 2017 Excel Lab Exercises Practice and Take home
2017 Excel Lab Exercises Practice and Take home
3. The above function is written as an outer IF function which has one grade in its true part if the condition is satisfied and the next grade.
 ms-excel-exercises.pdf
ms-excel-exercises.pdf
BIS202 Exercises. 5
 Succession Planning
Succession Planning
IF Function Practice (from the Proficiency Exercises). File: LogicPractice An Excel nested IF function can be written with this syntax: =IF(condition-to ...
 Microsoft Excel 2010
Microsoft Excel 2010
on pre-defined criteria. Using 'IF' statements. Go to the If Statement sheet. Practice Exercise Basic IF Statements. Go to the Basic If Exercise sheet. See
 Excel Logic Exercises Decision Models Course
Excel Logic Exercises Decision Models Course
For example you might use both the IF and AND statements or you could express the same thing with a nested IF statement. A. Write the formula to calculate the
 Chapter 3 - Logical Functions
Chapter 3 - Logical Functions
In this example the IF function is used to indicate where figures in a Here the =TRUE in the second IF statement is left out because. Excel automatically ...
 PRACTICE QUESTIONS Valuations & Business Modelling
PRACTICE QUESTIONS Valuations & Business Modelling
02-May-2019 ii) Adjusting the historical financial statements: Business valuation is largely an economic analysis exercise. Not surprisingly the company's ...
 Exercises 1. Descriptive Statistics 2. Probability and Expected Value
Exercises 1. Descriptive Statistics 2. Probability and Expected Value
For example if the missing salary were 50
 1 EXCEL EXERCISE #1: Grade Sheet 1. Enter the information in the
1 EXCEL EXERCISE #1: Grade Sheet 1. Enter the information in the
Copy the formula in cell H5 to cells H6 through H9. c. The IF command evaluates the first logical test (i.e. G5>89). If the statement is true an. “A
 Succession Planning
Succession Planning
Logic Practice on Paper – Using Logical Functions in Modeling. Exercise 2. Using Excel's IF Function. File: LogicPractice.xls Worksheet: “IF”.
 Chapter 3 - Logical Functions
Chapter 3 - Logical Functions
Microsoft Excel 2010 - Level 2 The IF function is the key logical function used for decision making. ... Before starting this exercise.
 UQ Library
UQ Library
16 Sep 2020 Practice Exercise Basic IF Statements . ... Practice Exercise Vlookup . ... Ask I.T. Microsoft Excel 2013: Manipulating Data ...
 MS Excel Exercises - Nanopdf
MS Excel Exercises - Nanopdf
Exercise 1. • Introduction to Excel files Worksheets
 Lesson Plan Title: Simplifying the IF/IIf Function Goal of Lesson: To
Lesson Plan Title: Simplifying the IF/IIf Function Goal of Lesson: To
1 Jan 1998 Student Independent Exercise- Students are to complete Exercises A thru D after entering the following worksheet in Excel. A. B. C. D. E. F. 1.
 Work with the IF function
Work with the IF function
In this exercise you'll use the IF function to figure out if a salary deduction should be 5 or 6%. You'll have Excel do some multiplication at the front of the
 ICT IGCSE Practical – Revision Presentation Spreadsheets
ICT IGCSE Practical – Revision Presentation Spreadsheets
Even if you update the numbers in the cell the formula range. Simple Functions. Functions are predefined formulas and are already available in Excel.
