 IEC/FDIS 31010
IEC/FDIS 31010
International standard ISO/IEC 31010 has been prepared by IEC technical committee 56: Dependability together with the ISO TMB “Risk management” working group.
 Manajemen risiko – Teknik penilaian risiko
Manajemen risiko – Teknik penilaian risiko
ISO 31010:2016 dengan judul Manajemen risiko – ... Apabila pengguna menemukan keraguan dalam Standar ini maka disarankan untuk melihat standar aslinya yaitu IEC/ ...
 NLi1` 11 :`31010: Gestão de riscos - Técnicas para o processo de
NLi1` 11 :`31010: Gestão de riscos - Técnicas para o processo de
Aug 3 2559 BE ... 0310&+ 1D 13:43:37 de uso exclusivo de INSTITUTO N CIONAL DE TECNOLOGIA. ABNT NBR ISO/IEC 31010:2012. Página. PrefácioNacional .
 MALAYSIAN STANDARD
MALAYSIAN STANDARD
International standard IEC/ISO 31010 has been prepared by IEC technical committee 56: Dependability together with the ISO TMB “Risk management” working group.
 Risk assessment techniques ISO 31010
Risk assessment techniques ISO 31010
• ISO / IEC Guide 73 Risk management -. Vocabulary. • ISO 31010
 Untitled
Untitled
Apr 24 2556 BE 1 de 104. Page 6. NORMA TÉCNICA COLOMBIANA. NTC-IEC/ISO 31010. ¿cuál es la probabilidad de su ocurrencia en el futuro? ¿existen factores que ...
 ISO 31000:2009 IEC/ISO 31010:2009 & ISO Guide 73:2009
ISO 31000:2009 IEC/ISO 31010:2009 & ISO Guide 73:2009
Nov 27 2552 BE 2009 ISO/IEC 31010 published. Page 4. KNOWLEDGE. ABOUT OUTCOMES. Well-defined outcomes.
 IEC-ISO 31010: el uso de técnicas para la evaluación del riesgo
IEC-ISO 31010: el uso de técnicas para la evaluación del riesgo
RESUMEN. La norma IEC-ISO 31010 creada en 2009 y actualizada en 2018
 ДСТУ IEC/ISO 31010:2013 Керування ризиком. Методи
ДСТУ IEC/ISO 31010:2013 Керування ризиком. Методи
ДСTY IEC/ISO 31010:2013. НАЦІОНАЛЬНИЙ ВСТУП. Цей стандарт в письмовий переклад IEC/ISO 31010:2009 Risk management - Risk assessment techniques (Керування
 ก ก Tools and Techniques for Enterprise Risk Management (ERM
ก ก Tools and Techniques for Enterprise Risk Management (ERM
ISO 31010 - Risk Assessment Technique. ERM Framework Comparison. Conclusion ISO 31010. 2010. COSO. ISO 31000. COSO Internal Control Framework. Monitoring.
 IEC/FDIS 31010
IEC/FDIS 31010
31010. Risk management — Risk assessment techniques International standard ISO/IEC 31010 has been prepared by IEC technical committee 56:.
 ISO 31010 Risk assessment techniques 1
ISO 31010 Risk assessment techniques 1
A graphical model of variables and their cause-effect relationships expressed using probabilities. A basic Bayesian network has variables representing
 Risk management - Risk assessment techniques (IEC/ISO 31010
Risk management - Risk assessment techniques (IEC/ISO 31010
1 May 2010 ISO 22000. NOTE Harmonized as EN ISO 22000. I.S. EN 31010:2010. This is a free 14 page sample. Access the full version online.
 ISO 31000:2009 IEC/ISO 31010:2009 & ISO Guide 73:2009
ISO 31000:2009 IEC/ISO 31010:2009 & ISO Guide 73:2009
27 Nov 2009 IEC/ISO 31010:2009. & ISO Guide 73:2009. International Standards for the. Management of Risk. Kevin W Knight AM. CHAIRMAN. UNECE GRM.
 Risk assessment techniques ISO 31010
Risk assessment techniques ISO 31010
This International Standard is a companion standard ISO 31000. ISO / IEC Guide 73 Risk management -. Vocabulary. • ISO 31010
 Manajemen risiko – Teknik penilaian risiko
Manajemen risiko – Teknik penilaian risiko
SNI IEC/ISO 31010:2016. Manajemen risiko – Teknik penilaian risiko. Risk management – Risk assessment techniques. (IEC/ISO 31010:2009 IDT). ICS 03.100.001.
