 Exercices-BD.pdf - Séquence – La bande dessinée
Exercices-BD.pdf - Séquence – La bande dessinée
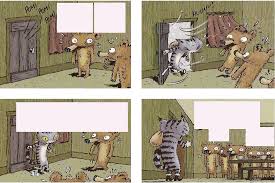
Les bulles. Objectif : Repérer les codes de lecture liés à la bulle. Ecris les dialogues à l'intérieur des bonnes bulles. Ce1. 1. Prénom : Date : Page 9
 La parole aux personnages
La parole aux personnages
Il existe aussi des BD sans paroles. Dans une BD le contenu des bulles
 Lecture : La bande dessinée
Lecture : La bande dessinée
La BD est souvent désignée comme étant le « neuvième art ». Sans doute parce dans les bulles correspondantes. Attention cela doit avoir du sens ...
 Gaspard et le phylactère magique
Gaspard et le phylactère magique
✓ La conclusion donnera les différentes typologies des bulles utilisées en BD (cf. Complète les bulles en conjuguant le verbe. DESSINER au présent. Conjugue ...
 Essais de dosimètres neutrons à bulles modèle BD 100 R-PND et
Essais de dosimètres neutrons à bulles modèle BD 100 R-PND et
RÉSUMÉ. Après avoir rappelé les missions du Centre technique d'homologation de l'ins- trumentation de radioprotection (CTHIR) et le rôle du groupe de
 Massalek Atarbiya Wa Atakwine La bande dessinée comme support
Massalek Atarbiya Wa Atakwine La bande dessinée comme support
et remplir les bulles de la BD intitulée 'Le corbeau et le renard' et ce en s'appuyant sur les images et sur la leçon de communication. Durant la conception
 Livret jeu BD Landerneau
Livret jeu BD Landerneau
24 août 2020 REPLACE-LES DANS L'ORDRE CI-DESSOUS
 Les bulles de la BD
Les bulles de la BD
Les bulles de la BD. Les personnages s'expriment grâce au texte qui est placé dans les bulles appelées aussi phylactère. Chaque bulle possède une queue ou
 La bande dessinEe
La bande dessinEe
☞ Après quelques exercices de prépara on tu pourras réaliser ton projet. Projet d'écriture n°3: la BD Observe ces vignettes et complète les bulles. Page 3 ...
 démarches 2019 Mes groupes dappartenance
démarches 2019 Mes groupes dappartenance
Ils iront ensuite compléter les bulles de leur propre Atomium. Dans le cercle Bulles de l'Atomium bulles de BD. Pourquoi des bulles à l'Atomium? Autre ...
 La parole aux personnages
La parole aux personnages
les caractéristiques d'une bande dessinée afin de compléter les bulles d'une histoire. Réalisation. • Expliquer aux élèves que la BD comporte son propre
 Les bulles de la BD
Les bulles de la BD
Les bulles de la BD. Les personnages s'expriment grâce au texte qui est placé dans les bulles appelées aussi phylactère. Chaque bulle possède une queue ou
 LA BD : du dialogue aux bulles
LA BD : du dialogue aux bulles
Complète les bulles à l'aide des textes écrits sous chaque vignette. Fiche ruedesecoles remis en page maliluno.eklablog.com
 Reforming Infrastructure: Privatization Regulation and Competition
Reforming Infrastructure: Privatization Regulation and Competition
Privatization's bad reputation is not fully deserved. Still complete independence for regulators is not possible or even ... The Antitrust Bulle-.
 SEAT Winter Complete Wheels 2022
SEAT Winter Complete Wheels 2022
Model. Type. 14". 15". 16". 17". 18". 19". 20". Mii. Steel. Barum. Alloy. Continental. Ibiza. Steel. Semperit. Abrera. Bridgestone. Arona. Steel. Barum.
 dossier pédagogique le texte dans la Bande Dessinée sommaire
dossier pédagogique le texte dans la Bande Dessinée sommaire
N'hésitez pas à le compléter avec du vocabulaire autour du texte en BD : la bulle : c'est le terme le plus souvent utilisé pour désigner.
