 Grade 7 Science Unit 3: Mixtures and Solutions
Grade 7 Science Unit 3: Mixtures and Solutions
It allows you to recover BOTH the and the from a solution. 5. Paper Chromatography. Used to separate the substances in a mixture such as. Used to separate the.
 Laboratory Solution Preparation
Laboratory Solution Preparation
Solution: A uniform homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. The individual substances may be present in varying amounts. Solvent: The substance which
 EMERGENCY RESPONSE GUIDEBOOK
EMERGENCY RESPONSE GUIDEBOOK
solution. 1910 157 Calcium oxide. 1911 119 Diborane. 1911 119 Diborane compressed. 1911 119 Diborane mixtures. 1912 115 Methyl chloride and Methylene chloride ...
 Mixtures and Solutions Types of Mixtures
Mixtures and Solutions Types of Mixtures
Types of Mixtures. Concept: Science Worksheet. Grade: Six. Mixtures. Homogeneous mixture (Solution). Made up of one part only. Ex: Salty water. Heterogeneous.
 Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet
Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet
solutions. and are known as. Mixtures can also be non-uniform (called heterogeneous). Mixtures can be separated into their components by chemical or physical
 Key Worksheet Solution Equilibrium
Key Worksheet Solution Equilibrium
WORKSHEET: SOLUTION EQUILIBRIUM (Weak acids and bases buffers
 HOW TO USE THE HAZARDOUS MATERIALS REGULATIONS
HOW TO USE THE HAZARDOUS MATERIALS REGULATIONS
The hazmat also is a marine pollutant when: • the material is listed in Appendix B (HMT § 172.101) and. • when in solution or mixture
 ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
The beaker is shaken gently to stir the solution. There will be two liquid layers in this mixture. The electrodes are placed so that they penetrate below the
 Chem 111 Chemical Equilibrium Worksheet Answer Keys
Chem 111 Chemical Equilibrium Worksheet Answer Keys
A mixture of 9.22 moles of A 10.11 moles of B
 Grade 7 Science - Unit Lesson Guide Mixtures and Solution
Grade 7 Science - Unit Lesson Guide Mixtures and Solution
Ensure that students have completed the investigation worksheet. Evaluate each outcome that is listed individually. 38. Page 39. Investigating Solutions
 Worksheet: Mixtures and Solutions
Worksheet: Mixtures and Solutions
Worksheet: Mixtures and Solutions. Name: Class: 1. State with a reason
 Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet
Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet
In Column B list whether the substance is an element (E)
 5 Separating mixtures
5 Separating mixtures
Water is a good solvent because many chemicals can dissolve in it. Fizzy soft drinks are aqueous solutions. Substances that dissolve in a liquid are said to be.
 lwtech-learning-lab-math-algebra-word-problems-2.pdf
lwtech-learning-lab-math-algebra-word-problems-2.pdf
Mixtures: A mixture containing 6% boric acid is to be mixed with 2 quarts of a mixture which is. 15% boric acid in order to obtain a solution which is 12%
 SISUS: Stable Isotope Sourcing using Sampling Getting Started
SISUS: Stable Isotope Sourcing using Sampling Getting Started
May 30 2007 2.2 Worksheet 2
 WORKSHEET: SOLUTION EQUILIBRIUM (Weak acids and bases
WORKSHEET: SOLUTION EQUILIBRIUM (Weak acids and bases
How many moles of HNO2 must be added to a 1.00 liter of 0.370 M NaNO2 to give a buffer of. pH= 4.20? (Ignore any volume change due to the addition of HNO2)
 110 WS Solution Stoichiometry Key.pdf
110 WS Solution Stoichiometry Key.pdf
1] How many grams of calcium phosphate can be produced from the reaction of 2.50 L of 0.250 M Calcium chloride with and excess of phosphoric acid?
 CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER WORKSHEET HOMOGENEOUS VS
CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER WORKSHEET HOMOGENEOUS VS
PURE SUBSTANCES VS. MIXTURES. Classify the following as pure substances (element or compound) or mixtures. 1. sodium Pure substance (E). 11
 Gumdrop Atoms Activity – Atoms Worksheet
Gumdrop Atoms Activity – Atoms Worksheet
Positive +1. 3. What charge does an electron have? Negative
 Untitled
Untitled
mixture was diluted to 100.00 mL in a volumetric flask. The absorbance of the new solution was. 0.500. a) Denoting the initial unknown concentration as
 [PDF] Worksheet: Mixtures and Solutions
[PDF] Worksheet: Mixtures and Solutions
Name: Class: 1 State with a reason whether each of the following is a homogeneous mixture (solution) or a heterogeneous mixture (mechanical mixture):
 [PDF] Mixtures and Solutions
[PDF] Mixtures and Solutions
Types of Mixtures Concept: Science Worksheet Grade: Six Mixtures Homogeneous A solution is a homogenous mixture in which two substances
 [PDF] Grade 7 Science Unit 3: Mixtures and Solutions - inetTeacher
[PDF] Grade 7 Science Unit 3: Mixtures and Solutions - inetTeacher
Grade 7 Science Unit 3: Mixtures and Solutions Chapter 9: Many useful products depend on technology for separating mixtures and solutions Name:
 [PDF] Mixture Problems – Extra Practice
[PDF] Mixture Problems – Extra Practice
Mixture Problems – Extra Practice 1 Mike has coffee worth $4 per pound that he wishes to mix with 20 pounds of coffee worth $7 per pound to get a mixture
 Worksheets 03 7C MIXTURES PDF PDF Solution Filtration - Scribd
Worksheets 03 7C MIXTURES PDF PDF Solution Filtration - Scribd
Mixtures Mixtures Mixture? Getting Flotation Sedimentation Importance Decanting Useful of Water Substances Evaporation Filtration Distillation
 Mixtures & Solutions - Ms Walkers Website
Mixtures & Solutions - Ms Walkers Website
Mixtures and Solutions Vocabulary Flash Cards on Quizlet 1 The Particle Theory of Matter 1_particle_theory_of_matter pdf
 [PDF] Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet
[PDF] Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet
Elements Compounds Mixtures Worksheet Part 1: Read the following information on elements compounds and mixtures Fill in the blanks where necessary
 [DOC] Mixtures and Solutions - Scarsdale Public Schools
[DOC] Mixtures and Solutions - Scarsdale Public Schools
Mixture two or more materials stirred together; Property – a characteristic of an object A solution is made of two parts the solvent and the solute
 [DOC] Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet - Obion County Schools
[DOC] Elements Compounds & Mixtures Worksheet - Obion County Schools
Elements Compounds Mixtures Worksheet Part 1: Read the following information on elements compounds and mixtures Fill in the blanks using the word bank
Grade 7 Science
Unit 3: Mixtures and Solutions
Chapter 9: Many useful products depend on
technology for separating mixtures and solutions. Name:Homeroom #:
2Separating Mixtures
Mixtures Method of Separation Explanation
1. Salt Water
2. Muddy Water
3. Nuts and Bolts
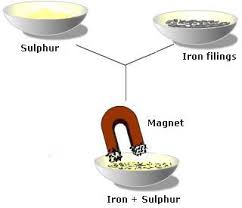
4. Iron filings and sand
5.Vegetable oil and sand
6. Vegetable oil and water
7. Salt and pepper
Are the components you have separated still mixtures or are they pure? Explain your answer.Separation Techniques
1. Mechanical Sorting
Used to separate the parts of a mixture based on such as particle size.Examples: and
32. Filtration
A common way to separate particles from a mixture.Examples:
3. Evaporation
Changes of state from a to a
Used to recover a solid from a
4. Distillation
Uses two changes of state: and
It allows you to recover BOTH the and the from a solution.5. Paper Chromatography
Used to separate the substances in a mixture such asUsed to separate the in a mixture.
4Key Words
Evaporation:
Filtration:
Mechanical Sorting:
Paper Chromatography:
Simple Distillation:
Comprehension Questions
1. Why is it easier to separate the parts of a heterogeneous mixture than the parts of a
homogeneous mixture?2. Why is the size of the holes in a filter important for filtration?
