 LINEAR PROGRAMMING(MTS5B08) V SEMESTER MULTIPLE
LINEAR PROGRAMMING(MTS5B08) V SEMESTER MULTIPLE
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS AND. ANSWERS. 1. Solution which satifies all the constraints of linear programming problem is called. (a) Feasible solution. (b)
 MA 162 Exam 2 Fall 2016 - Name
MA 162 Exam 2 Fall 2016 - Name
Record your answers to the multiple choice questions below on this page by (5 points) A linear programming problem has objective function P = 3x + 2y and the ...
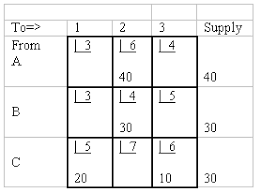 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Multiple Choice Questions
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Multiple Choice Questions
Objective function in Linear Programming problems has always finite value at the optimal solution-TRUE. 33. A finite optimal solution can be not unique- FALSE.
 Topics: Linear Programming Problem
Topics: Linear Programming Problem
Multiple Choice Questions. 2016. Q.6. In minimization problem better solution can be formed if positive quantities are assigned to a) Positive basic
 Unit : 1
Unit : 1
The first step in formulating a linear programming problem should be to identify the objective The graphical approach to the solution of linear programming ...
 LINEAR PROGRAMMING(MTS5B08) V SEMESTER MULTIPLE
LINEAR PROGRAMMING(MTS5B08) V SEMESTER MULTIPLE
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS AND. ANSWERS. 1. Solution which satifies all the constraints of linear programming problem is called. (a) Feasible solution. (b)
 Multiple Choice Questions BCA IV Sem OPERATIONS RESEARCH
Multiple Choice Questions BCA IV Sem OPERATIONS RESEARCH
Any solution to a LPP which satisfies the non- negativity restrictions of the (i) All linear programming problems may not have unique solutions. (ii) The ...
 Question Answering via Integer Programming over Semi-Structured
Question Answering via Integer Programming over Semi-Structured
optimization problem i.e.
 Integer Programming
Integer Programming
An integer linear program is a linear program further constrained by the integrality restrictions. Thus in a maximization problem
 MATH M118 Practice Test Chapter 7
MATH M118 Practice Test Chapter 7
Problems #1-10: Identify the best answer from the given choices operating costs write the objective function and ALL constraints for this linear programming ...
 Multiple Choice Questions OPERATIONS RESEARCH
Multiple Choice Questions OPERATIONS RESEARCH
a given problem and also derives a solution from the model using What refers to Linear Programming that includes an evaluation of relative risks and.
 Chapter 1
Chapter 1
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) for TYBMS (2) ______ specifies the objective or goal of solving the LPP. (a) Objective function. (b) Decision Variables.
 MA 162 Exam 2 Fall 2016 - Name
MA 162 Exam 2 Fall 2016 - Name
Please indicate your answers for the multiple choice questions here by (5 points) A linear programming problem has objective function P = 3x + 2y and ...
 Operations Research Second Edition
Operations Research Second Edition
Linear Programming models (Solution by Simplex method) . Linear Programming - II (Transportation Problem) . ... Multiple choice question and answers .
 A geometric approach In addition to constraints linear programming
A geometric approach In addition to constraints linear programming
The values of the objective function are. 60 190 and 210. Hence Michael can maximize his score by answering 3 essay questions and. 30 short-answer questions. 7
 Unit : 1
Unit : 1
Q : 3 Multiple choice questions. Maximization of objective function in LPP means ... Alternative solution exist in a linear programming problem when.