 Freuds Library A Comprehensive Catalogue Compiled and edited
Freuds Library A Comprehensive Catalogue Compiled and edited
14 Sept 2019 Freud Sigmund (1985): The complete letters of Sigmund Freud to Wilhelm Fliess 1887–1904
 Lire un incipit de BD (1) Date: ……………………. Titre de lalbum
Lire un incipit de BD (1) Date: ……………………. Titre de lalbum
Le lettrage: écriture des lettres dans les bulles et encadrés narratifs. Propositions pour compléter les documents de la séance 2. Lire un incipit de BD ...
 Droplet Digital™ PCR Applications Guide
Droplet Digital™ PCR Applications Guide
Select Apply to load the wells and when finished select OK. Once the plate layout is complete select Run to begin the droplet reading process.
 THE COMPLETE LARVAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE PRONGHORN
THE COMPLETE LARVAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE PRONGHORN
with others gives a complete snap-shot over the entire suite Bradford R. W.
 [PDF] Les bulles de la BD - BDnF la fabrique à BD
[PDF] Les bulles de la BD - BDnF la fabrique à BD
Les personnages s'expriment grâce au texte qui est placé dans les bulles appelées aussi phylactère Chaque bulle possède une queue ou appendice La pointe de
 [PDF] [PDF] Gaspard et le phylactère magique - bd BOUM
[PDF] [PDF] Gaspard et le phylactère magique - bd BOUM
A côté de la bouche d'un personnage la bulle contient ses paroles ou ses pensées One shot = Histoire complète en un seul album
 [PDF] Exercices-BDpdf - Séquence – La bande dessinée
[PDF] Exercices-BDpdf - Séquence – La bande dessinée
Objectif : Distinguer une BD d'autres types de livres en analysant ses codes Colle les bulles à côté du bon personnage ; attention à bien placer
 [PDF] dossier pédagogique le texte dans la Bande Dessinée sommaire
[PDF] dossier pédagogique le texte dans la Bande Dessinée sommaire
Voici donc un rapide survol du vocabulaire autour du texte en BD : la bulle : c'est le terme le plus souvent utilisé pour désigner l'emplacement cerné d'un
 [PDF] La bande dessinée
[PDF] La bande dessinée
On trouve soit des BD qui racontent une seule et longue histoire (comme Astérix Tintin ) les bulles grâce auxquelles les personnages parlent
 [PDF] Séance n° 2 : Interpréter des signes et des bulles
[PDF] Séance n° 2 : Interpréter des signes et des bulles
On peut fabriquer sur grand format une affiche à compléter au cours de l'année ou du cycle avec la découverte d'autres signes formes de bulles
 [PDF] Lecture : La bande dessinée - Enseignonsbe
[PDF] Lecture : La bande dessinée - Enseignonsbe
La BD c'est une suite d'images qui forme un récit une histoire dont le Elles peuvent être utilisées dans les bulles (le cri d'un personnage par
 21 idées de Bd à compléter fle planche bd bande dessinée
21 idées de Bd à compléter fle planche bd bande dessinée
1 déc 2017 - Découvrez le tableau "Bd à compléter" de Lu Luberlue sur Pinterest Voir plus d'idées sur le thème fle planche bd bande dessinée
 [PDF] Lettrage et bulles en BD - Serge Paulus
[PDF] Lettrage et bulles en BD - Serge Paulus
Création d'une bulle: utilisation d'un calque de forme - Derrière l'outil rectangle on prend la forme personnalisée Lettrage et bulles en BD
Comment compléter les bulles d'une BD ?
Les bulles sont placées sur la page dans un ordre bien précis. On commence toujours par la bulle la plus haute dans une case, puis celle en dessous et ainsi de suite. Si deux cases sont au même niveau, on lit toujours celle de gauche avant celle de droite.Quels sont les types de bulles dans une BD ?
