 AUXINT-INDUCED WATER UPTAKE BY AVENA COLEOPTILE
AUXINT-INDUCED WATER UPTAKE BY AVENA COLEOPTILE
This is apparently small and not detectable by the present methods of meas- urement. When sections are placed in hypertonic solution their cells are rapidly
 Effects of Hypertonic Solution on Action Potential and Input
Effects of Hypertonic Solution on Action Potential and Input
19 Jun 1982 Exposing the muscle cell to hypertonic solution may induce cell dehydration and hence changes in the ion concentrations of myoplasm ...
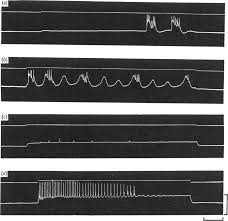 On the nature of the oscillations of the membrane potential (slow
On the nature of the oscillations of the membrane potential (slow
agents indicating that muscarinic stimulants produced their effects by acting directly on the smooth muscle cell. 5. In hypertonic solution slow waves occurred
 Cell volume variation under different concentrations of saline
Cell volume variation under different concentrations of saline
of hemoglobin from red cells it is then reasonable to assume that this level of hypertonic NaCl solutions could provoke cellular damage. Keeping in mind
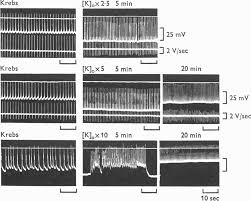 3. When the muscles were perfused with hypertonic solution
3. When the muscles were perfused with hypertonic solution
properties. They concluded that the smooth muscle cells of the portal vein could be classified as visceral smooth muscle from the electrical properties.
 Effect of Osmosis on Gummy Bears in Salt Solutions
Effect of Osmosis on Gummy Bears in Salt Solutions
In comparison to the cell's (or item's) concentration a solution can be isotonic
 III. Alterations of cell volume in extremely hypotonic the cells
III. Alterations of cell volume in extremely hypotonic the cells
volume changes in hypotonic solutions is closely related to the study of. "osmotic" hwemolysis. The methods available for the measurement of red cell volume in.
 On the nature of the oscillations of the membrane potential (slow
On the nature of the oscillations of the membrane potential (slow
Hypertonic solution. In hypertonic solution the membrane potential was All records from the same cell in hypertonic solution 35° C. Records (a) and (b) ...
 Impairment of Red Cell Transit through the Canine Lungs following
Impairment of Red Cell Transit through the Canine Lungs following
ABSTRACT. Rapid injections of hypertonic sucrose sodium chloride
 Influence of Ripening and Turgor on the Tensile Properties of Pears
Influence of Ripening and Turgor on the Tensile Properties of Pears
concentrated than the cell sap (hypertonic solutions). When similar tissue osmotic solution. The slices were vacuum infiltrated and incu- bated in the ...
 BIOL 347L Laboratory Three
BIOL 347L Laboratory Three
A Hypertonic solution has more solute (so LESS water) than the cell. A cell placed in this solution will give up water (osmosis) and shrink. A Hypotonic
 Effects of Hypertonic Solution on Action Potential and Input
Effects of Hypertonic Solution on Action Potential and Input
19-Jun-1982 to be directly related to the development of cell dehydration. The hypertonic solutions produced a slight increase in the resting potential.
 3. When the muscles were perfused with hypertonic solution
3. When the muscles were perfused with hypertonic solution
properties. They concluded that the smooth muscle cells of the portal vein could be classified as visceral smooth muscle from the electrical properties.
 On the nature of the oscillations of the membrane potential (slow
On the nature of the oscillations of the membrane potential (slow
agents indicating that muscarinic stimulants produced their effects by acting directly on the smooth muscle cell. 5. In hypertonic solution slow waves
 Introduction Fixation is an attempt at stabilizing biological systems
Introduction Fixation is an attempt at stabilizing biological systems
Tonicity. A solution is said to be isotonic with a cell if the cell neither swells nor shrinks when immersed in it. Hypertonic solutions cause shrinkage
 Ovid: Rebound Swelling of Astroglial Cells Exposed to Hypertonic
Ovid: Rebound Swelling of Astroglial Cells Exposed to Hypertonic
hypertonic solutions containing radiolabeled mannitol and its cellular uptake was determined. Results: Hypertonic mannitol exposure produced initial cell
 SICKLING PHENOMENON PRODUCED BY HYPERTONIC
SICKLING PHENOMENON PRODUCED BY HYPERTONIC
crose and uirea. The sickling phenomenon was also elicited in patients with sickle-cell anemia by hypertonic solutions of mannitol and sucrose.