 MS IEC/ISO 31010 – Risk Management - Risk Assessment
MS IEC/ISO 31010 – Risk Management - Risk Assessment
Setting the Scene – Risk Management Framework (MS ISO/IEC 31000). • Framework for managing risk. • Risk Management Process. • MS IEC/ISO 31010 – Risk
 NTE INEN-IEC/ISO 31010
NTE INEN-IEC/ISO 31010
Esta norma nacional es una traducción idéntica de la Norma Internacional IEC/ISO 31010:2009. NORMA. TÉCNICA. ECUATORIANA. GESTIÓN DE RIESGOS - TÉCNICAS DE
 PECB Change Log Form
PECB Change Log Form
23 Aug 2019 Replaced the parts where IEC/ISO 31010:2009 was used with the newest edition of this standard i.e. IEC 31010:2019.
 MALAYSIAN STANDARD
MALAYSIAN STANDARD
This Malaysian Standard is identical with IEC/ISO 31010:2009 Risk management - Risk assessment techniques
ISO 31000:2009
IEC/ISO 31010:2009
& ISO Guide 73:2009International Standards for the
Management of Risk
Kevin W Knight AM
CHAIRMAN
UNECE GRM
P 0 BOX 226, NUNDAH Qld 4012, Australia
E-mail: kknight@bigpond.net.au
02/17We all manage risk consciously or unconsciously
-but rarely systematicallyManaging risk means forward thinking
Managing risk means responsible thinking
Managing risk means balanced thinking
Managing risk is all about maximising opportunity
and minimising threats The risk management process provides a framework to facilitate more effective decision makingManaging Risk
History of the ISO and
Risk Management
Over 80 separate ISO and IEC Technical Committees are addressing aspects of risk management27thJune 2002, ISO/IEC Guide 73, Risk Management -
2004 ISO Technical Management Board (TMB)
approached by Australia and JapanAS/NZS 4360:2004 to be adopted by ISO.
June 2005, TMB sets up Working Group (WG)
15.11.2009 ISO 31000 & ISO Guide 73 published
27.11.2009 ISO/IEC 31010 published.
KNOWLEDGE
ABOUT OUTCOMES
Well-defined
outcomesPoorly
defined outcomesSome basis for
probabilitiesrisk ambiguityKNOWLEDGE
ABOUTLIKELIHOODS
³INCERTITUDE´
No basis for
probabilitiesuncertaintyignoranceUniversity of Cambridge.
The Pivotal Definition
risk effect of uncertainty on objectives NOTE 1 An effect is a deviation from the expected positive and/or negative. NOTE 2 Objectives can have different aspects (such as financial, health and safety, and environmental goals) and can apply at different levels (such as strategic, organization-wide, project, product and process). NOTE 3 Risk is often characterized by reference to potential events and consequences, or a combination of these. NOTE 4 Risk is often expressed in terms of a combination of the consequences of an event (including changes in circumstances) and the associated likelihood of occurrence. NOTE 5 Uncertainty is the state, even partial, of deficiency of information related to, understanding or knowledge of, an event, its consequence, or likelihood. [ISO Guide 73:2009] risk owner person or entity with the accountability and authority to manage a risk control measure that is modifying risk NOTE 1 Controls include any process, policy, device, practice, or other actions which modify risk.NOTE 2 Controls may not always exert the intended
or assumed modifying effect. [ISO Guide 73:2009]Accountable
Responsible
Liability for the outcomes of actions or
decisionsNOTE: Includes failure to act or make
decisions OR being obligated to answer for a decision OR obligation to answer for an action.Obligation to carry out duties or
decisions, or control over others as directed OR having the obligation to act OR obligation to carry out instructions.Yet to be defined
AS/NZS ISO 31000:2009
-Users AS/NZS ISO 31000:2009 is intended to be used by a wide range of stakeholders including: those responsible for implementing risk management within their organization; those who need to ensure that an organization manages risk; those who need to manage risk for the organization as a whole or within a specific area or activity; in managing risk; anddevelopers of standards, guides, procedures, and codes of practice that in whole or in part set out how risk is to be managed within the specific context of these documents.