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Multiple Choice Questions
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Multiple Choice Questions
32. Objective function in Linear Programming problems has always finite value at the optimal solution-TRUE. 33. A finite optimal solution can be not unique-
 Integer Programming
Integer Programming
An integer linear program is a linear program further constrained by the integrality restrictions. Thus in a maximization problem
 Linear Programming
Linear Programming
The objective function also specifies a direction of optimization either to maximize or minimize. An optimal solution for the model is the best solution as
 Linear programming graphically
Linear programming graphically
The values of the objective function at these corners are 60 190 and 210. Hence Michael can maximize his score by answering 3 essay questions and 30 short-
 Linear Programming MCQ [Free PDF] - Objective Question Answer
Linear Programming MCQ [Free PDF] - Objective Question Answer
20 avr 2023 · Get Linear Programming Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ Quiz) with answers and detailed solutions Download these Free Linear Programming MCQ
 Linear Programming Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Linear Programming Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Linear Multiple Choice Questions and Answers for competitive exams These short objective type questions with answers are very important for Board exams as
 LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM Solved MCQs - McqMate
LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM Solved MCQs - McqMate
Solved MCQs for LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM with PDF download and FREE mock test The value of objective function is maximum under linear constraints
 Linear Programming Problems MCQs PDF - Quiz Questions Answers
Linear Programming Problems MCQs PDF - Quiz Questions Answers
Linear Programming Problems Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Linear Programming Problems quiz answers PDF to learn online business mathematics course
 [PDF] Topics: Linear Programming Problem - ResearchGate
[PDF] Topics: Linear Programming Problem - ResearchGate
Multiple Choice Questions 2016 Topics: Linear In linear programming lack of points for a solution set is said to a) have no feasible solution
 Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming MCQs (with answers)
Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming MCQs (with answers)
Class 12 Maths Chapter 12 Linear Programming MCQs are available for students with answers The multiple-choice questions are prepared according to the
 multiple choice questions on linear programming problems with
multiple choice questions on linear programming problems with
Maths Chapter 12 – Linear Programming MCQ Question Answers for Various Entrance Exams ; 1 In maximization problem optimal solution occurring at
 mcq on linear programming pdf - wapakbiz
mcq on linear programming pdf - wapakbiz
Linear Programming Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Free download in PDF Linear Programming MCQ [Free PDF] MCQs of Linear Programming Problem 1
 linear programming multiple choice questions and answers pdf
linear programming multiple choice questions and answers pdf
The Test: Linear Programming - 1 questions and answers have been prepared according to PDF multiple choice questions on linear programming problems
What are the 5 types of linear programming problems?
There are different methods to solve an linear programming problem. Such as Graphical method, Simplex method, Ellipsoid method, Interior point methods.How to solve a linear programming problems there are 4 main steps?
LPP applications may include production scheduling, inventory policies, investment portfolio, allocation of advertising budget, construction of warehouses, etc. In this article, we would focus on the different components of the output generated by Microsoft excel while solving a basic LPP model.
Linear programming, graphically
We've seen examples of problems that lead to linear constraintson some unknown quantities.Now we are going to add an extra ingredient: some
quantity that we want to maximize or minimize, such as prot, or costs. If the quantity to be maximized/minimized can be written as a linear combination of the variables, it is called a linear objective function. Linear programmingis the business of nding a point in the feasible set for the constraints, which gives an optimum value (maximum or a minimum) for the objective function. We'll see how a linear programming problem can be solved graphically.Example | constraints
A juice stand sells two types of fresh juice in 12 oz cups, the Refresher and the Super-Duper. The Refresher is made from 3 oranges, 2 apples and a slice of ginger. The Super Duper is made from one slice of watermelon, 3 apples and one orange. The owners of the juice stand have 50 oranges,40 apples, 10 slices of watermelon and 15 slices of ginger.