 osmosis-in-onion-cells.pdf
osmosis-in-onion-cells.pdf
When discussing the way solutions separate by selective permeability the terms isotonic
 Untitled
Untitled
Water will flow into the cell causing it to swell or burst. Period: Biology. Osmosis. Isotonic. Solution. X. Date: Hypotonic Hypertonic. Solution Solution.
 Electrophysiological effects of osmotic cell shrinkage in rat
Electrophysiological effects of osmotic cell shrinkage in rat
06-May-2010 Insulin release was measured using intact islets by radioimmunoassay. exposure to a 33% hypertonic bath solution resulted in an initial ...
 Cell Diffusion & Permeability Lab - Stanford University
Cell Diffusion & Permeability Lab - Stanford University
Key Concepts: The prefix hyper- refers to “high” as in hypertension (high blood pressure) A hypertonic solution has a higher amount of solute (the solid that is being dissolved) and a lower amount of solvent (the liquid that is dissolving the solute)
 What happens to RBC in hypertonic solution? – Sage-Advices
What happens to RBC in hypertonic solution? – Sage-Advices
Hypertonic Solution Hypertonic: The solution has a higher concentration of solutes and a lower concentration of water than inside the cell (High solute; Low water)? Result: Water moves from inside the cell into the solution: Cell shrinks (Plasmolysis)! • Osmosis Animations for isotonic hypertonic and hypotonic solutions shrinks
 Lab 3: Osmosis and Diffusion - Montana State University Billings
Lab 3: Osmosis and Diffusion - Montana State University Billings
membrane a hypotonic solution will cause a cell to swell from the osmotic uptake of water Conversely if a cell is placed in a solution with a high particle (low water) concentration relative to the cell that cell will lose water The latter cell is in a hypertonic solution defined as a solution that will make a cell shrink because of the
 306 Isotonic Hypotonic & Hypertonic Notes
306 Isotonic Hypotonic & Hypertonic Notes
Hypotonic solutions are used when the cell is dehydrated and fluids need to be put back intracellularly This happens when patients develop diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemia Important: Watch out for depleting the circulatory system of fluid since you are trying to push extracellular fluid into the cell to re-hydrate it
 Searches related to hypertonic solution cell filetype:pdf
Searches related to hypertonic solution cell filetype:pdf
Cells hypertonic to their surrounding solutions cause water to move into the cell and cause it to expand The cell has a higher number of particles (solutes) dissolved in it than the solution outside of the cell membrane This causes turgor pressure in plants that make the plants rigid for support
What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution?
- Hypertonic solutions cause cells to shrivel and shrink in size, which can cause problems and inhibit proper cell functioning. When solutions surrounding cells are hypertonic, this will cause the organism to become dehydrated, which can lead to problems such as organ failure. How does tonicity affect cells?
What is the difference between a hypertonic solution and a hypotonic solution?
- A hypertonic solution has high osmotic pressure, whereas a hypotonic solution has low osmotic pressure. The concentration of solute is more in hypertonic solution than the hypotonic fluid. The concentration of solvent is low in hypertonic and high in hypotonic. Is hemolysis good or bad?
What are some common hypertonic solutions?
- Common examples of hypertonic solutions are D5 in 0.9% normal saline and D5 in lactated ringers. The administration of hypertonic solutions should be monitored extremely closely, as they can quickly lead to fluid overload. Can blood cells burst? Red blood cell lysis is more commonly known as hemolysis, or sometimes haemolysis.
What are the effects of a hypertonic solution on plant cells?
- Hypertonic solutions make plant cells lose water. Hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration. When plant cells are placed in such solutions, water will move from inside the plant cell to the outside of the cell, resulting in the shrinking of the cell (the cell is said to be plasmolyzed). This occurs because of osmosis.