 Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller Theory and
Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller Theory and
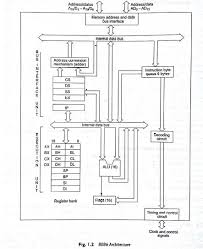
ARCHITECTURE: A microprocessor is a programmable electronics chip that has computing and decision making capabilities similar to central processing unit of a
 UNIT I – 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
UNIT I – 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
Microprocessor and Microcontroller. 57 data Registers as software ports 0x21 Note: It may be noted that the data in latch buffer and port pins may not be.
 LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2017-18) MALLA
LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2017-18) MALLA
All these limitations lead to the launching of 8086 microprocessor. • In the family of 16 bit microprocessors Intel's 8086 was the first one to be launched in
 LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2019-20)
LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2019-20)
Ayala The 8051 Microcontroller
 Preview Microprocessor Tutorial (PDF Version)
Preview Microprocessor Tutorial (PDF Version)
A microprocessor is a controlling unit of a micro-computer fabricated on a small chip capable of performing Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU) operations and
 Microprocessor BCA - And Computer Architecture
Microprocessor BCA - And Computer Architecture
Notes Prepared By. Raju Poudel. MCA Purbanchal University. Page 2. Prepared by: Raju Poudel [MCA]. 2. Unit I Fundamentals of Microprocessor. Introduction to
 MICROPROCESSOR & MICROCONTROLLER
MICROPROCESSOR & MICROCONTROLLER
Write notes on 8051 serial port programming. 5. Explain about external memory interfacing to 8051. 6. Write notes on 8051 timer and counter programming. 7
 LECTURE NOTES
LECTURE NOTES
Sample embedded system on MSP430 microcontroller. UNIT-IV. I/O ports pull up/down resistors concepts Interrupts and interrupt programming
 8085 Microprocessor Notes PDF
8085 Microprocessor Notes PDF
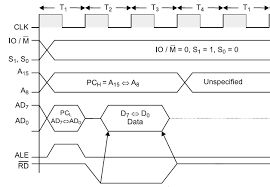
The lower order address bus is multiplexed with the data bus to minimize the chip size. The 8085 microprocessor is an 8-bit processor available as a. 40-pin IC
 unit – i – 8085 microprocessor
unit – i – 8085 microprocessor
Differences between: Microcomputer Microprocessor and Microcontroller Note: The assembler uses the name of the string to determine whether the ...
 Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller Theory and
Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller Theory and
ARCHITECTURE: A microprocessor is a programmable electronics chip that has computing and decision making capabilities similar to central processing unit of a
 LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2017-18) MALLA
LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2017-18) MALLA
were compatible with microprocessor 8086 with slight or no modifications. Page 9. Architecture of 8086. • The architecture of 8086 supports a 16 bit ALU
 PDF Microprocessors - Tutorialspoint
PDF Microprocessors - Tutorialspoint
Microprocessors i. About the Tutorial. A microprocessor is a controlling unit of a micro-computer fabricated on a small chip.
 unit – i – 8085 microprocessor
unit – i – 8085 microprocessor
Microcomputer is a computer with a microprocessor as its CPU. Note: The assembler uses the name of the string to determine whether the string is of type.
 LECTURE NOTES MICROPROCESSORS AND INTERFACING
LECTURE NOTES MICROPROCESSORS AND INTERFACING
UNIT – I. 8086 MICROPROCESSOR: 8086 architecture- Functional Diagram Register Organization
 UNIT I – 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
UNIT I – 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
personal computers the terms microprocessor and CPU are used interchangeably. Note: TXRDY status word indicates that transmit data character is.
 LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2019-20)
LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2019-20)
UNIT -IV. INTRODUCTION TO MICROCONTROLLERS: Overview of 8051 Microcontroller Architecture
 nptel-lecture-notes-microprocessor.pdf
nptel-lecture-notes-microprocessor.pdf
NPTEL MICROPROCESSOR AND INTERFACING LECTURE NOTES. ANKALK DE MICROPROCESSOR TUTORIAL IN PDF CURRENT AFFAIRS. 201. It is an important of microprocessors.
 LECTURE NOTES MICROPROCESSORS AND
LECTURE NOTES MICROPROCESSORS AND
Mr.M.LAKSHMI RAVITEJA. Mr. N.PAPARAO. Mrs.C.DEEPTHI. Mr.S.LAKSHMANA CHARI. ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING. INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING.
 8085 Microprocessor
8085 Microprocessor
Microprocessors and Microcontrollers/Architecture of Microprocessors. Lecture Notes. Module 1 learning unit 1. • A Computer is a programmable machine.
 [PDF] Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller - VSSUT
[PDF] Lecture Note On Microprocessor and Microcontroller - VSSUT
ARCHITECTURE: A microprocessor is a programmable electronics chip that has computing and decision making capabilities similar to central processing unit of a
 [PDF] MICROPROCESSOR & MICROCONTROLLERpdf - mrcetacin
[PDF] MICROPROCESSOR & MICROCONTROLLERpdf - mrcetacin
MICROPROCESSOR MICROCONTROLLER LECTURE NOTES B TECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2017-18) Prepared by: Mr K Murali Krishna Associate Professor
 [PDF] LECTURE NOTES BTECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2019-20) - mrcetacin
[PDF] LECTURE NOTES BTECH (III YEAR – II SEM) (2019-20) - mrcetacin
To develop an in-depth understanding of the operation of microprocessors and microcontrollers machine language programming interfacing techniques 3 To
 [PDF] PDF Microprocessors - tutorialspointcom
[PDF] PDF Microprocessors - tutorialspointcom
In this tutorial we will discuss the architecture pin diagram and other key concepts of microprocessors Audience This tutorial is designed for all those
 [PDF] UNIT I – 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
[PDF] UNIT I – 8085 MICROPROCESSOR
The Intel 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Intel in 1977 It was binary compatible with the more-famous Intel 8080 but required less supporting
 [PDF] MICROPROCESSOR & MICROCONTROLLER
[PDF] MICROPROCESSOR & MICROCONTROLLER
Objectives: To Study the Architecture of 8085 and 8086 microprocessor ? To learn the design aspects of I/O and Memory Interfacing circuits
 [PDF] Microprocessors - MADE EASY
[PDF] Microprocessors - MADE EASY
Microprocessors Electrical Engineering Publications 1 2 History of Microprocessors 1 5 The 8085 Microprocessor Pinout and Signals
 8085 & 8086 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Notes pdf
8085 & 8086 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Notes pdf
9th May 2023 - 8085 8086 handwritten microprocessor and microcontroller notes pdf free download microprocessor pdf notes lecture for cse
 [PDF] unit – i – 8085 microprocessor - Sathyabama
[PDF] unit – i – 8085 microprocessor - Sathyabama
The microprocessors functions as the CPU in the stored program model of the digital computer Its job is to generate all system timing signals and synchronize
 [PDF] microprocessors and interfacing devices - IARE
[PDF] microprocessors and interfacing devices - IARE
Instruction formats addressing modes instruction set assembler directives macros Simple programs involving logical branch and call instructions Sorting
What is microprocessor in PDF?
A microprocessor is a controlling unit of a micro-computer, fabricated on a small chip capable of performing Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU) operations and communicating with the other devices connected to it.What is microprocessor notes?
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU).What are the 5 types of microprocessors?
Microprocessors are classified into five types, namely: CISC-Complex Instruction Set Microprocessors, RISC-Reduced Instruction Set Microprocessor, ASIC- Application Specific Integrated Circuit, Superscalar Processors, DSP's-Digital Signal Microprocessors.- 8086 Microprocessor is an enhanced version of 8085Microprocessor that was designed by Intel in 1976. It is a 16-bit Microprocessor having 20 address lines and16 data lines that provides up to 1MB storage. It consists of powerful instruction set, which provides operations like multiplication and division easily.
Microprocessors
i A microprocessor is a controlling unit of a micro-computer, fabricated on a small chip capable of performing Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU) operations and communicating with the other devices connected to it. In this tutorial, we will discuss the architecture, pin diagram and other key concepts of microprocessors. in Computer Science. It will help them understand the basic concepts related toMicroprocessors.
In this tutorial, all the topics have been explained from elementary level. Therefore, a beginner can understand this tutorial very easily. However if you have a prior knowledge of computer architecture in general, then it will be quite easy to grasp the concepts explained here.Copyright 2016 by Tutorials Point (I) Pvt. Ltd.