 2017 Excel Lab Exercises Practice and Take home
2017 Excel Lab Exercises Practice and Take home
Excel Practice Exercises Lab Session #2. Decision making using IF SUMIF
 Basic IF Statement - Massey University
Basic IF Statement - Massey University
perform an IF statement before you directly type your statement into the cell An IF statement is a conditional test on values and formulas that returns one value if a condition you specify is TRUE and another value if it is FALSE IF(logical_testvalue_if_truevalue_if_false) Basic IF Statement
 IF Statement - Overview Syntax and How It Works
IF Statement - Overview Syntax and How It Works
Excel IF Function The most common and powerful of the logical functions in Excel is the IF function This function is particularly powerful because it can test for a particular condition in the worksheet and: do a calculation if the condition is TRUE; or another calculation if the condition is FALSE Excel IF Function
 Excel Logic & the IF Function - Pacific University
Excel Logic & the IF Function - Pacific University
Excel Logic & the IF Function • Comparison Operators –You can use comparison operators to compare two numbers functions formulas or labels and return either true or false –Examples include: • =2*3=4+2 • =A1>0 • =average(a1:a10)>60 • Every conditional test must include at least one comparison operator As an example in the
 Homework 1—Excel Basics - UW Faculty Web Server
Homework 1—Excel Basics - UW Faculty Web Server
Select the file on your computer and click Open For this exercise open the data file called “ExcelBasicsDataSet xls” To get a copy of the data set go to the course website http://faculty washington edu/tamre/stp shtml and select the Data Sets link found on the upper left of the page
 Excel Practice Spreadsheet - University of Alberta
Excel Practice Spreadsheet - University of Alberta
To launch the Microsoft Excel program locate the Microsoft Excel icon and double click To launch the program from the Start menu in the ED South 155 lab you can select Start > Programs > Microsoft Office > Microsoft Excel 2003 Once you have launched Microsoft Excel you should see the program
 Searches related to if statement practice exercises in excel filetype:pdf
Searches related to if statement practice exercises in excel filetype:pdf
The best formula to calculate Profits for January is: =SUM(B2:B3) =B2-B3 =B4-(B2+B3) =A4-(A2+A3) =SUBTRACT(B2:B3) 5 The best formula to calculate the Average for Profits is: =(B4+C4+D4)/3 =MEAN(B4:E4) =AVERAGE(B4:D4) =AVERAGE(B4:E4) 6 As a general rule Excel will _____-align numbers right left top bottom Topic 3: 7
What is the if statement in Excel?
- The IF statement is a decision-making statement that guides a program to make decisions based on specified criteria. The IF statement executes one set of code if a specified condition is met (TRUE) or another set of code evaluates to FALSE. It is a built-in function in Excel, and it can be used as a VBA function in Excel.
What is the difference between logical test and if statement in Excel?
- Basically, excel logical test is used to evaluate the condition whether it is true or false. An IF statement is mainly used to test any condition that will give you more than two outcomes. If you are using a single If then it will give you two outcomes. For more than two outcomes you need to use If statement inside another If statement.
What are logical functions in Excel?
- ?The logical functions in Excel are a small group consisting of six functions ?These functions are noted for their black-or- white results ?A logical function can return only one of two values: TRUE or FALSE
Excel 2016
Processing Data
Course objectives:
1. Use conditional formatting effectively
2. Use IF and VLOOKUP functions for data analysis
3. Use PivotTables for flexible data presentation
4. Use Sort and filter effectively
Student Training and Support
Phone: (07) 334 64312
Email: askus@library.uq.edu.au
Web: https://web.library.uq.edu.au/library-services/training/Staff Training
(Bookings)Phone (07) 3365 2666 Email staffdev@uq.edu.au
Web http://www.uq.edu.au/staffdevelopment
Staff may contact their trainer with enquiries and feedback related to training content. Please contact Staff Development for booking enquiries or your local I.T. support for general technical enquiries.
Reproduced or adapted from original content provided under Creative Commons license by The University of Queensland LibraryTable of Contents
Relative & Absolute Cell References ............................................................................. 4
Relative cell references ............................................................................. 4
Absolute cell references ............................................................................ 4
Date Calculations and Conditional Formatting ............................................................. 5
Date calculations ...................................................................................... 5
Apply conditional formatting ...................................................................... 5
Apply conditional formatting to a whole row .............................................. 6'IF' Function ..................................................................................................................... 7
Using IF" statements ................................................................................ 7
Practice Exercise Basic IF Statements ..................................................... 7VLookup Function ........................................................................................................... 8
Using V lookup.......................................................................................... 8
Practice Exercise Vlookup ........................................................................ 9Pivot Table ....................................................................................................................... 9
Create a pivot table ................................................................................. 9
Add data to PivotTable .......................................................................... 11Edit PivotTable ...................................................................................... 11
Pivot Table Slicers ......................................................................................................... 12
Practice Exercise Pivot Table Exercise ................................................. 13Create a PivotChart .............................................................................. 14
Extras Sorting & Filtering Lists .................................................................................... 15
Sort by single criteria............................................................................. 15
Sort by multiple criteria .......................................................................... 15
Filtering with AutoFilter .......................................................................... 16
Progressive filtering .............................................................................. 17
Find Unique Values and Remove Duplicates .............................................................. 17
Find unique values ................................................................................ 17
Protection ...................................................................................................................... 18
Worksheet protection ............................................................................ 18Unprotected cells .................................................................................. 19
Goal Seek ....................................................................................................................... 19
Use Goal Seek" tool ............................................................................. 20
Naming Cells .................................................................................................................. 21
Naming cells via ribbon ......................................................................... 21Answers ......................................................................................................................... 21
Exercise document:
Go to https://web.library.uq.edu.au/library-services/training/training-resources and click Excel. Locate
and click the Processing Data.xlsx link. Make sure you are on the Relative and Absolute Reference sheet when the workbook opens.UQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
3 of 21 Ask I.T. Microsoft Excel 2013: Manipulating Data
UQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
Notes4 of 21 Microsoft Excel: Processing Data
Relative & Absolute Cell References
Relative cell references
Calculate "% Paid"
1. Select cell M2
2. Enter =L2/K2
3. Press Enter
4. Select cell M2
5. Select the % button from the
Number group on the Home tab
6. Click the "Increase Decimal"
button twice7. Use the Autofill tool to fill the
remaining results in the columnNote: this will also carry down the % formatting.