Les façons de faire les bulles en BD sont aussi nombreuses que les dessinateurs : chacun a son propre style. La plus courante est la bulle ronde, mais nous en trouvons aussi des rectangulaires, des octogonales, ainsi que des bulles à angles arrondis ou bien droits, etc.Quel logiciel pour faire de la BD ?
Comic Life, CAZ, Make Beliefs Comix, etc., découvre sans plus attendre les meilleurs outils pour réaliser une bande dessinée en tant que débutant.
1# Comic Life : outil de bande dessinée parfait pour les débutants. 2# Make Beliefs Comix. 3# Story Board. 4# BirdsDessines. 5# BD Studio Practic.- Des bulles apparaissent dans la série américaine Hogan's Alley (alias The Yellow Kid), créée en 1894 par Richard Felton Outcault ; c'est cependant une autre série américaine, The Katzenjammers Kids (Pim Pam Poum), créée en 1897 par Rudolph Dirks, qui systématise leur utilisation.
REFORMINGINFRASTRUCTURE
Privatization, Regulation, and Competition
REFORMINGINFRASTRUCTURE
A WORLD BANK POLICY RESEARCH REPORT
Infrastructure is crucial for generating growth,
alleviating poverty, and increasing international competitiveness. For much of the 20 th century and in most countries, the network utilities that delivered infrastructure services - such as electricity ,natural gas, telecommunications, railroads, and water supply - were vertically and horizontally integrated state monopolies.This approach often resulted in extremely weak services, especially in developing and transition economies, and particularly for poor people. Common problems included low productivity,high costs,poor quality,insufficient revenue, and shortfalls in investment. Recognizing infrastructure's importance,many countries over the past two decades have implemented far-reaching reforms - restructuring, privatizing,and establishing new approaches to regulation.Reforming Infrastructureidentifies the challenges involved in this massive policy redirection within the historical,economic,and institutional context of developing and transition economies.It also assesses the outcomes of these policy changes, as well as their distributional consequences - especially for poor households and other disadvantaged groups. Drawing on a range of international experiences and empirical studies, it recommends directions for future reforms and research to improve infrastructure performance - identifying pricing policies that strike a balance between economic efficiency and social equity,suggesting rules governing access to bottleneck infrastructure facilities, and proposingways to increase poor people's access to these crucial services.ISBN 0-8213-5070-6REFORMING INFRASTRUCTURE:Privatization, Regulation, and Competition
Reforming
Infrastructure
Privatization, Regulation,
and CompetitionA World Bank
Policy Research Report
Reforming
Infrastructure
Privatization, Regulation,
and CompetitionA copublication of the World Bank
and Oxford University PressIoannis N. Kessides © 2004 The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank1818 H Street, NW
Washington, DC 20433
Telephone 202-473-1000
Internet www.worldbank.org
E-mail feedback@worldbank.org
All rights reserved.
123407060504
A copublication of the World Bank and Oxford University Press. This volume is a product of the staff of the World Bank. The findings, interpretations, and conclusions expressed herein do not necessarily reflect the views of the Board of Executive Directors of the World Bank or the governments they represent. The World Bank does not guarantee the accuracy of the data included in this work. The boundaries, colors, denominations, and other information shown on any map in this work do not imply any judgment on the part of the World Bank concerning the legal sta- tus of any territory or the endorsement or acceptance of such boundaries.Rights and Permissions
The material in this work is copyrighted. Copying and/or transmitting portions or all of this work without permission may be a violation of applicable law. The World Bank en- courages dissemination of its work and will normally grant permission promptly. For permission to photocopy or reprint any part of this work, please send a request with complete information to the Copyright Clearance Center, Inc., 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923, USA, telephone 978-750-8400, fax 978-750-4470, www.copyright. com. All other queries on rights and licenses, including subsidiary rights, should be addressed to the Office of the Publisher, World Bank, 1818 H Street NW, Washington, DC 20433, fax 202-522-2422, e-mail pubrights@worldbank.org. Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Reforming infrastructure : privatization, regulation, and competition. p. cm. Ñ (A World Bank policy research report)Includes bibliographical references.
