 Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Aromatic carboxylic acids (i.e. with a CO2H directly connected to a benzene ring) are named after the parent compound
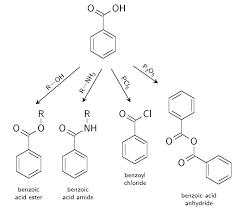 UNIT- II: Aromatic Acids - Acidity effect of substituents on acidity and
UNIT- II: Aromatic Acids - Acidity effect of substituents on acidity and
➢ Why Benzoic acid will not undergo Friedel-Craft Reaction? - Because -COOH group present in aromatic carboxylic acids is an electron withdrawing group causing.
 Identification of Organic Compound by Organic Qualitative Analysis
Identification of Organic Compound by Organic Qualitative Analysis
vii) Colourless. Simple acid alcohol
 Reduction of Carboxylic Acids by Nocardia Aldehyde
Reduction of Carboxylic Acids by Nocardia Aldehyde
including many aromatic carboxylic acids as well as a very wide range of 2 The abbreviations used are: Car carboxylic acid reductase; PPTases
 AMINO ACIDS CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES
AMINO ACIDS CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES
Monoamino-dicarboxyli amino acid: Aspartic and glutamic acid. Page 23. • Diamino-monocarboxylic amino acids: Lysine arginine
 Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
Chapter 3 Alcohols Phenols
https://www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudrea/index_2353/Chapter_03_2SPP.pdf
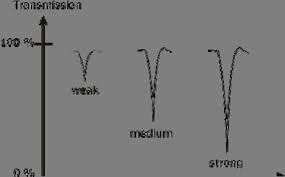 INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
A carboxylic acid functional group combines the features of alcohols and ketones because it has both the O-H bond and the C=O bond. Therefore carboxylic acids.
 testsforfunctionalgroups - inorganiccompounds
testsforfunctionalgroups - inorganiccompounds
Organic compounds containing carboxyl functional groups are called carboxylic acids. sodium carbonate solution to neutralise excess sulphuric acid and excess ...
 Expanding the realm of bioderived chemicals using biogenic
Expanding the realm of bioderived chemicals using biogenic
carboxylic acids by carboxylic acid reductase (CAR) or a fungal nonribosomal peptide (DSD) from Podospora pauciseta aromatic carboxylic acid reductase (ACAR) ...
 ORGANIC CH B. Sc. II YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY HEMISTRY-II
ORGANIC CH B. Sc. II YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY HEMISTRY-II
acrylic acid propenoic acid. IUPAC nomenclature of aromatic carboxylic acids: Aromatic carboxylic acids are named by adding the suffix "-carboxylic acid" to
 CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Acidity of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids: Inductive Effect. 25. When an aromatic carboxylic acid has a substituent that does not have lone pairs of electrons or
 Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters
Esters may be broken apart under acidic conditions by water (a hydrolysis reaction) to form a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. • This is essentially the reverse
 UNIT- II: Aromatic Acids - Acidity effect of substituents on acidity and
UNIT- II: Aromatic Acids - Acidity effect of substituents on acidity and
There are several categories of aromatic acids including: (i) Phenolic acids: substances containing an aromatic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function
 Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Aldehydes
to which carboxyl carbon is attached. The presence of electron withdrawing group on the phenyl of aromatic carboxylic acid increases their acidity while
 Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Carboxylic Acids
From alkylbenzenes. Aromatic carboxylic acids can be prepared by vigorous oxidation of alkyl benzenes with chromic acid or acidic or alkaline potassium.
 Identification of Organic Compound by Organic Qualitative Analysis
Identification of Organic Compound by Organic Qualitative Analysis
Aromatic acid amide
 ORGANIC CH B. Sc. II YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY HEMISTRY-II
ORGANIC CH B. Sc. II YEAR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY HEMISTRY-II
study physical and chemical properties of phenols their acidic characters. attached to benzene ring are not phenols but are called aromatic alcohols.
 AMINO ACIDS CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES
AMINO ACIDS CLASSIFICATION AND PROPERTIES
The major key elements if amino acids are carbon Number of amino and carboxylic groups ... hydrophobic
 Structure and functions of Amino Acids and Proteins
Structure and functions of Amino Acids and Proteins
09-May-2019 •They have a primary amino group and a carboxylic acid group substituent on the ... as: Aliphatic aromatic
 14: Substituent Effects
14: Substituent Effects
Chapter 14. 14: Substituent Effects. Substituents and Their Effects. Carboxylic Acid Acidity. SN1 Reactions. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Reactions.

CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Carboxylic Acids
Introduction
attachedtothecarbonyl(C=O)group.Natural Carboxylic Acids
milkgenerallyhavesharpflavours.Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids
thecarboxylicacid.Structure of AcidNaturalSource Common
NameAnts (Formica)Formic acid
Vinegar (Acetum)Acetic acid
BasicFat (Propio)Propionicacid
Rancid butter (Butyrum)Butyric acid
Presentin aValerianherbValericacid
Goat (Caper)Caproicacid
HCOHOCH3COH
CH3CH2COH
CH3CH2CH2COH
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2COH
Common Names of Carboxylic Acids
lengthofthecarboxylicacid. # of CarbonsPrefixCommon Name of Acid1Form-Formic acid
2Acet-Acetic acid
3Propion-Propionicacid
4Butyr-Butyric acid
5Valer-Valeric acid
6Capro-Caproicacid
Aromatic acidBenzo-Benzoic acid
IUPAC Nomenclature of Aliphatic Carboxylic
Acids # of CarbonsStructure & IUPACName ofAlkane
Structure & IUPAC
Name of Acid
MethaneMethanoicacid
EthaneEthanoicacid
PropanePropanoicacid
HCH HCOHOCH3CH3CH3COH
CH3CH2CH3CH3CH2COH
Systematic Nomenclature of Substituted
Carboxylic Acids
arederivedby: all,thecarboxylgroups. groupi.ethecarboxylcarbonisC-1. numberingintheparentchain. acid.Systematic Nomenclature of Substituted
Carboxylic Acids
Example
usingthesamesequence.Systematic Nomenclature of Cyclic
Carboxylic Acids
cycloalkeneorarene. takentobeattachedtoC-1ofthering. CO2HCyclohexanecarboxylic acid
CHOCyclohexanecarbaldehyde
Na2Cr2O7
H2SO4Systematic Nomenclature of Substituted
Cyclic Carboxylic Acids
toC-1ofthering. namedasbenzenecarboxylicacid.IUPAC Nomenclature of Substituted
Aromatic Carboxylic Acids
Systematic Nomenclature of Dicarboxylic
Acids parenthydrocarboni.e.alkanedioicacid.Systematic NameCommonNameStructure
EthanedioicacidOxalic acidHO2C-CO2H
PropanedioicacidMalonicacidHO2CCH2CO2H
HexanedioicacidAdipicacidHO2C(CH2)4CO2H
Systematic Nomenclature of Substituted
DicarboxylicAcids
by: thenameoftheparenthydrocarbon. nameofthedicarboxylicacid.Systematic Nomenclature of Cyclic
DicarboxylicAcids
isomers.Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids
hydrogenion(proton).Substituent Effects on the Acidity of
Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids
acidityofthecarboxylicacid.ALKYL GROUPS:EFFECTS OF ELECTRON-DONATING GROUPS
Name of AcidStructurepKaEffect
MethanoicacidHCO2H3.8
EthanoicacidCH3CO2H4.7Weakeningacidity
PropanoicacidCH3CH2CO2H4.9Negligible effect
HeptanoicacidCH3(CH2)5CO2H4.9
Substituent Effects on the Acidity of
Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids
ELECTRON WITHDRAWING GROUPS
Name of AcidStructurepKaEffect
EthanoicacidCH3CO2H4.7
MethoxyethanoicacidCH3OCH2CO2H3.6
acidityCyanoethanoicacidNC-CH2CO2H 2.5NitroethanoicacidO2N-CH2CO2H 1.7
withdrawinggroups.Substituent Effects on the Acidity of
Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids
carboxylateanion. -HALOGENS: EFFECT OF ELECTRONEGATIVITY ON ACIDITYName of AcidStructurepKaEffect
EthanoicacidCH3CO2H4.7
aciditywithincreasing electronegativityChloroethanoicacidClCH2CO2H2.9
BromoethanoicacidBrCH2CO2H 2.9
Substituent Effects on the Acidity of
Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids
anionandthehighertheiracidities.CUMMULATIVE EFFECT OF SUBSTITUENTS ON ACIDITY
Name of AcidStructurepKaEffect
additiveDichloroethanoicacidCl2CHCO2H1.3TrichloroethanoicacidCl3CCO2H 0.9
Substituent Effects on the Acidity of
Aliphatic Carboxylic Acids
(numberof-bonds).EFFECT OF BOND DISTANCE ON ACIDITY
Name of AcidStructurepKaEffect
effectduetothe inductiveeffect decreases rapidlywith distance.3-Chloropropanoic acidClCH2CH2CO2H4.0
4-Chlorobutanoic acidClCH2CH2CH2CO2H4.5
Acidity of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids
throughʌbonds.Acidity of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids:
Inductive Effect
invokedinexplainingitsdegreeofacidity.Acidity of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids:
Inductive Effect
unsubstitutedbenzoicacid. derivatives.Acidity of Aromatic Carboxylic Acids: the
Resonance Effect
thanbenzoicacid. acids.Resonance Structures of Isomeric
Nitrobenzoates
m-Nitrobenzoic acid p-Nitrobenzoic acid Resonance Structures of carboxylate anions derived from ionization of isomeric nitrobenzoic acidsOOOOOO
OOOOOOOO
OOOO OOOO o-Nitrobenzoic acid COOOO OCOO OCOOHighly stabilizing
Highly stabilizing
Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids
Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Carboxylic Acids
RCH2OHOxidizing AgentRCO2H
syntheticallyinefficient.Synthesis of Carboxylic Acids
Oxidation of Primary Alcohols to Carboxylic Acids
potassiumpermanganate.quotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_4[PDF] acidity of carboxylic acid and alcohol
[PDF] acidity of carboxylic acid and phenol
[PDF] acidity of carboxylic acid slideshare
[PDF] acidity of carboxylic acids and derivatives
[PDF] acidity of carboxylic acids with halogens
[PDF] acidity of drinking water
[PDF] acidity of phenol
[PDF] acidity of water
[PDF] acidity order of carboxylic acid derivatives
[PDF] acip certification
[PDF] acknowledgement for seminar report in engineering pdf
[PDF] acls and bls course in symbiosis 2020
[PDF] acls apply
[PDF] acls fellowship application