Absolute cell references
Absolute cell references
- This uses the exact address of a cell regardless of the position of the cell that contains the formula.Calculate % of Total Fees Paid
1. Select cell N2
2. Type in =L2/L28
3. Click the % button
4. Click the increase decimals
button5. Use the AutoFill tool to fill the
remaining resultsNote: an error will display as Excel will use relative cell references by default. To correct this the dividing cell
reference should be a fixed cell or an absolute reference6. Edit formula in cell N2 by double
clicking.7. Click in L28 cell reference
8. Use the function key F4 to change
the formula to an absolute reference =L2/$L$28UQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
Notes5 of 21 Microsoft Excel: Processing Data
1. Use AutoFill to calculate the
remaining resultsDate Calculations and Conditional Formatting
Date calculations
Display hidden data
1. Select column D and column F
2. Right click on selection
3. Select Unhide
Calculate Age from Date of Birth
Note: Subtracting a date of birth from the current date will display the number of days between the two dates. To
find out the age in years, divide by 365 .25 (the .25 allows for leap years).4. Select cell E2
5. Type in formula
=ROUNDDOWN((TODAY()-D2)/365.25,0)6. Press Enter
7. Use the AutoFill tool to calculate the
remaining results.Note: The Rounddown function has the following structure. =Rounddown(number,num_digits). In the above
formula the number portion is generated by the formula (TODAY()-d2)/365.25. The num_digits portion is
designated zero meaning all the values after the decimal round down to zero e.g. 28.96 becomes 28.00.
Apply conditional formatting
Apply formats to students over 26 years
1. Select range to be formatted:E2:E27
2. Select Conditional Formatting on
the Home tab3. Hover over Highlight Cell Rules
4. Select Greater Than...
5. Type in 26
6. Adjust formats to suit
7. Click OK
UQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
Notes6 of 21 Microsoft Excel: Processing Data
Apply conditional formatting to a whole row
Apply formats to students over 26 years
1. Select range to be formatted:A2:N2
2. Select the Conditional Formatting button
from the Styles group on the Home tab3. Select New Rule...
4. Select "Use a formula to determine which
cells to format"5. Enter =$E2>26
Note: This makes the column reference an absolute reference which means the condition will always be based on the content of that column but on a range of rows6. Click the Format... button
7. Apply formatting as required
8. Click OK
9. Click on OK
1. Select Manage Rules
2. Go to the Applies To field
3. Change the range to $A$2:$N$27
Note: This will ensure the conditional formatting criteria will apply to all rows in the defined range4. Click on OK
UQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
Notes7 of 21 Microsoft Excel: Processing Data
Data Analysis
Excel can analyse a specified range of data using a variety of tools and can subsequently display results calculated from a formula or from user specified options 'IF' Function The IF function will analyse data and provide results defined by the user. The analysis returns either a true or false answer. The displayed results can be text or calculated values.Average
and Final Exam grades will analyse exam results and provide a grade for students based on pre-defined criteria.Using 'IF' statements
Go to the If Statement sheet
Practice Exercise Basic IF Statements
Go to the Basic If Exercise sheet.
See page
21 for the answer.
1. Select cell D2
2. Enter formula =IF(C2>=B2,C2*2%,0)
3. Select cell E2
4. Enter formula
=IF(D2>=300,"Excellent","Poor")5. Copy the answers down the columns
1. Follow the instructions below the table
2. Create the Average (Overall Score) and IF (Final Grade) statements in their respective
columns3. Copy the answers down the columns
UQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
Notes8 of 21 Microsoft Excel: Processing Data
VLookup Function
You can also use the VLOOKUP function as an alternative to the IF function for elaborate tests. Lookup functions will analyse data and compare it against a predefined range prior to displaying the result.This works on the principle:
a) Here's a value. b) Go to another location and find a match for my value, c) When a match is found show the cell contents from within a specified column number A vertical array (or table) has headings in the first row and data in column beneath. This is the most common layout for information within Excel.Note: If the Headers are in the first column and the data is in rows then you would use the HLookup function.
Using V lookup
Use VLOOKUP to extract data from tables of information1. Go to the "Vlookup" sheet
2. Go to cell E22
3. Click the Insert Function button on the
formula bar4. Type VLOOKUP
5. Click Go
6. Select VLOOKUP
7. Click OK
1. Enter the Name VLOOKUP function as:
The cell to check (Lookup_value): D22
The range to compare (Table_array):
D4:M17
Column containing information
(Col_index_num): 2Exact or Approximate match
(Range_lookup): False (exact)Select cell F22
2. Enter the Overall Score VLOOKUP
function as:The cell to check (Lookup_value): D22
The range to compare (Table_array):
D4:M17
Column containing information
(Col_index_num): 10 Exact or Approximate match (Range_lookup): False (exact)Select cell G22
3. Enter the data opposite into the Table 1
area on the spreadsheet 1 2 3UQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
Notes9 of 21 Microsoft Excel: Processing Data
4. Enter the Final Grade VLOOKUP
function as:The cell to check (Lookup_value): F22
The range to compare (Table_array): A4:B9
Column containing information
(Col_index_num): 2Exact or Approximate match
(Range_lookup): True (range)5. AutoFill down
4Note: As we are looking for an approximate match the data in column 1 of the table array A4:B9 must be sorted
in ascending order.Practice Exercise Vlookup
Go to the VLookup Exercise sheet.
1. Follow the 6 instructions at the top right
2. Create a vertical lookup function to
extract the name of the currency3. Create a vertical lookup function to
display the amount of converted currency.4. See page 21 for the answer.
Pivot Table
Pivot tables
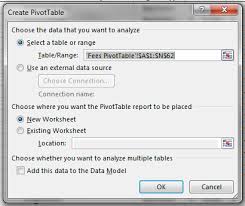
allow you to extract and arrange elements of your data to present it in an alternative table. With pivot table s you can group and summarise list data into a format that is easy for reporting and analysis. A pivot table won't automatically update if the raw data changes and you will need to refresh to update any changes in the data.Create a pivot table
1. Select the Fees PivotTable Data sheet
2. Click any individual cell within the data
3. Click Insert tab
4. Click Pivot Table button
UQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
Notes10 of 21 Microsoft Excel: Processing Data
5. In the Create Pivot Table dialog box check
the correct data range has been selected and entered6. Click on New Worksheet
7. Click OK
A new worksheet opens
8. Rename the worksheet Pivot
The fields available are displayed in the
PivotTable Field
s List at the right of the screenNote: These are used to build the PivotTable.
Pivot Table categories define 3 main areas of information:Filters Column/Row Labels Values
Gives an overall view
which can be refinedGroups of data:
e.g. Dept, Model, Product Type,Locations, Salespeople
Groups of data:
e.g. AmountsUQ Library
Staff and Student I.T. Training
Notes11 of 21 Microsoft Excel: Processing Data
Add data to PivotTable
To display fees owing in each faculty
Drag & Drop
the following fields into the appropriate sections...Year of Study into Column section
Faculty into Rows section
Fees Owing into Values section
Note 1:
The Report Filter allows you to apply filters to the Pivot Table to display select portions only e.g. Filter by Degree Type Note 2: The PivotTable will automatically reflect changes as you work unless you select "Defer Layout Update." This allows you to click the "Update" button when complete.Edit PivotTable
To rearrange the Pivot Table reposition fields as
needed.10. Drag Year of Study from Column to Row
quotesdbs_dbs8.pdfusesText_14[PDF] if two events are independent
[PDF] if x 1/3=k and k=3 what is the value of x
[PDF] if you are contacted by a member of the media about information you are not authorized to share
[PDF] if you go to the court of appeals you will see how many judges
[PDF] if you're writing a formal business report
[PDF] if else statement java exercises pdf
[PDF] ifc logo
[PDF] ifm maurice campus france
[PDF] ifort compiler options
[PDF] ifpi investing in music
[PDF] ifr abbreviations
[PDF] ifr approach chart legend
[PDF] ifr approach plate legend
[PDF] ifr charts explained
