 Clicker Question Bank for Numerical Analysis (Version 1.0 – May 14
Clicker Question Bank for Numerical Analysis (Version 1.0 – May 14
٢٥/٠٥/٢٠٢٠ Answer: (D). { Source: Holistic Numerical Methods [5] MC Question Solution Ch 05.01 Background of Interpolation.pdf }. Clicker Question Bank ...
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE PROBLEMS The problems that
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE PROBLEMS The problems that
and n = 20. Compare the answers and the errors for each of these methods. Problem 26. How would you go about solving the differential equation d2x.
 Chapter 10 Numerical Solution Methods for Engineering Analysis
Chapter 10 Numerical Solution Methods for Engineering Analysis
We will learn from this chapter on the use of some of these numerical methods that will not only enable engineers to solve many mathematical problems but they
 Math 6370/6371: Numerical Analysis Sample Preliminary Exam
Math 6370/6371: Numerical Analysis Sample Preliminary Exam
Sample Preliminary Exam Questions. 1. (Gaussian Elimination and Schur Complement) (Runge-Kutta Method and Numerical Solution of ODEs). Consider Heun's method.
 Numerical Methods Previous Year Questions & Detailed Solutions
Numerical Methods Previous Year Questions & Detailed Solutions
By Taylor's series method solution of y'=x. 2. + y. 2. ; y(0) = 1 is. 1) y=l+x – x. 2. 2) y = 1-x+x. 2. 3) y=x+ x. 2. +x. 3. 4) y=l+x+x. 2. +. 4. 3 x3. 19.
 NUMERICAL METHODS & PROBABILITY THEORY (20A54402)
NUMERICAL METHODS & PROBABILITY THEORY (20A54402)
SYLLABUS. UNIT I. Solution of Algebraic & Transcendental Equations: Introduction-Bisection method-Iterative method-Regula falsi method-Newton. Raphson method
 Core 3 Numerical Methods Questions
Core 3 Numerical Methods Questions
Page 1. Core 3 Numerical Methods Questions. Page 2. Page 3. Page 4. Page 5. Core 3 Numerical Methods Answers. Page 6. Page 7. Page 8.
 NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
٠٣/٠٤/٢٠٢٠ to study the various numerical methods of solving such equations. In most of these methods we replace the differential equation by a difference ...
 528406-question-paper-numerical-methods.pdf
528406-question-paper-numerical-methods.pdf
Answer all the questions. • Do not write in the barcodes. • You are permitted to use a scientific or graphical calculator in this paper. •
 B.Tech 4th Semester MATHEMATICS-IV UNIT-1 NUMERICAL
B.Tech 4th Semester MATHEMATICS-IV UNIT-1 NUMERICAL
We use numerical method to find approximate solution of problems by numerical calculations with aid of questions see the book: “Fundamentals of Mathematical ...
 Clicker Question Bank for Numerical Analysis (Version 1.0 – May 14
Clicker Question Bank for Numerical Analysis (Version 1.0 – May 14
25-May-2020 { Source: Holistic Numerical Methods [5] quiz 01 02 } ... Methods [5]
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE PROBLEMS The problems that
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS PRACTICE PROBLEMS The problems that
Compare the answers and the errors for each of these methods. Problem 26. How would you go about solving the differential equation d2x dt2. = ?x with.
 Numerical Methods Previous Year Questions & Detailed Solutions
Numerical Methods Previous Year Questions & Detailed Solutions
Numerical Methods. 1. Download Study Materials on www.examsdaily. Previous Year Questions & Detailed Solutions ... By Taylor's series method solution of.
 Chapter 10 Numerical Solution Methods for Engineering Analysis
Chapter 10 Numerical Solution Methods for Engineering Analysis
We will learn from this chapter on the use of some of these numerical methods that will not only enable engineers to solve many mathematical problems but they
 NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
do this for Euler's method will also make it easier to answer the same questions for other more efficient numerical methods. For the error analysis
 Numerical Method Mathematics Objective Type Question Answer
Numerical Method Mathematics Objective Type Question Answer
15-Jun-2022 acquire the Numerical. Method Mathematics Objective Type Question Answer belong to that we provide here and check out the link. You could buy ...
 Applied Numerical Analysis.pdf
Applied Numerical Analysis.pdf
0.1 Analysis Versus Numerical Analysis The Euler Method and Its Modifications 335 ... Find answers to these questions from that Web site.
 MATH 2140 00001 2 Numerical Methods I WITH ANSWERS 5 1 5
MATH 2140 00001 2 Numerical Methods I WITH ANSWERS 5 1 5
INSTRUCTIONS: i. Answer ALL of the following questions. ii. The full mark for this examination is 100. iii. Calculators are allowed but they must not be
 MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS – PROBLEMS AND EXERCISES II
MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS – PROBLEMS AND EXERCISES II
02-May-2014 Answer the following questions. Explain your answer. 1. Can the intersection of a sequence of nested intervals be empty?
 1.10 Eulers Method
1.10 Eulers Method
16-Feb-2007 where I is given in Equation (1.9.26) and c is an arbitrary constant. 1.10. Numerical Solution to First-Order Differential Equations.
 Math 6370/6371: Numerical Analysis Sample Preliminary Exam
Math 6370/6371: Numerical Analysis Sample Preliminary Exam
Numerical Analysis 18 (Cholesky Factorization) Given an m-by-msymmetric and positive de nite matrix A how do you e ciently solve the following problems using the Cholesky factorization of A? (a) Solve the linear system Akx= b where kis a positive integer (b) Compute 1= cTA b (c) Solve the matrix equation AX= B where Bis m-by-n
 Introduction to Numerical Analysis - UC Santa Barbara
Introduction to Numerical Analysis - UC Santa Barbara
1 1 What is Numerical Analysis? This is an introductory course of numerical analysis which comprises the design analysis and implementation of constructive methods and algorithms for the solution of mathematical problems Numerical analysis has vast applications both in mathematics and in modern science and technology
 Math128B: Numerical Analysis Sample Final Exam
Math128B: Numerical Analysis Sample Final Exam
Math128B: Numerical Analysis Sample Final Exam This is a closed book closed notes exam You need to justify every one of your answers Completely correct answers given without justi?cation will receive little credit Do as much as you can Partial solutions will get partial credit Look over the whole exam to ?nd problems that you can do
 Numerical Analysis 1 Lecture notes - University of Connecticut
Numerical Analysis 1 Lecture notes - University of Connecticut
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms for the problem of continuous mathematics We strongly encourage to read this essay whoever is interested in the subject it is only 5 pages long This lecture notes start with interpolation which is not orthodox but in my opinion it is an interesting topic that
 Lectures on Numerical Analysis - University of Pennsylvania
Lectures on Numerical Analysis - University of Pennsylvania
Lectures on Numerical Analysis Dennis Deturck and Herbert S Wilf Department of Mathematics University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia PA 19104-6395 Copyright 2002 Dennis Deturck and Herbert Wilf April 30 2002
 Searches related to numerical analysis questions and answers pdf filetype:pdf
Searches related to numerical analysis questions and answers pdf filetype:pdf
Math 371: Numerical Analysis Fall 2015 Solutions to Exam 1 Practice Questions 1 Convert the following base-10 expansions into binary expansions (a) 9:75 Solution 1001:11 (b) 0:1 Solution 2(0:1) = 0+0:2 2(0:2) = 0+0:4 2(0:4) = 0+0:8 2(0:8) = 1+0:6 2(0:6) = 1+0:2 The pattern 0011 will then repeat so the expansion is 0:00011
Chapter 10
Numerical Solution Methods for Engineering Analysis (Chapter 10 Numerical solution methods)© Tai-Ran HsuBased on the textbook on "Applied Engineering
Analysis", by Tai-Ran Hsu, published by John
Wiley & Sons, 2018 (ISBN 97811119071204)
Applied Engineering Analysis
- slides for class teaching* 1 2Chapter Learning Objectives
(p.339) perform integrations, and solve differential equations. performing integrations, and solving differential equations by the Runge-Kutta methods. solutions to the problems that are not readily or possibly solved by closed-form solution methods. solution points, and the accuracy of the solution is largely depending on the size of the increments of the variable selected for the solutions. packages such as Mathematica and MatLAB. 3 10.1Introduction
Numerical methods are techniques by which the mathematical problems involved with the engineering analysis cannot readily or possibly be solved by analytical methods such as those presented in previous chapters of this book. We will learn from this chapter on the use of some of these numerical methods that will not only enable engineers to solve many mathematical problems, but they will alsoallow engineers to minimizethe needs for the many hypotheses and idealization of the conditions, as stipulated in Section 1.4 (p.8) for engineering analysis.
This chapter will cover the principles of commonly used numerical techniques for: (1) the solution of nonlinear polynomial and transcendental equations, (2) Integration with integrals that involve complex forms of functions, and (3) the solution of differential equations by selected finite difference methods, (4) overviews of two popular commercial software packages called Mathematica andMatLAB.
