 Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees
Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees
• A minimum spanning tree is a spanning tree where the sum of the weights on the • Solution 1: Kruskal's algorithm. – Work with edges. – Two steps: • Sort ...
 The Capacitated Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
The Capacitated Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
Another important and natural improvement heuristic is to compute the MST of the s-trees which are part of the solution obtained by a construction algorithm.
 Chapter 14 Minimum Spanning Tree
Chapter 14 Minimum Spanning Tree
We call this a shortcut edge. Example 14.8. The figure on the right shows a solution to TSP with shortcuts drawn in red. Starting at a
 Weight-Constrained Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
Weight-Constrained Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
٢٧ ربيع الآخر ١٤٢٨ هـ Example 1.3 Minimum Cost Reliability Constrained Spanning Tree. An ... The solution of the algorithm is a tree T with c(T) = n and w(T)=1 ...
 Minimal Spanning Tree and Shortest Path Problems
Minimal Spanning Tree and Shortest Path Problems
١٦ رجب ١٤٤١ هـ Figure 3: A shortest path tree in a network with Euclidean distances as weights (Example 2). Dijkstra's algorithm. The standard solution to the ...
 Lecture 7: Minimum Spanning Trees and Prims Algorithm
Lecture 7: Minimum Spanning Trees and Prims Algorithm
A Minimum Spanning Tree in an undirected connected weighted graph is a spanning tree of minimum weight. (among all spanning trees). Example:.
 Applications of minimum spanning trees
Applications of minimum spanning trees
There's a straightforward way to use the MST to get a. 2-approximation to the optimal solution to the traveling salesman problem and the. Christofides
 COSC-311 Sample Midterm Questions 1 Minimum Spanning Trees
COSC-311 Sample Midterm Questions 1 Minimum Spanning Trees
Ryan's cool new Minimum Spanning Tree algorithm works as follows on a graph with n vertices: • Initialize set T = ∅ and S = u where u is a randomly chosen
 The constrained minimum spanning tree problem
The constrained minimum spanning tree problem
Keywords: Approximation algorithm minimum spanning trees
 3 1. The minimum spanning tree problem We met this problem in our
3 1. The minimum spanning tree problem We met this problem in our
consider traveling from IGA to M in the first solution to our MST example). (b) There are many spanning sub-graphs of a given graph. It is extremely time
 Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees
Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees
Minimum Spanning Trees. • Solution 1: Kruskal's algorithm. – Work with edges. – Two steps: • Sort edges by increasing edge weight.
 COSC-311 Sample Midterm Questions 1 Minimum Spanning Trees
COSC-311 Sample Midterm Questions 1 Minimum Spanning Trees
COSC-311 Sample Midterm Questions not represented in the sample problems. ... Ryan's cool new Minimum Spanning Tree algorithm works as follows on a ...
 Weight-Constrained Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
Weight-Constrained Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
May 14 2007 Example 1.3 Minimum Cost Reliability Constrained Spanning Tree ... optimal solution of the weight-constrained minimal spanning tree problem.
 Chapter 6: Graph Theory
Chapter 6: Graph Theory
circuits. The red edges are the MST (minimum spanning tree). Example 6.2.5: Using Kruskal's Algorithm. Figure 6.2.7: Weighted Graph 2.
 Algorithms for the Min- Max Regret Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
Algorithms for the Min- Max Regret Minimum Spanning Tree Problem
Jul 3 2017 Is possible to observe that using an initial solution brings an improvement of
 Minimum Spanning Trees
Minimum Spanning Trees
The MST problem has many applications: For example think about connecting cities with minimal amount of wire or roads (cities are vertices
 Applications of minimum spanning trees
Applications of minimum spanning trees
There's a straightforward way to use the MST to get a. 2-approximation to the optimal solution to the traveling salesman problem and the. Christofides'
 Ch.07 Shortest Route Minimal Spanning Tree
Ch.07 Shortest Route Minimal Spanning Tree
http://contents.kocw.or.kr/KOCW/document/2015/chungang/ahnbonghyun/09.pdf
 Chapter 15 Minimum Spanning Tree
Chapter 15 Minimum Spanning Tree
Example 15.2. undirected connected graph using minimum spanning trees. Since the solution to TSP visits every vertex once (returning to the origin) ...
 A linear programming approach to increasing the weight of all
A linear programming approach to increasing the weight of all
minimum spanning trees is equal to some target value. We formulate Section 5 we give the algorithm that builds a primal and a dual solution.
