 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (DBMS)
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (DBMS)
In contrast in a three-tier architecture
 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
DBMS architecture is critical in the design development
 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS LECTURE NOTES MALLA
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS LECTURE NOTES MALLA
3) DBMS system works on the centralized system i.e.; all the users from all In contrast
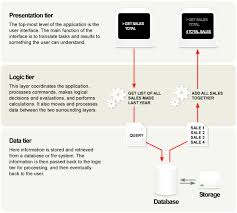 Web App Architectures.pdf
Web App Architectures.pdf
DBMS. Page 4. 4. User1. View1. User2. View2. Conceptual Schema. Internal Schema. Disk 3-tier Architecture vs. MVC Architecture. □ Communication. □ 3-tier: ...
 DBMS - Architecture
DBMS - Architecture
Here the application tier is entirely independent of the database in terms of operation design
 LECTURE NOTES ON DATA MINING& DATA WAREHOUSING
LECTURE NOTES ON DATA MINING& DATA WAREHOUSING
2 A Three Tier Data Warehouse Architecture: Tier-1: The bottom tier is a warehouse database server that is almost always a relationaldatabase system. Back
 Fundamentals of Database Systems Seventh Edition
Fundamentals of Database Systems Seventh Edition
22-Jan-2020 ... three-schema. DBMS architecture which allows three schema levels: □ An internal schema describes the physical storage structure of the ...
 AICTE Model Curriculum: Diploma in Engineering & Technology
AICTE Model Curriculum: Diploma in Engineering & Technology
AICTE constituted subject-wise team of 3-4 experts to revise the model curriculum of diploma courses. Similar exercise is done for programmes at UG and PG level
 COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING
COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING
View) Three level architecture of DBMS
 1 ANNA UNIVERSITY CHENNAI NON - AUTONOMOUS
1 ANNA UNIVERSITY CHENNAI NON - AUTONOMOUS
3 Design/development of solutions: Design solutions for complex engineering problems and design system components or processes that meet the specified needs
 DBMS Architecture: 1-Tier 2-Tier & 3-Tier
DBMS Architecture: 1-Tier 2-Tier & 3-Tier
DBMS Architecture: 1-Tier 2-Tier & 3-Tier. What is Database Architecture? DBMS architecture helps in design
 DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (DBMS)
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (DBMS)
A database-management system (DBMS) is a collection of interrelated data and a set of programs to In contrast in a three-tier architecture
 Web App Architectures.pdf
Web App Architectures.pdf
Data Independence in Rel. DBMS N-tier architectures try to separate the components into different tiers/layers ... The 3-Tier Architecture for Web Apps.
 3-Tier Architecture
3-Tier Architecture
Development Issues: • Complex application rules difficult to implement in database server – requires more code for the client.
 DATABASE SYSTEM CONCEPTS AND ARCHITECTURE
DATABASE SYSTEM CONCEPTS AND ARCHITECTURE
Three-Schema Architecture and Data Independence. • Database Languages and Interfaces 3-TIER CLIENT-SERVER DBMS. ARCHITECTURE.
 Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 1: Introduction
DBMS contains information about a particular enterprise. ? DBMS provides an environment that §Three-tier architecture: E.g. web-based applications and.
 Advanced Database Management System
Advanced Database Management System
DBMS 3-TIER ARCHITECTURE. 6. 1.6. INSTANCE AND SCHEMA. 7. 1.7. DATA INDEPENDENCE. 7. 1.8. DATABASE USERS AND ADMINISTRATORS. 8. 2. DISTRIBUTED DATABASES.
 Creating 3-tier Architecture
Creating 3-tier Architecture
A three-tier style in which clients do not connect directly to the database. Web Services
 Untitled
Untitled
This tutorial explains the basics of DBMS such as its architecture data models
 Bookmark File PDF Fundamentals Of Database Systems Elmasri
Bookmark File PDF Fundamentals Of Database Systems Elmasri
Database Systems Elmasri Navathe Ppt Chapter after getting deal. relational algebra PHP
3-Tier Architecture
3-Tier Architecture
Prepared By
Channu Kambalyal
Page 1 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
Table of Contents
1.0 Traditional Host Systems........................................................................
................32.0 Distributed Systems........................................................................
........................43.0 Client/Server Model........................................................................
........................54.0 Distributed Client/Server Model........................................................................
......65.0 Inter-process Communication........................................................................
.........76.0 Benefits of the Client/Server Model........................................................................
87.0 Client/Server 2-Tier Architecture........................................................................
....98.0 3-Tier Client/Server Architecture........................................................................
..119.0 Middleware........................................................................
