 Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Tetralogy of Falot (TOF)l consists of four defects: Ventricular septal defect (VSD):An opening in the wall between the two lower chambers Pulmonary stenosis: A narrowing of the pulmonary valve and main pulmonary artery The aorta is enlarged and may sit on top of the VSD Ventricular hypertrophy: The muscular wall of the lower-right
 Tetralogy of Fallot Repair Guideline
Tetralogy of Fallot Repair Guideline
Tetralogy of Fallot Repair Guideline Common Complications Tamponade • Consider fluid bolus • Consider echocardiogram • Notify cardiologist • Notify surgeon
 Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot
1 Tetralogy of Fallot Epidemiology: Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease in all age groups,
 FallOut - CDMS
FallOut - CDMS
FallOut™ herbicide is absorbed through the foliage and roots of plants where it rapidly inhibits growth of susceptible weeds Leaves of susceptible plants appear chlorotic and the growing point subsequently dies
 Multimodality Imaging Guidelines for Patients with Repaired
Multimodality Imaging Guidelines for Patients with Repaired
a Overview of Modal-ity 120 b Strengths and Limita-tions 123 c Assessment of Repaired TOF with CMR 123 RVOT 123 PAs 123 PR 123 TV Morphology and Function 124
 Fallout Wastelands - firedennet
Fallout Wastelands - firedennet
e 5 working on Fallout: Wastelands until I reached a point where I couldn’t continue working on it without doing a complete overhaul Which is, of course, what I did I looked back through some of the more complex games my friends and I had tried and
 Creating Cultures of Trauma-Informed Care (CCTIC): A Self
Creating Cultures of Trauma-Informed Care (CCTIC): A Self
Creating Cultures of Trauma-Informed Care (CCTIC): A Self-Assessment and Planning Protocol Community Connections; Washington, D C Roger D Fallot, Ph D and Maxine
 Fallout: Leaking Data on Meltdown-resistant CPUs
Fallout: Leaking Data on Meltdown-resistant CPUs
Fallout: Leaking Data on Meltdown-resistant CPUs Claudio Canella1, Daniel Genkin2, Lukas Giner1, Daniel Gruss1, Moritz Lipp1, Marina Minkin2, Daniel Moghimi3, Frank Piessens4, Michael Schwarz1, Berk Sunar3, Jo Van Bulck4, Yuval Yarom5
[PDF] code de construction du québec gratuit
[PDF] classement des usages principaux cnb
[PDF] code national du batiment 2010 pdf download
[PDF] classification des batiments selon leur usage
[PDF] code de construction du québec 2005
[PDF] préface de batouala
[PDF] roman batouala pdf
[PDF] battement binaural gratuit
[PDF] son binaural gratuit
[PDF] ondes theta
[PDF] sons binauraux avis
[PDF] i doser
[PDF] baudelaire les fleurs du mal
[PDF] baudelaire poeme
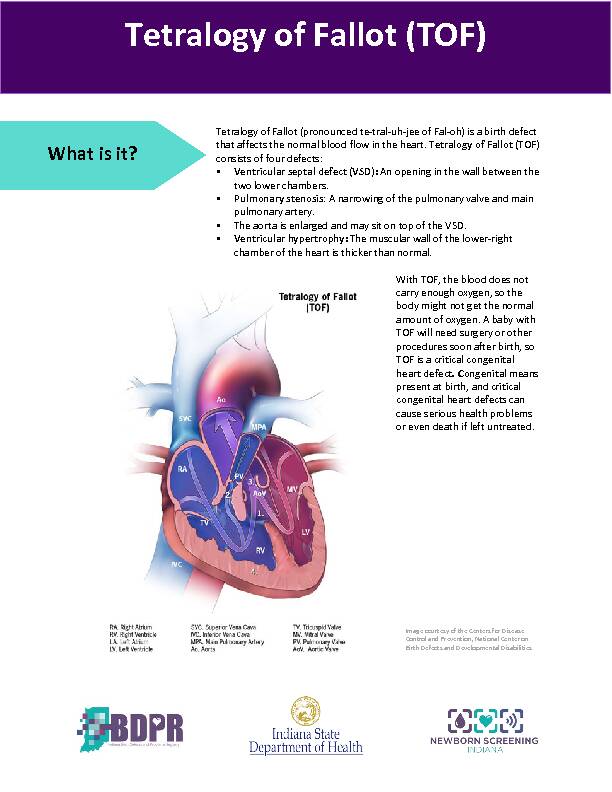 Tetralogy of Fallot (pronounced te-tral-uh-jee of Fal-oh) is a birth defect that affects the normal blood flow in the heart.
Tetralogy of Fallot (pronounced te-tral-uh-jee of Fal-oh) is a birth defect that affects the normal blood flow in the heart.