 Comparison of buffered and non‑buffered lidocaine: pH and pain
Comparison of buffered and non‑buffered lidocaine: pH and pain
16 Sept 2022 Stewart JH Cole GW and Klein JA: Neutralized lidocaine with epinephrine for local anesthesia. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 15: 1081‑1088
 DATA SHEET
DATA SHEET
with pH 4.0-6.5. Page 2. MARCAIN ± Adrenaline Data Generally the dose of local anaesthetic solutions containing adrenaline equals that of plain solutions.
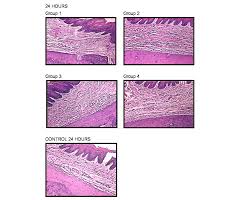 The influence of local anesthetic solutions storage on tissue
The influence of local anesthetic solutions storage on tissue
This increased inflammatory reaction could be attributed to the pH of the LAS studied. The pH of commercial LAS added with sympathomi- metic amines (epinephrine
 XYLOCAINE® 2%
XYLOCAINE® 2%
Adequate precautions should be taken to avoid prolonged contact between local anaesthetic solutions containing adrenaline (epinephrine) (low pH) and metal
 Xylocaine 1% Solution for Injection
Xylocaine 1% Solution for Injection
the local anaesthetic and the duration of exposure of the tissue to the local anaesthetic. solutions containing adrenaline (low pH) and metal surfaces (e.g. ...
 Buffered local anesthetics reduce injection pain and provide
Buffered local anesthetics reduce injection pain and provide
The pH of lidocaine (without epinephrine) in preparations used for local anesthesia varies between 3.5 and 7.0 (Cepeda et al. 2010)
 pHâ•adjustment and discomfort caused by the intradermal injection
pHâ•adjustment and discomfort caused by the intradermal injection
local anaesthesia with I % lignocaine I % lignocaine with adrenaline or the corresponding pH-adjusted solutions. The local anaesthetic solutions were.
 Stability of Adrenalin in Dental Local Anesthetics on the Different
Stability of Adrenalin in Dental Local Anesthetics on the Different
The re- sults suggest that the racemization reaction may prove to be an important route for loss of biological activity of adrenaline at pH values much below pH
 Efficacy of Sodium Bicarbonate Addition into Local Anesthetic
Efficacy of Sodium Bicarbonate Addition into Local Anesthetic
24 Oct 2022 Neutralized lidocaine with epinephrine for local anesthesia ... Randomised control trial of pH buffered lignocaine with adrenaline in outpatient ...
 Alkalinisation of local anaesthetic solutions
Alkalinisation of local anaesthetic solutions
Local anaesthetics are basic drugs which have a pKa (derived at a lower pH than the same solution without adrenaline ('plain solution').
 Comparison of buffered and non?buffered lidocaine: pH and pain
Comparison of buffered and non?buffered lidocaine: pH and pain
16 sept. 2022 Commonly used local anaesthetic (LA) solutions ... the pH of commercially available lidocaine with epinephrine. (pH 3.3?5.5) is lower than ...
 Buffered local anesthetics reduce injection pain and provide
Buffered local anesthetics reduce injection pain and provide
The pH of lidocaine (without epinephrine) in preparations used for local anesthesia varies between 3.5 and 7.0 (Cepeda et al. 2010)
 Use of Local Anesthesia for Pediatric Dental Patients
Use of Local Anesthesia for Pediatric Dental Patients
19 avr. 2007 the myocardium is sensitized to epinephrine and such ... The effect of adjusting the pH of local anesthetics in dentistry.
 Recommendations to use vasoconstrictors in dentistry and Oral
Recommendations to use vasoconstrictors in dentistry and Oral
local anaesthetic with adrenaline in the event of other with a pH of 68
 DATA SHEET
DATA SHEET
31 mai 2018 The pH of the solution is 3.3-5.0. ... of 3-5 mL short-acting local anaesthetic containing adrenaline is recommended. An.
