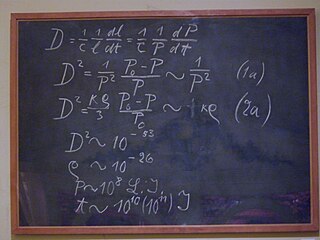Categories
Sigma eight cosmology
Cosmology field of study
Cosmology fields
Cosmology fine tuning
Cosmology first use
Cosmology filament
Cosmology first cause
Fiducial cosmology
Cosmological fine-tuning argument
Filipino cosmology
Finnish cosmology
Firmament cosmology
Cosmological field equation
Cosmology gifts
Cosmology giants
Cosmology girl meaning in hindi
Class cosmology github
Cosmology history timeline
Cosmology history definition
Cosmology hindi mai