Letxdenote the number of Refreshers they make and lety denote the number of Super-Dupers they make. Last time, we saw that the set of constraints onxandy was:3x+y⩽50 2x+3y⩽40
x⩽15y⩽10 x⩾0y⩾0Example | the feasible set
Here is thefeasible set, the set of combinations ofxandy that are possible given the limited supply of ingredients:5101520246810122x + 3y = 40
y=10 x=153x+y=50
Example | adding an objective
Now suppose that Refreshers sell for$6 each and
Super-Dupers sell for$8 each. Let's suppose also that the juice stand will sell all of the drinks they can make on this day, so their revenue for the day is 6x+8y. If a goal of the juice stand is to maximize revenue, then they want to maximizethe value of 6x+8y, given the constraints on production.In other words they want to nd a point(x;y)in the
feasible set which gives a maximum value for theobjective function6x+8y. [Note that the value of the objective function (6x+8y= revenue) varies as(x;y)varies over the points in the feasible set. For example if(x;y)=(2;5), revenue=6(2)+8(5)=$52, whereas if(x;y)=(5;10), revenue=6(5)+8(10)=$110.]Terminology
Suppose we are given a problem that involves assigning values x,yto some quantities. The choices ofx,ymay be subject to someconstraints: linear inequalities of the form a0x+a1y⩽b; a0x+a1y a 0x+a1y⩾b; a0x+a1y>b;
wherea0,a1andbare constants. There is a linearobjective function: an expression of the form cx+dy, wherecanddare constants, and we wish to nd the maximum or minimum value that the objective function can take on the feasible set. We use the termoptimal valueto cover both maximizing and minimizing. Alinear programmingproblem is the problem of nding a point (x0;y0)?F, the feasible set where all constraints are satised, withO(x0;y0)as big as possible (if we are doing a maximum problem), or as small as possible (if we are minimizing). A BIG IDEA of linear programming
If the feasible set of a linear programming problem is bounded (contained inside some big circle; equivalently, there is no direction in which you can travel indenitely while staying in the feasible set), then, whether the problem is a minimization or a maximization, there will be an optimum value. Furthermore: there will be somecorner pointof the feasible region that is an optimum if there is more than one optimum corner point then there will be exactly two of them, they will be adjacent, and any point in the line between them will also be optimum. The picture on the next page, taken from page 238 of the text, illustrates this graphically. A BIG IDEA of linear programming
Example | solving the problem
We now know that the maximum of 6x+8yon the feasible set occurs at a corner of the feasible set since the feasible set is bounded (it may occur at more than one corner, but it occurs at at least one). We already have a picture of the feasible set and below, we have labelled the corners, A, B, C, D and E.510152024681012
2x + 3y = 40
y=10 x=15 3x+y=50
A B C D Equotesdbs_dbs12.pdfusesText_18
0x+a1y⩾b; a0x+a1y>b;
wherea0,a1andbare constants. There is a linearobjective function: an expression of the form cx+dy, wherecanddare constants, and we wish to nd the maximum or minimum value that the objective function can take on the feasible set. We use the termoptimal valueto cover both maximizing and minimizing. Alinear programmingproblem is the problem of nding a point (x0;y0)?F, the feasible set where all constraints are satised, withO(x0;y0)as big as possible (if we are doing a maximum problem), or as small as possible (if we are minimizing).A BIG IDEA of linear programming
If the feasible set of a linear programming problem is bounded (contained inside some big circle; equivalently, there is no direction in which you can travel indenitely while staying in the feasible set), then, whether the problem is a minimization or a maximization, there will be an optimum value. Furthermore: there will be somecorner pointof the feasible region that is an optimum if there is more than one optimum corner point then there will be exactly two of them, they will be adjacent, and any point in the line between them will also be optimum. The picture on the next page, taken from page 238 of the text, illustrates this graphically.A BIG IDEA of linear programming
Example | solving the problem
We now know that the maximum of 6x+8yon the feasible set occurs at a corner of the feasible set since the feasible set is bounded (it may occur at more than one corner, but it occurs at at least one). We already have a picture of the feasible set and below, we have labelled the corners, A, B,C, D and E.510152024681012
2x + 3y = 40
y=10 x=153x+y=50
A B C D Equotesdbs_dbs12.pdfusesText_18[PDF] multiple choice questions on organic reaction mechanism
[PDF] multiple choice questions on organizing in management
[PDF] multiple choice questions on organometallic chemistry
[PDF] multiple choice questions on principles of management pdf
[PDF] multiple choice questions with answers on company act 2013 pdf
[PDF] multiple feedback low pass filter
[PDF] multiple fonts on resume
[PDF] multiple in text citations apa
[PDF] multiple inheritance in python 3
[PDF] multiple inheritance in python 3 example
[PDF] multiple linear least squares fit excel
[PDF] multiple regression analysis excel interpretation
[PDF] multiple regression in excel 2013
[PDF] multiple regression table
