- 2.
Sophie Caused World War I and II.
Summary: Archduke Franz Ferdinand's decision to take his bored wife Sophie on an official trip to Bosnia led to their assassination, which caused WWI.
If he'd chosen not to appease his wife and take the trip, things might have been very different How was the butterfly effect proven?
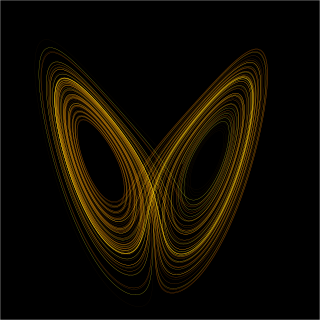
Lorenz originally used a seagull causing a storm but was pers귭 to make it more poetic with the use of a butterfly and tornado by 1972.
He discovered the effect when he observed runs of his weather model with initial condition data that were rounded in a seemingly inconsequential manner..
Is the butterfly effect part of psychology?
The butterfly effect started in meteorology, but you can see it at play in many areas of life and work, such as psychology, economics, politics, and more..
What is an example of the butterfly effect chaos theory?
It is a tenet of chaos theory that, in dynamical systems, the outcome of any process is sensitive to its starting point—or in the famous cliché, the flap of a butterfly's wings in the Amazon can cause a tornado in Texas..
What is the butterfly effect complexity theory?
The butterfly effect rests on the notion that the world is deeply interconnected, such that one small occurrence can influence a much larger complex system.
The effect is named after an allegory for chaos theory; it evokes the idea that a small butterfly flapping its wings could, hypothetically, cause a typhoon..
What is the butterfly effect mechanism?
The famous butterfly effect, which exemplifies chaos theory, is made possible by the exponential divergence of two paths or trajectories evolving under identical equations of motion from slightly different initial conditions and is a hallmark of nonlinear dynamics in classical mechanics..
What is the butterfly effect strategy?
This is known as the butterfly effect.
It is the idea that small and seemingly insignificant actions, such as a butterfly flapping its wing, can evolve into much greater events.
It is part of chaos theory, which states that events are interconnected in ways that are difficult to predict..
What is the butterfly effect time theory?
By implication, if you could go back and alter the past even slightly, a different future would evolve within the system.
The future containing your present would vanish.
The butterfly effect is well accepted in our everyday world, where classical physics describes systems above the atomic scale..
Where did the butterfly effect theory come from?
The term "butterfly effect" was coined by meteorologist Edward Lorenz, who discovered in the 1960's that tiny, butterfly—scale changes to the starting point of his computer weather models resulted in anything from sunny skies to violent storms—with no way to predict in advance what the outcome might be..
Where is the butterfly effect?
The butterfly effect is the idea that small things can have non-linear impacts on a complex system.
The concept is imagined with a butterfly flapping its wings and causing a typhoon.
Of course, a single act like the butterfly flapping its wings cannot cause a typhoon..
Which theory is connected to the butterfly effect?
Chaos Theory: The butterfly effect is part of chaos theory, which states that there are limitations to predictions even in small discrete systems.
Chaos is possible because systems are extremely sensitive to initial conditions..
Why do we sometimes call this concept the butterfly effect?
The idea came to be known as the “butterfly effect” after Lorenz suggested that the flap of a butterfly's wings might ultimately cause a tornado.
And the butterfly effect, also known as “sensitive dependence on initial conditions,” has a profound corollary: forecasting the future can be nearly impossible.Feb 22, 2011.
Why is the butterfly effect important?
The two pertinent things that the butterfly effect teaches us is that small things matter, and we are all connected to a bigger system.
Our action now, today, would have been the result of a previous action and this could in turn, lead to a future action..
- The Butterfly Effect suggests that small initial changes in complex, dynamic systems can result in significantly different and often unpredictable outcomes over time.
- The famous butterfly effect, which exemplifies chaos theory, is made possible by the exponential divergence of two paths or trajectories evolving under identical equations of motion from slightly different initial conditions and is a hallmark of nonlinear dynamics in classical mechanics.
- The unexpected result led Lorenz to a powerful insight about the way nature works: small changes can have large consequences.
The idea came to be known as the “butterfly effect” after Lorenz suggested that the flap of a butterfly's wings might ultimately cause a tornado.