A Business PrinciplesApproach to the
Management of Risk
Corporate Governance
The way in which an organisation is governed and
controlled in order to achieve its objectives. The control environment makes an organisation reliable in achieving these objectives within a tolerabledegree of risk. It is the glue which holds the organisation together in pursuit of its objectives while risk management provides the resilience. Queensland Audit Office ±Report No. 7 1998-99: -Corporate Governance
³7OH V\VPHP N\ ROLŃO HQPLPLHV MUH
GLUHŃPHG MQG ŃRQPUROOHGB´
´FRUSRUMPH JRYHUQMQŃH JHQHUMOO\ UHIHUV
to the processes by which organisations are directed, controlled and held to account. It encompasses authority, accountability, stewardship, leadership, direction and controlH[HUŃLVHG LQ POH RUJMQLVMPLRQB´
SAA HB 254-2005
Governance, risk management and control assurance
Standards Australia. ISBN 0 7337 6892 X
ACCOUNTABILITY
SUPERVISION
GOVERNANCE
STRATEGIC
MANAGEMENT
MANAGEMENT
EXECUTIVE
MANAGEMENT
DECISION & CONTROL
OPERATIONAL MANAGEMENT
Potential greater
future role of risk managementTraditional and current
risk management applicationMandate and Commitment
(4.2)Implementing
RiskManagement
(4.4)Design of
Framework
(4.3)Continual
Improvement
of theFramework
(4.6)Monitoring
and Review of theFramework
(4.5)Framework
(Clause 4) a) Creates value b) Integral part of organizational processes c) Part of decision making d) Explicitly addresses uncertainty e) Systematic, structured and timely f) Based on the best available information g) Tailored h) Takes human and cultural factors into account i) Transparent and inclusive j) Dynamic, iterative and responsive to change k) Facilitates continual improvement and enhancement of the organizationPrinciples
(Clause 3)Process
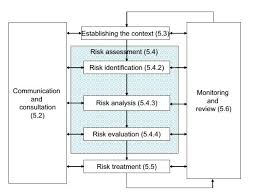
(Clause 5)Establishing
the context (5.3)Risk treatment
(5.5) Risk identification (5.4.2)Risk analysis
(5.4.3) Risk evaluation (5.4.4)Risk assessment
(5.4) M o n i t o r i n g r e v i e w (5.6) C o m u n i c a t i o n c o n s u l t a t i o n 5.2 ISO 31000:2009 Figure 1 ±Relationship between the principles, framework and processBusiness Principles Approach
AS/NZS ISO 31000:2009 Principles (Clause 3)
1.Create value
2.Be an integral part of organisational processes
3.Be part of decision making
4.Explicitly address uncertainty
5.Be systematic and structured
6.Be based on the best available information
7.Be tailored
8.Take into account human factors
9.Be transparent and inclusive
10.Be dynamic, iterative and responsive to change
11.Be capable of continual improvement and enhancement
Risk management should
create valueRM contributes to the
achievement of objectives.Protects value minimise
downside risk, protects people, systems and processes.Risk management should be an
integral part of organizational processesRM is not a stand-alone activity
from the management system of the organisation.RM is part of the process -not
Risk management should be
part of decision makingRisk management helps decision
makers make informed choices, prioritize actions and distinguish among alternative courses of action.Helps allocate scarce resources.
Risk management explicitly
addresses uncertaintyRisk management explicitly takes
account of uncertainty, the nature of that uncertainty, and how it can be addressed.RM addresses uncertainty, no
matter the level of uncertainty.Risk management should be
systematic and structuredquotesdbs_dbs14.pdfusesText_20[PDF] iso 80000
[PDF] iso 9000 2008
[PDF] iso 9000 wikipedia
[PDF] iso 9000:2008 pdf
[PDF] iso 9000:2015
[PDF] iso 9001 2000
[PDF] iso 9001 2015
[PDF] iso 9001 2015 pour les pme comment procéder pdf
[PDF] iso 9001 2015 ppt
[PDF] iso 9001 7.1 6
[PDF] iso 9001 avantages et inconvénients
[PDF] iso 9001 c'est quoi
[PDF] iso 9001 certification
[PDF] iso 9001 définition