4 10.2Engineering Analysis with Numerical Solutions
(p.340) There are a number of unique characteristics of numerical solution methods in engineeringanalysis. Following are just a few obvious ones:1) Numerical solutions are available only at selected (discrete) solution points, but not at all points
covered by the functions as in the case with analytical solution methods.2) Numerical methods are essentially "trail-and-error" processes. Typically, users need to
estimate an initial solution with selected increment of the variable to which the intended solution will cover. Unstable numerical solutions may result from improper selection of step sizes (the incremental steps) with solutions either in the form of "wild oscillation" or becoming unbounded in the trend of values.3) Most numerical solution methods results in errors in the solutions. There are two types of errors that
are inherent with numerical solutions:(a) Truncation errors - Because of the approximate nature of numerical solutions, they often consists
of lower order terms and higher order terms. The latter terms are often dropped in the computations for the sake of computational efficiency, resulting in error in the solution, and (b) Round-off errors -Most digital computers handle either numbers with 7 decimal points, or 14decimal points in numerical solutions. In the case of 32-bit computer with double precision (i.e. 14
decimal points length numbers), any number after the 14 th decimal point will be dropped. This may not sound like a big deal, but if a huge number of operations are involved in the computation, such error can accumulate and result in significant error in the end results. Both these errors are of accumulative natures. Consequently, errors in numerical solution may grow to be significant with solutions obtained after many step with the set increments. 5 10.3Solution of Nonlinear Equations
(p.341) We have learned the distinction between linear and nonlinear algebraic equations in Section 4.1. There are numerous occasions that engineers are requested to solve nonlinear equations such as the equation for the solution t f of the following nonlinear equation in Example 8.9 on page 270:We reported a solution of t
f =0.7 in Equation (10.2) by a "short cut" solution method, and also t f = 0.862 bya more accurate solution method such as the Newton- Raphson method described in Section 10.3.2. (10.2)
There are a number of numerical methods available to solve nonlinear equations such as in Equation (10.2);
what we will introduce here in the book are the following two methods that are readily available by using
digital computers:10.3.1
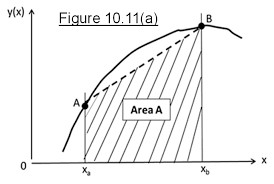
Solution using Microsoft Excel software (Example 10.1) (p.342): In this method, we will first express the equation in the form of f(x)=0 as shown in Figure 10.1. For example, we will express Equation (10.3) in Example 10.1 from the form of x 4 -2x 3 +x 2 -3x=-3 into the form: x 4 -2x 3 +x 2 -3x+3=0, in which we will get the function f(x) = x 4 -2x 3 +x 2 -3x+3.The roots "x" would lie in the range between x=x
i and x i+1 with which the values of f(x i ) and f(x i+1 ) bearing different positive or negative sign. The difference of (x i-1 ) and (x i or between x i+1 and x i is referred to be the increment of x-value, or is expressed as ǻx.Figure 10.1 Roots in Nonlinear Equation
f(x) = 0 610.3.1
Solution using Microsoft Excel software (Example 10.1) -Cont'd
Example 10.1
Solve the nonlinear polynomial Equation in (10.3): x 4 -2x 3 +x 2 -3x+3=0Solution:
We have Equation 10.3 expressed as f(x)=0 with f(x) = x 4 -2x 3 +x 2 -3x+3. We will use Microsoft Excel software to evaluate the function f(x) with an increment of the variable x, ǻx=0.5 beginning at x =0. The values of the function f(x) with x i (i = 1,2,3,....,9) are shown in the Table in the right, and the plot of function f(x) vs. variable x is depicted in Figure 10.2 ix f(x)1 0 3.00
2 0.5 1.56
31.0 0
41.5 -0.94
52.0 +1.00
6 2.5 9.56
7 3.0 30.00
8 3.5 69/06
9 4.0 135.00
We notice from the computed values of f(x) with variable x in Figure 10.2 that there are two roots of the
equation in the ranges of (x=1.0 and 1.5) and the other root in the range of (x = 1.5 and 2.0) because the
sign changes of the function f(x) cross these two ranges of x variable. The first root of x =1 is obvious
because it resulted in f(x) = 0. The search of the second root with computations of the function f(x) with
smaller increment of x between x = 1.5 and x=2.0 indicated an approximate root at x = 1.8 as illustrated in
the plot of the results in Figure 10.2.Figure 10.2
710.3.2
The Newton-Raphson Method -a popular method for solving nonlinear equations (p.342) This method offers rapid convergence to the roots of many nonlinear equations from the initial estimated roots. Figure 10.3 illustrates the principle of Newton/Raphson's method in solving nonlinear equations.The user needs to estimate a root at x = x
i for the equation f(x) = 0, from which he (she) may compute the function f(x i ) and at the same time the slope of the curve generated by the function f(x). This slope may be expressed f'(x i ), as expressed in the following equation:. 1 0)(' iii i xxxfxf (10.4) which leads to the following expression for the next estimated root at x = x i+1 to be: ii ii xfxfxx' 1 (10.5)Figure 10.3 Newton-Raphson Method
One would readily notice from Figure 10.3 that the computed approximated next root x i+1 is much closer to the real root (shown in filled circle) than the previously estimated value at x i 810.3.2
The Newton-Raphson Method-
Cont'd
Example 10.2
(p.343) Use the Newton-Raphson's method to find the roots of the following nonlinear polynomial equation: f(x) = xquotesdbs_dbs7.pdfusesText_13[PDF] numerical methods for computer science pdf
[PDF] numerical methods for engineering and science by saumyen guha pdf
[PDF] numerical methods for scientific and engineering computation 4th edition pdf
[PDF] numerical methods for solving system of nonlinear equations
[PDF] numerical methods in civil engineering book pdf
[PDF] numerical methods journal pdf
[PDF] numerical methods practical applications
[PDF] numerical methods problems and solutions pdf
[PDF] numerical solution of partial differential equations python
[PDF] numerical techniques
[PDF] numericals on indexing in dbms
[PDF] numero de cour de cassation rabat
[PDF] numéro de sécurité sociale 13 chiffres
[PDF] numéro de sécurité sociale 15 chiffres
