 Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Aromatic carboxylic acids (i.e. with a CO2H directly connected to a benzene ring) are named after the parent compound
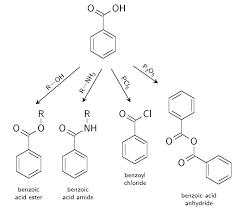 UNIT- II: Aromatic Acids - Acidity effect of substituents on acidity and
UNIT- II: Aromatic Acids - Acidity effect of substituents on acidity and
➢ Why Benzoic acid will not undergo Friedel-Craft Reaction? - Because -COOH group present in aromatic carboxylic acids is an electron withdrawing group causing.
 Identification of Organic Compound by Organic Qualitative Analysis
Identification of Organic Compound by Organic Qualitative Analysis
vii) Colourless. Simple acid alcohol
 Reduction of Carboxylic Acids by Nocardia Aldehyde
Reduction of Carboxylic Acids by Nocardia Aldehyde
including many aromatic carboxylic acids as well as a very wide range of 2 The abbreviations used are: Car carboxylic acid reductase; PPTases
 AMINO ACIDS CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES
AMINO ACIDS CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES
Monoamino-dicarboxyli amino acid: Aspartic and glutamic acid. Page 23. • Diamino-monocarboxylic amino acids: Lysine arginine
 Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/index_2353/Chapter_03_2SPP.pdf
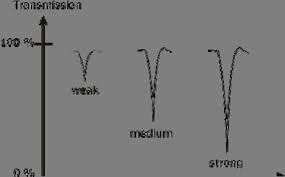 INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
A carboxylic acid functional group combines the features of alcohols and ketones because it has both the O-H bond and the C=O bond. Therefore carboxylic acids.
 testsforfunctionalgroups - inorganiccompounds
testsforfunctionalgroups - inorganiccompounds
Organic compounds containing carboxyl functional groups are called carboxylic acids. sodium carbonate solution to neutralise excess sulphuric acid and excess ...
 Expanding the realm of bioderived chemicals using biogenic
Expanding the realm of bioderived chemicals using biogenic
carboxylic acids by carboxylic acid reductase (CAR) or a fungal nonribosomal peptide (DSD) from Podospora pauciseta aromatic carboxylic acid reductase (ACAR) ...
 ORGANIC CH B. Sc. II YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY HEMISTRY-II
ORGANIC CH B. Sc. II YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY HEMISTRY-II
acrylic acid propenoic acid. IUPAC nomenclature of aromatic carboxylic acids: Aromatic carboxylic acids are named by adding the suffix "-carboxylic acid" to
 CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Acidity of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids: Inductive Effect. 25. When an aromatic carboxylic acid has a substituent that does not have lone pairs of electrons or
 Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Esters may be broken apart under acidic conditions by water (a hydrolysis reaction) to form a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. • This is essentially the reverse
 UNIT- II: Aromatic Acids - Acidity effect of substituents on acidity and
UNIT- II: Aromatic Acids - Acidity effect of substituents on acidity and
There are several categories of aromatic acids including: (i) Phenolic acids: substances containing an aromatic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function
 Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes
to which carboxyl carbon is attached. The presence of electron withdrawing group on the phenyl of aromatic carboxylic acid increases their acidity while
 Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
From alkylbenzenes. Aromatic carboxylic acids can be prepared by vigorous oxidation of alkyl benzenes with chromic acid or acidic or alkaline potassium.
 Identification of Organic Compound by Organic Qualitative Analysis
Identification of Organic Compound by Organic Qualitative Analysis
Aromatic acid amide
 ORGANIC CH B. Sc. II YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY HEMISTRY-II
ORGANIC CH B. Sc. II YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY HEMISTRY-II
study physical and chemical properties of phenols their acidic characters. attached to benzene ring are not phenols but are called aromatic alcohols.
 AMINO ACIDS CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES
AMINO ACIDS CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES
The major key elements if amino acids are carbon Number of amino and carboxylic groups ... hydrophobic
 Structure and functions of Amino Acids and Proteins
Structure and functions of Amino Acids and Proteins
09-May-2019 •They have a primary amino group and a carboxylic acid group substituent on the ... as: Aliphatic aromatic
 14: Substituent Effects
14: Substituent Effects
Chapter 14. 14: Substituent Effects. Substituents and Their Effects. Carboxylic Acid Acidity. SN1 Reactions. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions.