 Circular No. 15/2023-Customs
Circular No. 15/2023-Customs
7 जून 2023 the declaration of IUPAC name and CAS number of the constituent chemicals for ... IDENTIFIERS FOR DUAL USE PRODUCTS AS PER SCOMET LIST PUBLISHED ...
 IUPAC Provisional Recommendations
IUPAC Provisional Recommendations
Preferred IUPAC names belong to 'preferred IUPAC nomenclature' Any name list of names given here is to be considered limiting; however use of trivial and ...
 List of Insecticide
List of Insecticide
List of Fungicide & Bactericide. Sl..No. Trade name. Chemical concentration. Mode of. Action. Active ingredient. Recmdn. Against. 1 Aliette. Fosetyl-AL. S. 80 %
 LIST OF NARCOTIC DRUGS UNDER INTERNATIONAL CONTROL
LIST OF NARCOTIC DRUGS UNDER INTERNATIONAL CONTROL
For further information on the names and the chemical and structural formulas of the drugs see the. Multilingual Dictionary of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic
 [PDF] Naming Chemical Formulas Key
[PDF] Naming Chemical Formulas Key
Zewail- Answers to: Practice Chemical Formulas. Write chemical formulas for the ionic compounds made from each set of ions: Name of cation Name of anion.
 Chapter 1 Organic Compounds: Alkanes Organic chemistry
Chapter 1 Organic Compounds: Alkanes Organic chemistry
Learn the IUPAC system for naming alkanes and cycloalkanes. • Learn the important physical and chemical properties of the alkanes. Chapter 1. Organic Compounds:.
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WOORKSHEET ON NOMENCLATURE
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WOORKSHEET ON NOMENCLATURE
Alkanes a. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: 1. 2. 2-methylbutane. 23-dimethylbutane.
 Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/index_2353/Chapter_03_2SPP.pdf
 Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. IUPAC Recommendations and
Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. IUPAC Recommendations and
On the other hand although acetone is a retained name recommended for general nomenclature
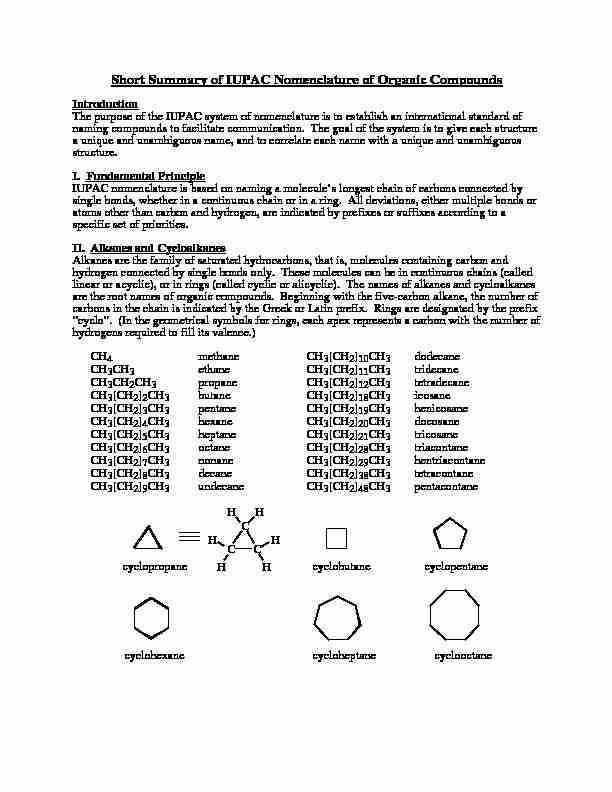
 Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
IUPAC nomenclature is based on naming a molecule's longest chain of carbons connected by single bonds whether in a continuous Alkyl (see list below).
 Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature Homologous Series of
Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature Homologous Series of
The IUPAC system of nomenclature was established at the functional group at the bottom of the list (alkane) has the lowest priority for naming.
 IUPAC Provisional Recommendations
IUPAC Provisional Recommendations
IUPAC Provisional Recommendations. Preferred IUPAC names. List of tables September
 Chapter 1 Organic Compounds: Alkanes Organic chemistry
Chapter 1 Organic Compounds: Alkanes Organic chemistry
Learn the IUPAC system for naming alkanes and cycloalkanes. • Learn the important physical and chemical properties of the alkanes. Chapter 1.
