 8086 Microprocessor
8086 Microprocessor
১৮ জানু ২০২৩ Multiplication and Division instructions also use the AX or. AL. Execution Unit (EU). Page 29. Architecture. 8086 Microprocessor.
 Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller Theory and
Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller Theory and
8086 Microprocessor Architecture and Operation: It is a 16 bit µp. 8086 has a 20 bit address bus can access upto 220 memory locations ( 1. MB) . It can
 8086- Architecture: Features
8086- Architecture: Features
or write operands from memory the BIU is free to look ahead in the program by pre-fetching the next sequential instruction. Page 18. 18. • These pre-fetching
 The 8086 Microprocessor
The 8086 Microprocessor
The architecture of 8086 is shown below in Fig. 11.3. It has got two separate functional units—Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and Execution Unit (EU). 8086
 Features of 8086 Microprocessor:
Features of 8086 Microprocessor:
The bus interface unit is the 8086 Internal Architecture to the outside world. It provides a full 16-bit bi- directional data bus and 20-bit address bus. The
 EC8691 MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS
EC8691 MICROPROCESSORS AND MICROCONTROLLERS
Four general-purpose 16-bit registers: AX BX
 8259A Programmable Interrupt Controller
8259A Programmable Interrupt Controller
✓ Internal architecture of 8259A. ✓ Interrupt Operation of 8259A. ✓ Programming Modes ICWs
 MILITARY INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
MILITARY INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Architecture and Marine Engineering. (NAME) began its journey from academic ... microprocessor using assembly language in a group project. M H. H. (H – High ...
 Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE
Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE
or write operands from memory the BIU is free to look ahead in the program by pre-fetching the next sequential instruction. Page 18. 18. Segmented Memory.
 Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller Theory and
Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller Theory and
8086 Microprocessor Architecture and Operation: It is a 16 bit µp. 8086 has a 20 bit address bus can access upto 220 memory locations ( 1. MB) . It
 LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2019-20)
LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2019-20)
8086 Architecture. Introduction to Microprocessors. A microprocessor is a computer processor which incorporates the functions of a computer's central
 8086 ARCHITECTURE
8086 ARCHITECTURE
an 8086 family microprocessor is at the lower address. The 8086 has two parts the Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and the Execution Unit.
 ADVANCED MICROPROCESSORS & PERIPHERALS
ADVANCED MICROPROCESSORS & PERIPHERALS
Chapter 1 covers 8086/8088 architecture in adequate detail. Chapter 9 covers 80286 along with its coprocessor. Chapter 10 covers the microprocessor 80386 and
 PDF Microprocessors - Tutorialspoint
PDF Microprocessors - Tutorialspoint
In this tutorial we will discuss the architecture
 Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE
Intel 8086 MICROPROCESSOR ARCHITECTURE
8086 has a 20 bit address bus can access up Intel 8086 Internal Architecture ... or write operands from memory the BIU is free to.
 LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2017-18) MALLA
LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2017-18) MALLA
The 8086 microprocessor has a much more powerful instruction set along with the architectural developments which imparts substantial programming flexibility
 Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture Notes
Computer Organization and Architecture Lecture Notes
The next major step in the evolution of the microprocessor was the introduction in 1972 of The 8086 is the first appearance of the x86 architecture.