 [PDF] Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees - UTK EECS
[PDF] Chapter 23 Minimum Spanning Trees - UTK EECS
Minimum Spanning Trees • Solution 1: Kruskal's algorithm – Work with edges – Two steps: • Sort edges by increasing edge weight
 [PDF] Lecture 7: Minimum Spanning Trees and Prims Algorithm
[PDF] Lecture 7: Minimum Spanning Trees and Prims Algorithm
A Minimum Spanning Tree in an undirected connected weighted graph is a spanning tree of minimum weight (among all spanning trees) Example:
 [PDF] Minimum Spanning Trees
[PDF] Minimum Spanning Trees
Answer: Run BFS or DFS; the resulting BFS- or DFS-tree are spanning trees of G The minimum spanning tree (MST) problem is the following: Given a connected
 [PDF] CSE 373: Minimum Spanning Trees: Prim and Kruskal - Washington
[PDF] CSE 373: Minimum Spanning Trees: Prim and Kruskal - Washington
26 fév 2018 · Minimum spanning trees: Applications Example questions: ? We want to connect phone lines to houses but laying down cable is expensive
 [PDF] Minimum Spanning Tree in Graph - CSE IIT Delhi
[PDF] Minimum Spanning Tree in Graph - CSE IIT Delhi
A minimum-cost spanning tree is a spanning tree that has the lowest cost Prim's algorithm: Start with any one node in the spanning tree and repeatedly
 [PDF] 86: Minimum Spanning Tree - Whitman People
[PDF] 86: Minimum Spanning Tree - Whitman People
For a network with n nodes a spanning tree is a group of n - 1 arcs that connects all nodes of the network and contains no loops Example
 [PDF] minimum spanning trees - Sathyabama
[PDF] minimum spanning trees - Sathyabama
MINIMUM SPANNING TREES Weight of an edge: Weight of an edge is just of the value of the edge or the cost of the edge For example a graph representing
 [PDF] ECE-250 Course Slides -- Minimum spanning trees
[PDF] ECE-250 Course Slides -- Minimum spanning trees
21 mar 2012 · Discuss the notion of minimum spanning trees ? Look into two algorithms to find a minimum spanning tree: – Prim's algorithm
 [PDF] Minimum Spanning Tree
[PDF] Minimum Spanning Tree
Algorithms ROBERT SEDGEWICK KEVIN WAYNE 4 3 MINIMUM SPANNING TREES ? introduction ? greedy algorithm ? edge-weighted graph API ? Kruskal's algorithm
 [PDF] Minimum Spanning Trees - Prim Kruskal NP-complete problems
[PDF] Minimum Spanning Trees - Prim Kruskal NP-complete problems
A spanning tree i e a subgraph being a tree and containing all vertices having minimum total weight (sum of all edge weights) 2 0 1 3 5 4 1 3
What is an example of a minimal spanning tree?
A minimum spanning tree is a special kind of tree that minimizes the lengths (or “weights”) of the edges of the tree. An example is a cable company wanting to lay line to multiple neighborhoods; by minimizing the amount of cable laid, the cable company will save money.How do you solve spanning tree problems?
Creating Minimum Spanning Tree Using Kruskal Algorithm
1Step 1: Sort all edges in increasing order of their edge weights.2Step 2: Pick the smallest edge.3Step 3: Check if the new edge creates a cycle or loop in a spanning tree.4Step 4: If it doesn't form the cycle, then include that edge in MST.What is minimum spanning tree of a graph example?
Given a graph G=(V,E), a subgraph of G that is connects all of the vertices and is a tree is called a spanning tree . For example, suppose we start with this graph: We can remove edges until we are left with a tree: the result is a spanning tree. Clearly, a spanning tree will have V-1 edges, like any other tree.- A spanning tree is a subset of Graph G, which has all the vertices covered with minimum possible number of edges. Hence, a spanning tree does not have cycles and it cannot be disconnected.. By this definition, we can draw a conclusion that every connected and undirected Graph G has at least one spanning tree.