All the content and graphics published in this e-book are the property of Tutorials Point (I) Pvt. Ltd. The user of this e-book is prohibited to reuse, retain, copy, distribute or republish any contents or a part of contents of this e-book in any manner without written consent of the publisher. We strive to update the contents of our website and tutorials as timely and as precisely as possible, however, the contents may contain inaccuracies or errors. Tutorials Point (I) Pvt. Ltd. provides no guarantee regarding the accuracy, timeliness or completeness of our website or its contents including this tutorial. If you discover any errors on our website or in this tutorial, please notify us at contact@tutorialspoint.com.Microprocessors
iiAbout the Tutorial ............................................................................................................................................ i
Audience ........................................................................................................................................................... i
Prerequisites ..................................................................................................................................................... i
Disclaimer & Copyright ..................................................................................................................................... i
Table of Contents ............................................................................................................................................ ii
MICROPROCESSOR ...................................................................................................................... 1
1. Microprocessor о Oǀerǀiew ...................................................................................................................... 2
How does a Microprocessor Work? ................................................................................................................ 2
Features of a Microprocessor .......................................................................................................................... 3
2. Microprocessor о Classification ................................................................................................................. 4
RISC Processor ................................................................................................................................................. 4
CISC Processor ................................................................................................................................................. 6
Special Processors ........................................................................................................................................... 7
8085 MICROPROCESSOR ............................................................................................................. 9
3. 8085 - Architecture ................................................................................................................................. 10
8085 Microprocessor - Functional Units ....................................................................................................... 10
8085 Architecture .......................................................................................................................................... 12
4. 8085 о Pin Configuration ......................................................................................................................... 13
5. 8085 о Addressing Modes Θ Interrupts ................................................................................................... 16
Addressing Modes in 8085 ............................................................................................................................ 16
Interrupts in 8085 .......................................................................................................................................... 16
6. 8085 - Instruction Sets ............................................................................................................................ 19
Control Instructions ....................................................................................................................................... 19
Branching Instructions ................................................................................................................................... 21
Arithmetic Instructions .................................................................................................................................. 24
Data Transfer Instructions ............................................................................................................................. 26
8085 - Demo Programs ................................................................................................................................. 29
8086 MICROPROCESSOR ........................................................................................................... 32
7. 8086 о Oǀerǀiew ..................................................................................................................................... 33
Features of 8086 ............................................................................................................................................ 33
Comparison between 8085 &8086 Microprocessor...................................................................................... 33
Architecture of 8086 ...................................................................................................................................... 34
8. 8086 - Functional Units........................................................................................................................... 35
EU (Execution Unit) ....................................................................................................................................... 35
BIU (Bus Interface Unit) ................................................................................................................................. 36
Microprocessors
iii9. 8086 о Pin Configuration ......................................................................................................................... 38
10. 8086 о Instruction Sets ............................................................................................................................ 43
Data Transfer Instructions ............................................................................................................................. 43
Arithmetic Instructions .................................................................................................................................. 44
Bit Manipulation Instructions ........................................................................................................................ 45
String Instructions ......................................................................................................................................... 46
Program Execution Transfer Instructions (Branch & Loop Instructions) ....................................................... 46
Processor Control Instructions ...................................................................................................................... 47
Iteration Control Instructions ........................................................................................................................ 47
Interrupt Instructions .................................................................................................................................... 48
11. 8086 о Interrupts .................................................................................................................................... 49
Hardware Interrupts ...................................................................................................................................... 49
Software Interrupts ....................................................................................................................................... 50
12. 8086 о Addressing Modes ....................................................................................................................... 53
MULTIPROCESSOR CONFIGURATION ........................................................................................ 55
13. Multiprocessor Configuration о Oǀerǀiew............................................................................................... 56
Coprocessor Configuration ............................................................................................................................ 56
Closely Coupled Configuration ...................................................................................................................... 57
Loosely Coupled Configuration ..................................................................................................................... 58
14. 8087 Numeric Data Processor ................................................................................................................. 60
8087 Architecture .......................................................................................................................................... 60
8087 Pin Description ..................................................................................................................................... 61
I/O INTERFACING ...................................................................................................................... 63
15. IͬO Interfacing о Oǀerǀiew ...................................................................................................................... 64
16. 8279 о Programmable Keyboard ............................................................................................................. 66
Operational Modes of 8279 .......................................................................................................................... 70
17. 8257 о DMA Controller ........................................................................................................................... 71
How DMA Operations are Performed? ......................................................................................................... 71
Features of 8257 ............................................................................................................................................ 71
8257 Architecture .......................................................................................................................................... 72
MICROCONTROLLERS ................................................................................................................ 76
18. Microcontrollers о Oǀerǀiew ................................................................................................................... 77
Difference between Microprocessor and Microcontroller............................................................................ 77
Types of Microcontrollers.............................................................................................................................. 77
Applications of Microcontrollers ................................................................................................................... 78
Microprocessors
iv19. 8051 ൞ Architecture ................................................................................................................................. 79
20. 8051 о Pin Description ............................................................................................................................ 80
21. 8051 о Input Output Ports....................................................................................................................... 82
Pins Current Limitations ................................................................................................................................ 83
22. 8051 о Interrupts .................................................................................................................................... 84
PERIPHERAL DEVICES ................................................................................................................ 86
23. Intel 8255A о Programmable Peripheral Interface .................................................................................. 87
Ports of 8255A ............................................................................................................................................... 87
Operating Modes ........................................................................................................................................... 87
Features of 8255A ......................................................................................................................................... 88
8255 ............................................................................................................................................................... 88
Architecture ................................................................................................................................................... 88
24. Intel 8255A о Pin Description .................................................................................................................. 89
25. Intel 8253 ൞ Programmable Interǀal Timer .............................................................................................. 91
Difference between 8253 and 8254 .............................................................................................................. 91
Features of 8253 / 54 .................................................................................................................................... 91