 Handout: Naming Organic Compounds Substituents Longest carbon
Handout: Naming Organic Compounds Substituents Longest carbon
Handout: Naming Organic Compounds. A. IUPAC Naming. General Rules: Prefix + Parent + Suffix. 1. Name parent+suffix: longest carbon chain + family suffix.
 Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/index_2353/Chapter_03_2SPP.pdf
 Root Names for Hydrocarbons
Root Names for Hydrocarbons
The names of organic molecules are divided into three parts; IUPAC Nomenclature for Hydrocarbons. Alkanes ... A list of numbers are separated from each.
 Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. IUPAC Recommendations and
Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. IUPAC Recommendations and
Division VIII Chemical Nomenclature and Structure Representation Division This list has been completed from 11 to 9999. The prefixes are formed by ...
 Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
However the common name benzaldehyde is also accepted by IUPAC. Other aromatic aldehydes are hence named as substituted benzaldehydes. 2022-23. Page 4
 HYDROCARBONS
HYDROCARBONS
name hydrocarbons according to. IUPAC system of nomenclature;. • recognise and write structures of isomers of alkanes alkenes
 [PDF] Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
[PDF] Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
IUPAC nomenclature is based on naming a molecule's longest chain of carbons connected by single bonds whether in a continuous chain or in a ring
 [PDF] Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
[PDF] Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
This summary contains an introduction to the recognition and naming of the various functional classes organic compounds as well as the relationship between
 IUPAC Name List PDF - Govtempdiary
IUPAC Name List PDF - Govtempdiary
17 juil 2022 · You can download the IUPAC Name List PDF for free using the direct download link given at the bottom of this article
 [PDF] Principles of Chemical Nomenclature - iupac
[PDF] Principles of Chemical Nomenclature - iupac
Principles of chemical nomenclature : a guide to IUPAC recommendations / G J Leigh For such a formula to be useful in lists or indexes an order
 [PDF] Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations and
[PDF] Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations and
The concept of preferred IUPAC names is developed as a contribution to the continuing evolution of the IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds This book (
 IUPAC Name List PDF - InstaPDF
IUPAC Name List PDF - InstaPDF
10 avr 2023 · [PDF] IUPAC Name List PDF free download using direct link download PDF of IUPAC Name List instanty from the link available at
 [PDF] Systematic Nomenclature (IUPAC System)
[PDF] Systematic Nomenclature (IUPAC System)
Identify and number the substituents and list them in alphabetical order 6 CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH CH3 CH2
 [PDF] Nomenclaturepdf
[PDF] Nomenclaturepdf
Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) • It provides an unambiguous structure • Official IUPAC naming recommendations are not always followed in practice and the
 [PDF] Naming Organic Compounds Substituents Longest carbon chain
[PDF] Naming Organic Compounds Substituents Longest carbon chain
A IUPAC Naming General Rules: Prefix + Parent + Suffix 1 Name parent+suffix: longest Family Name Format: #–substituent–#–substituentparentsuffix
How do you name an IUPAC list?
In summary, the name of the compound is written out with the substituents in alphabetical order followed by the base name (derived from the number of carbons in the parent chain). Commas are used between numbers and dashes are used between letters and numbers. There are no spaces in the name.What is your IUPAC name?
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry (informally called the Blue Book).What is 8 in IUPAC name?
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
 Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds IntroductionThe purpose of the IUPAC system of nomenclature is to establish an international standard ofnaming compounds to facilitate communication. The goal of the system is to give each structurea unique and unambiguous name, and to correlate each name with a unique and unambiguousstructure.
I. Fundamental Principle IUPAC nomenclature is based on naming a molecule's longest chain of carbons connected bysingle bonds, whether in a continuous chain or in a ring. All deviations, either multiple bonds oratoms other than carbon and hydrogen, are indicated by prefixes or suffixes according to aspecific set of priorities.
II. Alkanes and CycloalkanesAlkanes are the family of saturated hydrocarbons, that is, molecules containing carbon andhydrogen connected by single bonds only. These molecules can be in continuous chains (calledlinear or acyclic), or in rings (called cyclic or alicyclic). The names of alkanes and cycloalkanesare the root names of organic compounds. Beginning with the five-carbon alkane, the number ofcarbons in the chain is indicated by the Greek or Latin prefix. Rings are designated by the prefix"cyclo". (In the geometrical symbols for rings, each apex represents a carbon with the number ofhydrogens required to fill its valence.)