ISBN 0-8213-5070-6
1. Public utilities. 2. Privatization. 3. Public utilitiesÑGovernment policy.
4. Infrastructure (Economics) I. World Bank. II. Series.
HD2763.R427 2004
363.6Ñdc 22
2004043841
Cover photos (clockwise from top left): © Adrian Lyon/Getty; World Bank Photo Library;© Corbis; World Bank Photo Library
Cover designed by Richard Fletcher of Fletcher Design vContents
Forewordxi
The Report Teamxv
Executive Summary1
State-owned Monopolies Often Exhibited Poor Performance...2 . . .Leading to a New Model for Financing and ProvidingInfrastructure3
The New Model Poses RisksÑBut Also Holds ConsiderablePromise4
What Effects Have Reforms Had?9
Developing Good Regulation Remains a Major Challenge17Many Prices and Subsidies Still Require Reform19
An Agenda for ActionÑFrom Institution Building to Policymaking211. The New Paradigm for Network Utilities 29
Why Are Network Utilities So Important? 29
From State to MarketÑChanging Views on Utilities 30The Dawn of a New Utility Model 35
Framework for Assessing Reforms and Regulations 42 Recent Experiences with Privatization and ReformÑPromises and Perils 51
Second Generation ReformsÑChoices and Challenges 632. Crafting Regulation for Privatized Infrastructure 79
The Emergence of Post-Privatization Regulation 79
The Evolution and Elements of Effective Regulation 81The Structure of Regulatory Institutions 95
The Importance of Regulatory Commitment 100
Getting the Economics Right 110
Mechanisms to Regulate Prices 112
Moving toward More Practical Regulation 123
CONTENTS
vi3. Restructuring Electricity Supply 131
Background to Electricity Reform 132
Addressing the Problems of State Ownership 141
Regulatory Challenges 158
Reform Experiences and Lessons 167
4. Managing Private Participation in Transportation 183
Railroads: Restructuring Regulation for the Public Interest 184 Ports: Alternatives for Organizing a Multiproduct Activity 2055. Reforming the Water Sector 219
Economics of Water Supply 220
Options for Competition and Market Structure 227
Choosing Regulation 235
Reform Experiences and Lessons 252
6. An Agenda for Action 259
Assessing ReformÕs Effects on Performance and Distribution 260 Pricing ReformÑBalancing Efficiency and Equity 269Facilitating Access to Bottleneck Facilities 275
References 279
Boxes1.1 Milestones in Infrastructure Reform in the United States,
the United Kingdom, and the European Union 321.2 The Technological Revolution in Telecommunications 40
1.3 Power Generation in Brazil Shows That Privatization Is Not Always
the Best Approach 431.4 Disadvantages of Vertical Separation 48
1.5 Prerequisites for Effective Privatization 58
1.6 Using Competition Policy to Avoid Regulatory Capture 69
1.7 TelmexÕs Market Power in the Internet Market 70
1.8 Consumer Participation in ColombiaÕs Rulemaking 76
2.1 Regulation in ArgentinaÑRepeating U.S. Mistakes 82
2.2 Recent Shortcomings and Achievements in Infrastructure
Regulation 84
2.3 Decentralized Water Services in Mexico and Morocco 98
2.4 LatviaÕs Public Utilities Regulation Commission 99
2.5 Examples of Allegedly Opportunistic Government Behavior 102
2.6 Regulatory Rigidity in Chile 110
2.7 Cost-Plus Mechanisms 113
2.8 Price Constraints Imposed by Price Cap Plans 116
2.9 Hybrid Regulatory Mechanisms 119
2.10 African Cooperation on Telecommunications Regulation 127
3.1 Rationale for Structural Integration of the Electricity Industry 133
3.2 Power Shortages in the Philippines 137
viiCONTENTS
3.3 Opening the Electricity MarketÑPhotovoltaic Systems