8086 ARCHITECTURE MICROPROCESSORS &INTERFACING
8086 ARCHITECTURE
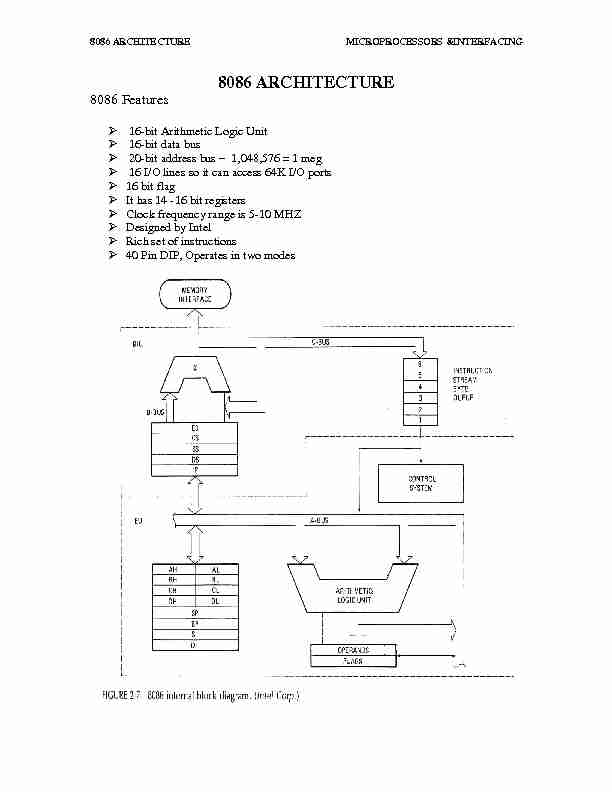
8086 Features
¾ 16-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit
¾ 16-bit data bus
¾ 20-bit address bus 1,048,576 = 1 meg
¾ 16 I/O lines so it can access 64K I/O ports
¾ 16 bit flag
¾ It has 14 -16 bit registers
¾ Clock frequency range is 5-10 MHZ
¾ Designed by Intel
¾ Rich set of instructions
¾ 40 Pin DIP, Operates in two modes
8086 ARCHITECTURE MICROPROCESSORS &INTERFACING
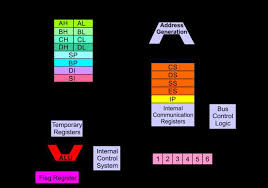
The address refers to a byte in memory. In the 8086, bytes at even addresses come in on the low half of the data bus (bits 0-7) and bytes at odd addresses come in on the upper half of the data bus (bits 8-15).The 8086 can read a 16-bit word at an even address in one operation and at an odd address in two operations. The least significant byte of a word on an 8086 family microprocessor is at the lower address. The 8086 has two parts, the Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and the Execution Unit (EU).The BIU fetches instructions, reads and writes data, and computes the 20-bit address. The EU decodes and executes the instructions using the 16-bit ALU.The BIU contains the following registers:
¾ IP - the Instruction Pointer
¾ CS - the Code Segment Register
¾ DS - the Data Segment Register
¾ SS - the Stack Segment Register
¾ ES - the Extra Segment Register
The BIU fetches instructions using the CS and IP, written CS: IP, to construct the 20- bit address. Data is fetched using a segment register (usually the DS) and an effective address (EA) computed by the EU depending on the addressing mode.The EU contains the following 16-bit registers:
¾ AX - the Accumulator
¾ BX - the Base Register
¾ CX - the Count Register
¾ DX - the Data Register
¾ SP - the Stack Pointer
¾ BP - the Base Pointer
¾ SI - the Source Index Register
¾ DI - the Destination Register
8086 ARCHITECTURE MICROPROCESSORS &INTERFACING
These are referred to as general-purpose registers, although, as seen by their names, they often have a special-purpose use for some instructions. The AX, BX, CX, and DX registers can be considered as two 8-bit registers, a High byte and a Low byte. This allows byte operations and compatibility with the previous generation of 8-bit processors, the 8080 and 8085. The 8-bit registers are:¾ AX --> AH,AL
¾ BX --> BH,BL
¾ CX --> CH,CL
¾ DX --> DH,DL
The ALU performs all basic computational operations: arithmetic, logical, and comparisons. The control unit orchestrates the operation of the other units. It fetches instructions from the on-chip cache, decodes them, and then executes them. Each instruction has the control unit direct the other function units through a sequence of steps that carry out the instruction's intent. The execution path taken by the control unit can depend upon status bits produced by the arithmetic logic unit or the floating-point unit (FPU) after the instruction sequence completes. This capability implements conditional execution control flow, which is a critical element for general-purpose computation. ES CS SS DS IP AH BH CH DH AL BL CL DL SP BP SI DI FLAGS AX BX CX DXExtra Segment
Code Segment
Stack Segment
Data Segment
Instruction Pointer
Accumulator
Base Register
Count Register
Data Register
Stack Pointer
Base Pointer
Source Index Register
Destination Index Register
BIU registers
(20 bit adder)EU registers
16 bit arithmetic
ES CS SS DS IP AH BH CH DH AL BL CL DL SP BP SI DI FLAGSquotesdbs_dbs7.pdfusesText_5[PDF] 8086 microprocessor book by ramesh gaonkar pdf
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor book pdf free download
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor books pdf free download
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor family pdf
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor instruction set ppt
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor instruction set ppt free download
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor notes pdf free download
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor pdf free download
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor pin configuration pdf
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor pin diagram explanation
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor pin diagram explanation ppt
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor pin diagram in hindi
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor pin diagram with explanation
[PDF] 8086 microprocessor powerpoint presentation