3. Which part or parts of a solution does evaporation recover; the solute, the solvent, or
both?4. Which part or parts of a solution does distillation recover; the solute, the solvent, or
both? 55. What is chromatography?
6. How does paper chromatography work?
7. Explain how you could separate each of the following mixtures:
a) Wood chips and pieces of granite rock. b) Iron filings and wood sawdust. c) Salt and pepper. 6Unit 3 Summary
Chapter 7 Matter can be classified as mixtures or pure substances. " Matter can be either mixtures or pure substances. (7.1) " Mixtures may be either heterogeneous or homogeneous. (7.1) " Homogeneous mixtures (solutions) have the same properties throughout. (7.1) " Heterogeneous mixtures have different visible parts with different properties. (7.1) " Matter is either a mixture or a pure substance based on the types of particles that make it up. (7.2) " Each pure substance has its own type of particle, which is different from the kinds of particles that make up all other pure substances. (7.2) Chapter 8 Some substances dissolve to form solutions faster and more easily than others. " In a solution, the substance that dissolves is the solute, and the substance in which the solute dissolves is the solvent. (8.1) " A substance is soluble in a solvent if it dissolves in the solvent. A substance is insoluble in a solvent if it does not dissolve in the solvent. (8.1) " A concentrated solution has a larger mass of solute for certain volume of solvent. A dilute solution has a smaller mass of solute for a certain volume of solvent. (8.2) " Solution concentration may be expressed in units of grams of solute per litre of solvent (g/L). (8.2) " A solution is saturated when as much solute has dissolved in a solvent as it can, at a certain temperature. (8.2) " Different solutes have different solubilities, which may be increased by increasing the temperature. (8.2) " Stirring a solution increases the rate of dissolving but not the solubility of the solute. (8.2) Chapter 9 Many useful products depend on technology for separating mixtures and solutions. " Heterogeneous mixtures may be separated by methods that include sorting by hand, mechanical sorting, and filtration. (9.1) " Mechanical sorting of a mixture is based on properties such as particle size and magnetism. (9.1) " Homogeneous mixtures may be separated by methods that include evaporation, distillation, and paper chromatography. (9.1) 7Unit 3 Review
Circle the letter of the best answer.
1. Which is the method that is used to separate and recover the parts of a liquid
solution?A. condensation
B. distillation
C. evaporation
D. saturation
2. Which of the following is an example of a solution?
A. oil in water
B. oxygen in air
C. pepper in water
D. dust in air
3. Which of the following is a homogeneous mixture?
A. antifreeze
B. gold ore
C. milk
D. petroleum
4. Which of the following lists contains all pure substances?
A. gold, oxygen, carbon dioxide
B. milk, water, copper
C. squeezed orange juice, silver, soda water
D. tea, salt, concrete
5. In the following list of substances, which is the most soluble in water?
A. carbon dioxide
B. ethanol
C. sugar
D. table salt
86. Which of the following labels for the picture below is correct?
A. solute + solvent = solution
B. solvent + solute = saturation
C. solvent + solute = soluble
D. solvent + solute = solution
In the space beside each letter, write the numeral of the choice that is the best match.Each numeral choice may be used only once.
7. Mixtures
8. Homogeneous
9. Heterogeneous
10. Matter
11. contain two or more components
12. composition varies within the sample and from one sample to another
A ___Pure Substances
C ___ D ___ B ___ E ___ F ___ G ___ H ___quotesdbs_dbs7.pdfusesText_5[PDF] mixtures and solutions worksheet grade 7
[PDF] mixtures and solutions worksheet pdf
[PDF] mixtures and solutions worksheets grade 6
[PDF] mixtures worksheet
[PDF] mjf 3d printer
[PDF] ml to liters
[PDF] ml/hr formula
[PDF] mla 8th edition quiz
[PDF] mla abstract format example
[PDF] mla abstract format purdue owl
[PDF] mla and apa format examples
[PDF] mla and apa quiz
[PDF] mla annotated bibliography example
[PDF] mla article citation generator