in Kenya 1413.4 Underpricing Undermines Electricity Expansion in Zimbabwe 143
3.5 Stranded Power Purchase Agreements in Poland 156
3.6 Lessons from CaliforniaÕs Experience 164
4.1 Limited Rail Options Result in Captive Shippers 191
4.2 Examples of Port Services 208
4.3 Organizational Structures of Ports 209
5.1 Water Systems in Small African Towns and Rural Areas 229
5.2 Problems with Service Contracts in Mexico City 230
5.3 Private Sector Transactions in Water and Sanitation 235
5.4 Objectives of Water Tariff Design 237
5.5 An Aborted Attempt at Water Concessioning in Atlanta,
Georgia 241
5.6 Creative Management of South AfricaÕs Commitment to
Free Water 247
5.7 Making New Connections Affordable in Buenos Aires 248
5.8 Adapting Quality Standards to Permit Extensions of Low-cost Service
in El Alto 2495.9 Providing Incentives to Extend Service in C™te dÕIvoire 250
6.1 The World Bank Wonders about Utility Privatizations 260
6.2 The Need for Data on Infrastructure Reform 261
6.3 Criteria for Designing Subsidies 267
6.4 Picking Apart Cross-Subsidies 271
Figures
1 In 1990Ð2001, Latin America and East Asia Received the Most
Private Investment in Infrastructure10
2 Private Investment in Infrastructure in Developing and Transition
Countries Peaked in 199711
3 Privatized Services Have Increased Access to Safe Water in a Variety
of Cities and Countries124 In 1989Ð94, Privatization Contributed to Faster Growth in Phone
Lines in Latin America13
5 Railway Concessions Sharply Increased Labor Productivity
in the 1990s146 In 2000, Electricity Prices Covered a Small Fraction of Long-Run
Marginal Costs in Many Transition Economies15
1.1 Latin America and the Caribbean Has Led Developing Regions in
Private Investment in Infrastructure, 1990Ð2001 341.2 The Optimal Size of Power Generating Plants Has Shrunk 39
1.3 There Are Now More Mobile Phone Users Than Fixed Phone
Lines 41
1.4 Latin Americans Increasingly Disapprove of Privatization 52
1.5 Privatization Has Led to Rapid Growth in Telecommunications
Networks 54
1.6 Private Competition Generated the Fastest Growth in
Telecommunications Lines in Latin America 56
CONTENTS
viii1.7 Electricity Prices Often Fail to Cover Costs in Europe and
Central Asia, 2000 66
1.8 Despite Liberalization, Entrants into the Local Exchange Account
for a Small Share of Latin American Telecom Markets,2001 Second Quarter 72
2.1 Results from a Survey of Telecommunications Regulators,
2001 93
2.2 Regulatory Indexes for Telecommunications in Latin America,
1980Ð97 94
3.1 Vertical Integration in Electricity 132
3.2 Customers per Electricity Employee in Selected African Countries,
1998 138
3.3 Projected Costs of Small-Scale Electricity Generation Technologies,
2000Ð15 139
3.4 The Single-Buyer Model for Electricity 148
3.5 The Wholesale Competition Model for Electricity 150
3.6 Average Ratios of Household to Industrial Electricity Prices,
1990Ð99 161
3.7 Types of Private Investment in Electricity, by Region,
1990Ð2001 170
3.8 Top 20 Recipients of Private Investment in Electricity,
1990Ð99 171
3.9 Post-Privatization Labor Productivity in Electricity Distribution
in Argentina, Chile, and the United Kingdom 1743.10 Energy Losses among ArgentinaÕs Distribution Companies,
at Privatization and in 1999 1753.11 Electricity Coverage in Peru, 1986Ð97 176
4.1 Railroad Freight in Transition Countries, 1988Ð2001 185
4.2 Cumulative Investment in Rail Projects with Private Participation
in Developing and Transition Countries, 1990Ð2001 1994.3 Performance of Class I U.S. Railroads, 1964Ð2000 200
