to commonly used commands.Standard Toolbar :The standard toolbar contains most common tasks asOpening, Saving, and printing worksheet. Cut or copy andpaste information etc.Formatting Toolbar :Formatting is the process of making you worksheet lookvisually attractive. The formatting toolbar contains the tools required to format theworksheet. These include fonts, font style, size, alignment, borders, colors etc.The formula Bar :Formula bar is the most important toolbar. It will be the focus ofyour attention while working in Excel. It consists of an area known as Name box anEdit formula area and a contents box.The Status Bar :TheStatus bar indicates the status of the current worksheet.The Worksheet Area :The area between the toolbars at the top and the status barat he button is the worksheet area or the primary working area. It is a grid of rowsand columns. The work areais bounded at top by column headings,The Scroll Bars :Owing to the large size of the worksheet, at any given time youwill be seeing only a small part of it-The Vertical Scroll bar :The vertical scroll bar graphically represents the totallength of current worksheet.The Horizontal scroll bar :The Horizontal scrollbar covers the right-half of the barat the button of the screen.
Page47
The Sheet Tabs :Excel uses the concept of Book to store your information. Abook is nothing but a signal file folder for holding a number of individual worksheets.In Excel, a file is termed as a "Workbook", and has an extension of XLS.To the left of the horizontal scroll bar, you will find a set of tabs marked as sheet1,sheet2, sheet3. These are the individual worksheets, which make up the Workbook.The Scroll Buttons :By default, you can see only three sheet tabs. To display othersheet tabs, if any, you can make use of :Tab Scrolling" buttons provided to the left ofthe sheet tabs. You can move among the sheet tabs using the Scrolling buttons.MOVING AROUND THE WORKSHEET USING KEYBOARDDATA TYPES SUPPORTED BY EXCELThere are three types of data.1. Label :Labels, also known as text or character types is descriptive type ofinformation, not meant for performing calculations.2. Values :Numbers represent data, which can be used for performingcalculations. This include data and time type of information, since excel convertsthese into numbers and stores them as such. We can perform datearithmetic ondates like adding and subtracting.3. Formulas and functions :The formulae or functions which performcalculations using data in other cells.SAVING THE WORKSHEETChoose File->Save or Ctrl + sEDIT KEY:If you have changes to do in the entered data then-Position your pointer on the cell-Press F2 function key-Make changesHence F2 is called as the Edit key.CLEARING CELL ENTRY :Select the cell to be cleared, and choose EDIT-> CLEAR from menuoptions.ENTERING FORMULAS:One of the important reasons for the popularity of spreadsheets is their abilityto perform automatic calculations using formula and functions. This activityintroduces you to the use of formulaand in the next activity you will get to knowabout functions.Mathematical operators that can be used in formulas:+:Plus-Adds two numbers or concatenating two strings-:Minus-Performs subtraction*:Asterisk-Performs multiplication/:divide-Performs division^:Caret-Performs Exponentiation
Page48
SELECTING ROWS, COLUMNS, AND RANGE BY SHORTCUTSExcel provides many convenient ways by which you can select rows,columns, ranges etc using mouse.INSERTING ROWINSERTING COLUMNDELETING ROWDELETING COLUMNCHANGING COLUMN WIDTHSETTING COLUMN WIDTH WITH AUTOFITCHANGING ROW HEIGHTALIGNING DATA IN CELLMerge & Center:RENAMING A WORKSHEETINSERTING A NEW WORKSHEETDELETING A WORKSHEETMOVING AND COPYING THE WORKSHEET IN SAME WORKBOOKFREEZING TITLESENTERING DATA WITH AUTOFILLFilling a Text series.Filing NumbersCREATING A CUSTOM SERIESFORMULAS AND FUNCTIONS* USING FORMULAS :1. Sum: Place pointer cell address G4 and give formula as= C4 + D4 + E4 + F4or=SUM(C4:f24)(Use of function)2. Percentage: Place pointer at cell address H4 and give formula as=G4/4 & then apply the percent formatNote : Using Fill Handle, Calculate the total & Percentage for further RecordsUSING FUNCTIONS1.SUM(Range)2.AVERAGE(Range)3.MAX(Range)4.MIN(Range)5.IF(Condition, True, False)6.TODAY()7.NOW ( )8.FACT(No)9.INT(No)10.MOD (No. 1, No. 2)11.SQRT (No.)12.ROUND
DATABASE MANAGEMENT IN EXCELDatabase is the third component of Microsoft excel, the other two beingWorksheet and Graphics.A database is simply a collection of data or information stored in the computerin a well-defined manner. Some of the routinemanagement operations which arefrequently required are:Adding of new data to the databaseEditing and updating of the existing dataSorting of data in any desired mannerSearching and retrieving of any type of stored dataPrinting ofselected dataSORTING THE DATABASESorting on Single Field :Ascending OrderSorting on Multiple FieldsCREATING REPORTS :-1.Area Chart:-In this type we can represent the data components which are changing.2. Column Chart :-A column chart isgraphical collection of vertical column representing thecorresponding data item or data list.3.Bar Chart :-Bar chart consists of horizontal bars representing the corresponding dataitem or list. Each bar in chart is a single data series.4. Line Chart:-The data item or list are represented in line format in increasing or decreasingline vibrated lines.5. Pie Chart :-Pie chart is the collection of arc parts representing percentwise correspondancedata item. The pie chart is devided into slices depending upon the data item list.6.Radar Chart:-Radar chart shows data changes in relation to centre point to each other.Radar chart can be used to plot several interrelated series and easily make visualcomparison.7.Scatter Chart :-In scatter chartthe data items are expressed int X and Y axis with relationshipof consolidate pair of number. This chart type is especially used for numericaldata analysis.8.3D Chart :-In to this type of chart we can view the created chart into all possible directionsinto three dimensions.
Page50
Creating ChartWe can create chart using chart wizard for creation of charts,(1)Select the data range (cell range) you want to include into chart .then.(2)Click on Insert Menu(3)Then click on Chart(4)It will have option(a)On this sheet(b)As new sheet(a)On this sheetThrough this option the chart is embedded on the current worksheet.(b)As new sheetIt inserts new worksheet with sheet name 'chart' and will embed the chart intothat chart sheet.CHART SHEETA sheet in a workbook containing a chart. When you create a chart sheet,Microsoft Excel inserts it in the workbook to the left of the worksheet it's based on.When a chart sheet is activated, you can add data and select, format, move andsizemost items.iiii
Page51
MICROSOFT POWERPOINT(More detailingthan GCC-TBC 30 w.p.m.)Page52
Page53
iiiiiPage54
iiiPage55
iiiquotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2[PDF] u.s. circuit courts of appeal
[PDF] u.s. corporate tax rate
[PDF] u.s. court of appeals for the federal circuit
[PDF] u.s. court system
[PDF] u.s. court system chart
[PDF] u.s. district courts
[PDF] u.s. legal system structure
[PDF] u.s. navy boiler explosions
[PDF] u.s. navy collisions at sea list
[PDF] u.s. submarine collisions
[PDF] u.s. treaty countries
[PDF] u.s. unemployment rate 2019
[PDF] u.s. unemployment rate 2020
[PDF] u.s. unemployment rate chart