 Effects of adrenaline and hyaluronidase on plasma concentrations
Effects of adrenaline and hyaluronidase on plasma concentrations
with adrenaline (5 ?g ml91); (III) local anaesthetic with hyaluronidase (75 iu ml91); or (IV) local (100 ?l) was added to adjust the samples to pH 11.
 JMCJMS
JMCJMS
adrenaline Sodium bicarbonate
 Local anaesthetic agent toxicity
Local anaesthetic agent toxicity
Refresher Course: Local anaesthesia agent toxicity. 2010;16(1). S Afr J Anaesthesiol Analg The clinical implication of this is that a decrease in pH.
 XYLOCAINE® 2%
XYLOCAINE® 2%
Adequate precautions should be taken to avoid prolonged contact between local anaesthetic solutions containing adrenaline (epinephrine) (low pH) and metal
 Local Anesthesia in Dentistry - SlideShare
Local Anesthesia in Dentistry - SlideShare
stability of adrenaline – the adrenaline added to some local anaesthetic solutions is unstable at the physiological pH and more stable at an acidic pH Commercially available acidic local anaesthetic solutions have a pH of typically 3 5 to 5 5 and have a shelf-life of three to four years
 Local anaesthetics in dentistry - Part 3 - SciELO
Local anaesthetics in dentistry - Part 3 - SciELO
Use of adrenaline should be deferred for patients who have suffered a cerebrovascular accident or stroke within the last six months After that time doses of adrenaline should be limited to less than 0 036 mg equivalent to two cartridges of local anaesthetic with 1:100000 adrenaline concentration 1617 HYPERTHYROIDISM
 Local anesthesia - Tishk International University
Local anesthesia - Tishk International University
Anesthesia literally means “no sensation” Derived from the Greek verb for “to perceive” Local anaesthetics (LAs) are the drugs that when applied topically or injected locally block nerve conduction and cause reversible loss of all sensation in the part supplied by the nerve
 Searches related to ph of local anesthesia with adrenaline filetype:pdf
Searches related to ph of local anesthesia with adrenaline filetype:pdf
Methodsof local anesthetic chemical formulations: (1) esters (eg procaine This revision included a new systematic literature searchbenzocaine of the tetracaine); and (2) amides (eg lidocaine- mepivaMEDLINE/Pubmed electronic database using the followingcaine prilocaine articaine)
What is the pH of local anesthetic?
- Based on tissue pH and anesthetic Pka . • Injectable local anesthetics are weak bases (pka=77.5-9.5) When a local anesthetic is injected into tissue it is neutralized and part of the ionized form is converted to non-ionized The non-ionized base is what diffuses into the nerve. 33
What is the concentration of adrenaline in local anaesthetics?
- Adrenaline can be used at concentration range from 1: 2 lakh to 1: 0.5 lakh; however, 1: 1 lakh concentration is often favoured for use. The enzyme hydrolyses ground substance (i.e. hyaluronic acid) so increases area of diffusion and hence area of effect of local anaesthetics.
Are local anaesthetics ionised at physiological pH?
- Most local anaesthetics are weak bases, with a pKa between 8 and 9, so that they are mainly but not completely ionised at physiological pH.your comments I agree with Dr Green, Dr V. Dinic and B. Smith. Tissue Acidosis (pH ~ 3-4,) caused a more ionised form, not permeable to the Cell membrane.
What is alkalinization in local anesthesia?
- BACKGROUND: Alkalinization, or buffering of local anesthesia, is a well-documented technique to mitigate low pH levels of the preparations with reports indicating clinical benefits such as decreased onset time and injection pain.
[PDF] phaeacians in the odyssey
[PDF] phagocytosed food is digested in
[PDF] phagocytosed meaning in urdu
[PDF] phagocytosed particle
[PDF] phagocytosed synonym
[PDF] pharma braille
[PDF] pharmaceutical analysis 1 pdf
[PDF] pharmaceutical application of artificial intelligence
[PDF] pharmaceutical cosmetics books pdf
[PDF] pharmacist drug information resources
[PDF] pharmacodynamie pharmacocinétique
[PDF] pharmacologie cours
[PDF] pharmacologie pdf
[PDF] pharmacologue définition simple