COSC-311 Sample Midterm Questions
Note: There will be four problems on the actual midterm. The problems on this handout are meant to give you a sense of the types of questions I might ask. This study guide is not comprehensive: there are topics we have covered in class that are not represented in the sample problems. Everything we have done in class or on homework is fair game for the midterm.1 Minimum Spanning Trees
Ryan's cool new Minimum Spanning Tree algorithm works as follows on a graph with nvertices: Initialize setT=;andS=u, whereuis a randomly chosen vertex. Iteraten1 times: Letvbe the vertex most recently added toS. Consider all edges fromvto some other vertexxthat has not yet been added toS. Among those edges, let (v;w) be the edge of lowest cost. Add edge (v;w) toTand add wtoS. Ifvdoesn't have any neighbors not already inS, go back to the second-most- recently added vertex, and keep backtracking until you nd a vertex that has at least one neighbor not already inS. Use that vertex instead ofvin this iteration.Sadly this algorithm does not work.
(a)State the theorem that tells us which edges are safe to add to a partial MSTT. (b)Explain why Ryan's algorithm doesn't t the criteria for this theorem. (c)Give an example of a graph with at least 3 vertices for which Ryan's algorithm returns the wrong answer. What does the algorithm do? What is the correct MST?2 Scheduling
In the Interval Scheduling problem, we were given a set of jobs, where each jobi required our resource starting at timea(i) and ending at timef(i), and only one job could be scheduled to use the resource at a time. If two jobs con ict, we must discard one of them. Our goal was to come up with a subset of jobsSsuch that there are no con icts among the jobs inS, andjSjis maximized. (a)Dana suggests the following greedy algorithm: letx(i) =f(i)a(i) be thesize of jobi, and letn(i) be the number of jobs con icting with jobi. Add toSthe jobi 1 with the smallestx(i)n(i), then throw out any jobs con icting withiand recur on the remaining jobs. Give a counterexample that shows that Dana's algorithm does not always produce the optimal solution. (b)What is the correct greedy algorithm to solve this problem optimally?3 More Minimum Spanning Trees
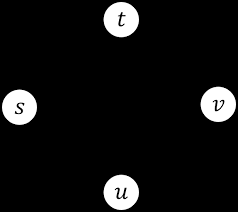
Here is a graph:(a)Draw the minimum spanning tree that would result from running Prim's algo- rithm on this graph, starting at vertexs. List the order in which edges are added to the tree. (b)Draw the minimum spanning tree that would result from running Kruskal's al- gorithm on this graph. List the order in which edges are added to the tree.4 Recurrences
Allie and Brandon each have come up with a divide-and-conquer algorithm to solve a problem. Allie's algorithm (algorithmA) splits a problem of sizeninto four pieces, each of sizen=2, solves the pieces recursively, and takes time 30nto combine the results. Brandon's algorithm (algorithmB) takes timen3to turn a problem of sizen into a smaller problem of sizen=2, which it then solves recursively. 2 (a)Write a recurrence for the runtime of Allie's algorithm,TA(n), and a recurrence for the runtime of Brandon's algorithm,TB(n). (b)Which algorithm has an asymptotically better runtime? Justify your answer by solving each recurrence using the Master Theorem.5 Shortest Paths
Here is a graph:(a)Run the Bellman-Ford algorithm on the graph to nd the shortest path froms to every other node. Show the table that you ll in while running the algorithm. (b)Now suppose you ran one extra iteration of Bellman-Ford. How could you use that last iteration to detect whether the graph has a negative-weight cycle?6 Making Change
Suppose you are traveling to a foreign country where the local currency has four coins with denominationsd1= 1,d2= 5,d3= 8, andd4= 14 cents. As usual, when making change the goal is to end up with as few coins as possible. (a)Give a counterexample to show that the greedy algorithm for making change no longer yields the optimal solution. (b)Write a recurrence for a dynamic programming algorithm that computes the minimum number of coins needed to make change forncents,C(n). 3quotesdbs_dbs9.pdfusesText_15[PDF] ministere de bercy la silver economie
[PDF] ministère de l'économie et de l'innovation
[PDF] ministère de l'éducation nationale côte d'ivoire
[PDF] ministère de l'éducation nationale d'haïti
[PDF] ministère de l'intérieur adresse bercy
[PDF] ministère de l'intérieur bercy
[PDF] ministere de la defense bercy
[PDF] ministere de la finance bercy
[PDF] ministère des finances du québec
[PDF] ministère des finances france adresse
[PDF] ministère des finances france organigramme
[PDF] ministère des finances france recrutement
[PDF] ministère des finances publiques france
[PDF] ministre de l'économie canada
