 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
itself specify the operands implicitly. It is also called as implicit addressing mode. Examples-. • The instruction “Complement Accumulator” is an implied mode
 Addressing Modes Introduction
Addressing Modes Introduction
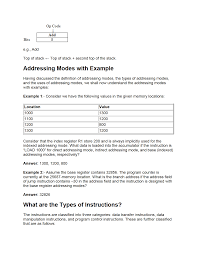
○Examples. »COM : Complement Accumulator. ▫Operand in AC is implied in the Explain different types of Addressing modes in 8085 and. 8086 micro processor.
 Addressing Modes of 8086
Addressing Modes of 8086
Thus addressing modes describe the types of operands and the way they are accessed For example the arithmetic
 Data Types and Addressing Modes 29
Data Types and Addressing Modes 29
A byte is eight bits a word is 2 bytes (16 bits)
 Addressing Modes Notes PDF
Addressing Modes Notes PDF
Implicit: The opcode itself specifies the addressing mode used. •. Explicit: The mode field is used in the instruction format to specify the type of addressing
 8085 Addressing Modes & Interrupts
8085 Addressing Modes & Interrupts
• Vector interrupt − In this type of interrupt the interrupt address is known to the processor. For example: RST7.5
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
Each of the instruction contains operations and operands. • Operation specifies the type of action to be performed. • For example: ADD SUB
 Lecture 4: Addressing modes
Lecture 4: Addressing modes
g An instruction in the MC68000 contains two types of information n The type g Example n The contents of A3 are copied onto A0. INSTRUCTION. MOVEA.L A3A0.
 8086 Addressing Modes
8086 Addressing Modes
Program Memory addressing Modes: This mode involves program memory addresses during various operations. Example: JMP AX in this instruction
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
• Available addressing modes depend on the address size used. ∗ 16-bit modes Example 3: Address and data size override mov EAX[EBX*ESI+2] ==> 66
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
itself specify the operands implicitly. It is also called as implicit addressing mode. Examples-. • The instruction “Complement Accumulator” is an implied mode
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
?Zero address instruction in stack are implied mode ?Example : LD ADR. ADR = Address part ... Explain different types of Addressing modes in 8085 and.
 Addressing Modes and Formats Computer Organization and
Addressing Modes and Formats Computer Organization and
Instruction Sets: Addressing Modes and. Formats Different types of addresses involve tradeoffs ... Example Intel direct address instructions.
 4. Addressing modes
4. Addressing modes
Efficient access to data of various sizes is so important that modern machines (32 bit machines) provide access to byte (8 bits) half-word (16 bits)
 1. Instruction Formats One address. Two address. Zero address
1. Instruction Formats One address. Two address. Zero address
2. Addressing modes with numeric examples. 3. Program control. Status bit conditions. Conditional branch instructions. 4. Program interrupts. 5. Types of
 Data Types and Addressing Modes 29
Data Types and Addressing Modes 29
The fundamental data types of the Intel Architecture are bytes words
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
two classes of comparison codes? — G L
 Addressing Modes
Addressing Modes
Examples. » Sum of 1-d array. » Sum of a column in a 2-d array. • Recursion. ? Examples Pentium offers several addressing modes to access.
 1. Addressing Modes
1. Addressing Modes
Addressing modes. Example. Instruction. Meaning. When used. Register. Add R4R3 A type of architecture that is based on a single computing unit.
 MSP430 addressing modes
MSP430 addressing modes
@Rn. Register indirect. The operand is in memory at the address held in Rn. 11. -. s n ? 0 2
 Addressing Modes - Carleton University
Addressing Modes - Carleton University
• Addressing modes • Simple addressing modes ? Register addressing mode ? Immediate addressing mode • Memory addressing modes ? 16-bit and 32-bit addressing » Operand and address size override prefixes ? Direct addressing ? Indirect addressing ? Based addressing ? Indexed addressing ? Based-indexed addressing • Examples
 Addressing Modes: Definition Types & Examples - Studycom
Addressing Modes: Definition Types & Examples - Studycom
The most used addressing modes are presented below; a left arrow meansassignment and M stands for memory We use an array notation formemory because we can view the memory as an array of bytes (or half-words or words whichever you prefer but the signi?cance of the notationmust be very clear) Register
 Addressing Modes Introduction
Addressing Modes Introduction
Application of Addressing Modes The 8085 has the following 5 different types of addressing 1 Immediate Addressing 2 Direct Addressing 3 Register Addressing 4 Register Indirect Addressing 5 Implied Addressing
 Searches related to types of addressing modes with examples pdf PDF
Searches related to types of addressing modes with examples pdf PDF
addressing modes Assembly Language Addressing Modes • Memory is accessed by calculating its effective address using the distance (or offset) of the data from the beginning of a segment (usually the data segment) • Memory Addressing modes: Direct Register Indirect Based or Indexed Base-indexed Base-indexed with displacement
Immediate
With immediate addressingmode, the actual data to be used as the operand is included in the instruction itself. Let's say we want to store operand 1 into a register and then add operand 2. With immediate addressing mode, the data values 1 and 2 would be part of the instruction itself as shown below. This would be a relatively fast option since ther...
Direct Addressing
When using direct addressing mode, the address of the operand is specified in the instruction. The processor will retrieve the data directly from the address specified in the instruction. In this figure, the example shows how the instruction tells the processor where to get the data from in memory. The variable addr_of_2is a pointer to the effectiv...
What are the different types of addressing modes?
Let's take a look at the different types of addressing modes, one at a time now. 1. Immediate With immediate addressing mode, the actual data to be used as the operand is included in the instruction itself. Let's say we want to store operand 1 into a register and then add operand 2.
What is direct addressing mode?
Direct Addressing Mode- The address field of the instruction contains the effective address of the operand. Only one reference to memory is required to fetch the operand. It is also called as absolute addressing mode. ADD X will increment the value stored in the accumulator by the value stored at memory location X. 5. Indirect Addressing Mode-
What is register addressing mode?
Register addressing mode indicates the operand data is stored in the register itself, so the instruction contains the address of the register. The data would be retrieved from the register. Here's how this would work: Figure 3. Register Retrieving data from the register is fast and the instructions are shorter because no memory is involved.
What is memory addressing mode?
The addressing mode specifies a rule for interpreting or modifying the address field of the instruction before the operand is actually executed. The 8086 memory addressing modes provide flexible access to memory, allowing you to easily access variables, arrays, records, pointers, and other complex data types.