...................................1310.0 Architectures in Discover Financial Services......................................................14
10.1 Current DAS Architecture........................................................................
........1410.2 Migration from DAS-Tuxedo based to J2EE - WebSphere based system......15
10.3 Future WebSphere Based System..................................................................16
11.0 Architecture Trends........................................................................
....................1711.1 Web Services, J2EE Connectors, Message Brokers, etc................................17
11.2 Business Process Management (BPM)...........................................................19
Page 2 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
1.0 Traditional Host Systems
A Central Processing System (Mainframe) provides all processing. Local Terminals are responsible for display and keyboard for user input and viewing capabilities. Local Terminals do not contain any intelligent processing capabilities.Mainframe
Computer
Keyboard
Computer
Keyboard
Computer
Keyboard
Figure 1.0.1 Non-Client-Server System
File Server and retrieval processing provided by File Server Word Processing and spreadsheet processing provided by PC workstation.Mainframe
Computer
Keyboard
Computer
Keyboard
Computer
Keyboard
Server
Server
Computer
Keyboard
Figure 1.0.2 Traditional Host System with LAN
Page 3 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
2.0 Distributed Systems
Distributed System
Both data and transaction processing are divided between one or more computers connected by a network, each computer playing a specific role in the system.Replication
Ensures data at all sites in a distributed system reflects any changes made anywhere in the system.Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
Computer
serverDatabase
serverDatabase
Host Host D a t a U p d a t e s D a t a U p d a t e s R o u t in g t a s k sRoutineTasks
Routine tasks
R o ut i n e ta s k s R o u ti n g T a s k sData Queries
Data Queries
Regional Centers
Corporate Data Centers
Data Replication
Figure 1.3. Distributed Data Centers
Page 4 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
3.0 Client/Server Model
Complements distributed systems
Responds to limitations found in the two host data processing models:1. The traditional mainframe host model, in which a single mainframe
provides shared data access to many dumb terminals, and;2. The local area network (LAN) model, in which many isolated systems
access a file server that provides no central processing power.Provides integration of data and services
Application Processing provided by multiple tiers -1. Database Server
2. Application Server
3. PC Workstation
serverDatabase
Application
Server
Application
Services
Computer
Computer
Computer
PCWorkstations
Database retrievel and updatingApplication LogicGUI presentationFigure 3.1 Client/Server 3-Tier Model
Page 5 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
4.0 Distributed Client/Server Model
Application processing provided by all tiers of the network -1. Mainframe
2. Application Servers
3. Workstations
Multiple databases to support distributed data requirements Supports high volume, load balancing and scalability (extendibility) Requires extensive network administration and application management.Application
Server
Computer
Computer
Computer
PCWorkstations
Database retrievel
and updatingApplication Logic
GUI presentationComputer
Computer
Computer
PCWorkstations
Application
Server
Application
Server
Computer
Computer
Computer
PCWorkstations
Mainframe
Database
Datab aseFigure 4.1 Distributed Client/Server Model
Page 6 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
5.0 Inter-process Communication
Basis for client/server computing
Client process communicates with server process
Each process performs separate functions
Data is passed between processes using IPC functionsServer Process
Client Process
Relational
Database
Get input from
userRequest
processing from serverReceive request
for processingRetreive and
process dataReturn values
Receive returned
valuesDisplay output to
userInter-process
Communication
Pipes FIFOsMessage Queues
Semaphores
Shared Memory
Sockets
Streams
Figure 5.1 Inter-Process Communication
Page 7 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
6.0 Benefits of the Client/Server Model
Divides Application Processing across multiple machines: Non-critical data and functions are processed on the clientCritical functions are processed on the server
Optimizes Client Workstations for data input and presentation (e.g., graphics and mouse support) Optimizes the Server for data processing and storage (e.g., large amount of memory and disk space) Scales Horizontally - Multiple servers, each server having capabilities and processing power, can be added to distribute processing load. Scales Vertically - Can be moved to more powerful machines, such as minicomputer or a mainframe to take advantage of the larger system's performance Reduces Data Replication - Data stored on the servers instead of each client, reducing the amount of data replication for the application.Page 8 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
7.0 Client/Server 2-Tier Architecture
Two-tier client/server architectures have 2 essential components1. A Client PC and
2. A Database Server
2-Tier Considerations:
Client program accesses database directly
o Requires a code change to port to a different database o Potential bottleneck for data requests o High volume of traffic due to data shippingClient program executes application logic
o Limited by processing capability of client workstation (memory, CPU) o Requires application code to be distributed to each client workstationServer Machine
Client Workstation
Client Program
GUI presentation
logic database requestFile Access
Routines
Client Workstation
Client Program
GUI presentation
logic database requestFile Access
Routines
Database Management
System
Database Files
D a t a r e q u e s t e d D a t a r e t u r n e d D a ta re q u e s te d D at a r et u r n e dFigure 7.1 Client/Server 2-Tier Architecture
Page 9 of 19
3-Tier Architecture
Two - Tier Pros and Cons
Advantages Disadvantages
Development Issues:
Simple structure
Easy to setup and maintain
Development Issues:
Complex application rules difficult to
implement in database server - requires more code for the clientComplex application rules difficult to
implement in client and have poor performanceChanges to business logic not
automatically enforced by a server - changes require new client side software to be distributed and installedNot portable to other database server
platformsPerformance:
Adequate performance for low to medium
volume environmentsBusiness logic and database are
physically close, which provides higher performance.Performance:
Inadequate performance for medium to
high volume environments, since database server is required to performquotesdbs_dbs17.pdfusesText_23[PDF] 3 tier architecture in sap
[PDF] 3 tier data warehouse architecture pdf
[PDF] 3 tier schema architecture in dbms
[PDF] 3 tier web based architecture pdf
[PDF] 3 tier architecture in web application development pdf
[PDF] 3.1 music that moves by step answer key
[PDF] 30 years war in sri lanka essay
[PDF] 30 years' war dbq
[PDF] 30 years' war sides
[PDF] 30 hour work week schedule example
[PDF] 304 not modified example
[PDF] 304 not modified exploit
[PDF] 304 not modified express
[PDF] 304 not modified nginx