4.4 Rail Labor Productivity in Argentina, 1974Ð2000 202
4.5 Cumulative Investment in Port Projects with Private Participation
in Developing and Transition Countries, 1990Ð2001 2115.1 Winners and Losers before and after Adjustments to a Water
Concession in Parana, Argentina 246
6.1 Telephone and Water Access in Urban and Rural Areas
of Developing Regions, 1990s 266Tables
1.1 Private Investment in Infrastructure in Developing and Transition
Economies, by Sector, 1990Ð2001 33
1.2 Noncompetitive and Competitive Components of Network
Industries 37
1.3 Exclusivity Periods for Incumbent Telecommunications Operators
in Latin America 59 ixCONTENTS
1.4 Access to Infrastructure Services in Urban and Rural Areas of
Developing Regions, late 1990s 65
1.5 Average Household Incomes and Energy Tariffs in Ukraine,
1992Ð98 67
2.1 Ranking of Infrastructure Regulation in Asia, by Sector and
Institutional Criteria, 1998 91
2.2 Example of Infrastructure Concessions in Developing and
Transition Economies 107
2.3 X factor Decisions in U.K. and U.S. Telecommunications Regulation,
1984ÐPresent 117
2.4 Features of Rate of Return and Price Cap Regulation 120
3.1 Net Electricity Consumption in Industrial and Developing Countries,
1990Ð2020 136
3.2 Options for the Structure of Electricity Markets 144
3.3 Cash Collection and Commercial Losses for Electricity Companies
in Southeastern Europe, 2000 1473.4 Market Shares of the Three Largest Generation, Transmission,
and Distribution Companies in Various Countries, 2000 1633.5 Electricity Reforms by Region, 1998 168
3.6 Private Investment in Electricity by Region, 1990Ð99 169
4.1 Market Structure and Ownership Options in Railroads,
Various Countries, 2001 196
4.2 Rail Freight Tariffs in the Initial Years of Concessions and in 1999,
Various Countries 203
4.3 Operating Performance of Ports in Colombia before and after Reforms,
1993 and 1996 212
5.1 Ratios of Prices Charged by Water Vendors and Public Utilities 222
5.2 Institutional Options for Water Supply 228
5.3 Initial Conditions and Reforms in Six Water Systems 253
5.4 Effects of Reforms on Access and Waste in Six Water Systems 255
xi I NFRASTRUCTURE INDUSTRIES AND SERVICES ARE CRUCIAL FOR generating economic growth, alleviating poverty, and increasing international competitiveness. Safe water is essential for life and health. Reliable electricity saves businesses and consumers from hav- ing to invest in expensive backup systems or more costly alternatives, and keeps rural women and children from having to spend long hours fetching firewood. Widely available and affordable telecommunica- tions and transportation services can foster grassroots entrepreneurship and so are critical to generating employment and advancing economic development. Recognizing infrastructureÕs importance, many countries have im- plemented far-reaching reforms over the past two decadesÑrestructur-quotesdbs_dbs22.pdfusesText_28[PDF] plancher chauffant thermak avis
[PDF] se présenter en détail
[PDF] l'accueil du malade définition
[PDF] plancher chauffant kp1
[PDF] comment accueillir un malade
[PDF] récit parcours professionnel
[PDF] accueil du malade pdf
[PDF] accueil du patient ? l'hopital
[PDF] accueil en milieu hospitalier pdf
[PDF] dtu plancher chauffant rt 2012
[PDF] installation plancher chauffant basse température
[PDF] récit de vie professionnelle exemple
[PDF] accueil du patient en milieu hospitalier ppt
[PDF] pose plancher chauffant eau