4methaneCH3[CH2]10CH3dodecaneCH
3CH3ethaneCH3[CH2]11CH3tridecaneCH
3CH2CH3propaneCH3[CH2]12CH3tetradecaneCH
3[CH2]2CH3butaneCH3[CH2]18CH3icosaneCH
3[CH2]3CH3 pentaneCH3[CH2]19CH3henicosaneCH
3[CH2]4CH3hexaneCH3[CH2]20CH3docosaneCH
CHH HHHShort Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature, p. 2
III. Nomenclature of Molecules Containing Substituents and Functional GroupsA. Priorities of Substituents and Functional GroupsLISTED HERE FROM HIGHEST TO LOWEST PRIORITY, except that the substituents withinGroup C have equivalent priority.
Family of Compound
Alkene
AlkyneStructurePrefix
----Suffix -ene -yneSuffix -oic acid (-carboxylic acid) -al(carbaldehyde) -one -ol -aminePrefix carboxy- oxo- (formyl) oxo- hydroxy- amino-StructureFamily of CompoundCarboxylic Acid
Aldehyde
Ketone
Alcohol
AmineRCO
CHO RCO CCGroup A - Functional Groups Indicated By Prefix Or Suffix Group B - Functional Groups Indicated By Suffix Only Group C - Substituents Indicated by Prefix Only Substituent Structure Prefix SuffixAlkyl (see list below)R - alkyl-------AlkoxyR - O - alkoxy-------HalogenF - fluoro---------Cl - chloro---------Br - bromo---------I - iodo---------Group C continued on next page
Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature, p. 3
Group C - Substituents, continued
Miscellaneous substituents and their prefixes 2CHCH 2CHCH 2CH2nitrovinylallylphenyl
Common alkyl groups - replace "ane" ending of alkane name with "yl". Alternate names forcomplex substituents are given in brackets.
methyl ethyl propyl (n-propyl)butyl (n-butyl)isopropyl [1-methylethyl]isobutyl [2-methylpropyl]sec-butyl[1-methylpropyl]tert-butyl or t-butyl[1,1-dimethylethyl]CH 3CH2CH3CH
2CH2CH3CH
2CH2CH2CH3CH
3CH 3CHCH 3CH 3CH 2CH2CH3CH
3CCH 3CH 3CH3B. Naming Substituted Alkanes and Cycloalkanes - Group C Substituents Only
1. Organic compounds containing substituents from Group C are named following this sequenceof steps, as indicated on the examples below:•Step 1. Find the longest continuous carbon chain. Determine the root name for thisparent chain. In cyclic compounds, the ring is usually considered the parent chain, unless it isattached to a longer chain of carbons; indicate a ring with the prefix "cyclo" before the rootname. (When there are two longest chains of equal length, use the chain with the greater numberof substituents.)•Step 2. Number the chain in the direction such that the position number of the firstsubstituent is the smaller number. If the first substituents from either end have the same number,then number so that the second substituent has the smaller number, etc.•Step 3. Determine the name and position number of each substituent. (A substituent ona nitrogen is designated with an "N" instead of a number; see Section III.D.1. below.)•Step 4. Indicate the number of identical groups by the prefixes di, tri, tetra, etc.•Step 5. Place the position numbers and names of the substituent groups, in alphabeticalorder, before the root name. In alphabetizing, ignore prefixes like sec-, tert-, di, tri, etc., butinclude iso and cyclo. Always include a position number for each substituent, regardless ofredundancies.
Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature, p. 4
Examples
1-sec-butyl-3-nitrocyclohexane(numbering determined by the alphabetical order of substituents)3-fluoro-4-isopropyl-2-methylheptane3-bromo-2-chloro-5-ethyl-4,4-dimethyloctane766
21874321
CHCH 2CH3H 3CNO
2CHCHCH
3CHCH2CH2CH3CH
3CH3CHCHC
BrCH 3CHCH2CH2CH3CH
3CH 3ClCH2CH3CH
C. Naming Molecules Containing Functional Groups from Group B - Suffix Only1. Alkenes - Follow the same steps as for alkanes, except:
a. Number the chain of carbons that includes the C=C so that the C =C has the lowerposition number, since it has a higher priority than any substituents;
b. Change "ane" to "ene" and assign a position number to the first carbon of the C =C;c. Designate geometrical isomers with a cis,trans or E,Z prefix. 1
2345buta-1,3-diene5-methylcyclopenta-
1,3-dieneCHCH
2CHCHF
FCH CHCH 2CH3Special case: When the chain cannot include the C=C, a substituent name is used. 3-vinylcyclohex-1-eneCHCH
22. Alkynes - Follow the same steps as for alkanes, except:
a. Number the chain of carbons that includes the CtC so that the functional group has thelower position number;
b. Change "ane" to "yne" and assign a position number to the first carbon of the CtC.Note: The Group B functional groups (alkene and alkyne) are considered to have equal priority:in a molecule with both a double and a triple bond, whichever is closer to the end of the chaindetermines the direction of numbering. In the case where each would have the same positionnumber, the double bond takes the lower number. In the name, "ene" comes before "yne"because of alphabetization. See examples on next page.
Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature, p. 5
("ene" and "yne" have equal priority unless they have the same position number, when "ene" takes the lower number)CH 3CHC CHHCCCH
2CHCH2HCCCCHCH
1122334455
("yne" closer to endof chain)(Notes: 1. An "e" is dropped if the letter following it is a vowel: "pent-3-en-1-yne" , not "3-pent-3-ene-1-yne". 2. An "a" is added if inclusion of di, tri, etc., would put two consonantsconsecutively: "buta-1,3-diene", not "but-1,3-diene".)
D. Naming Molecules Containing Functional Groups from Group A - Prefix or SuffixIn naming molecules containing one or more of the functional groups in Group A, the group ofhighest priority is indicated by suffix; the others are indicated by prefix, with priority equivalentto any other substituents. The table in Section III.A. defines the priorities; they are discussedbelow in order of increasing priority.
Now that the functional groups and substituents from Groups A, B, and C have been described, amodified set of steps for naming organic compounds can be applied to all simple structures:•Step 1. Find the highest priority functional group. Determine and name the longestcontinuous carbon chain that includes this group.•Step 2. Number the chain so that the highest priority functional group is assigned thelower number.•Step 3. If the carbon chain includes multiple bonds (Group B), replace "ane" with "ene"for an alkene or "yne" for an alkyne. Designate the position of the multiple bond with thenumber of the first carbon of the multiple bond.•Step 4. If the molecule includes Group A functional groups, replace the last "e" with thesuffix of the highest priority functional group, and include its position number.•Step 5. Indicate all Group C substituents, and Group A functional groups of lowerpriority, with a prefix. Place the prefixes, with appropriate position numbers, in alphabeticalorder before the root name.
1. Amines: prefix: amino-; suffix: -amine - substituents on nitrogen denoted by "N"N,N-diethylbut-3-en-2-amine3-methoxycyclohexan-1-amine
("1" is optional in this case)propan-1-amineCH3CH2CH2NH
2NH 2CH 3OCH2CHCHCH
3NCH2CH3CH
3CH2Short Summary of IUPAC Nomenclature, p. 6
2. Alcohols: prefix: hydroxy-; suffix: -ol
2-aminocyclobutan-1-ol
("1" is optional in this case)but-3-en-2-olethanolCH3CH2OHH
3CCHOH
quotesdbs_dbs7.pdfusesText_5[PDF] iupac name of lactams
[PDF] iupac nomenclature
[PDF] iupac nomenclature class 11 notes pdf
[PDF] iupac nomenclature class 11 questions pdf
[PDF] iupac nomenclature examples for class 11 pdf
[PDF] iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry class 11 pdf
[PDF] iupac nomenclature practice
[PDF] iupac nomenclature practice worksheets class 11 with answers pdf
[PDF] iupac nomenclature questions for class 11 pdf
[PDF] iupac nomenclature questions for class 11 pdf with answers
[PDF] iusd calendar
[PDF] iusd calendar 2019 2020 year round
[PDF] iusd calendar 2020 21
[PDF] iusd year round calendar 2020
