How do you identify a granuloma?
Your doctor or specialist will take a medical history and examine you if they suspect you have granulomas.
They may ask for tests such as a blood test, x-rays or CT scans, genetic tests or a needle biopsy.
With skin granulomas, your doctor may only need to do a physical examination to confirm a diagnosis..
What are the 5 types of granuloma?
Six types of granulomatous skin lesions are identified according to cellular constituents and associated changes: 1) tuberculoid, 2) sarcoidal, 3) necrobiotic, 4) suppurative 5) foreign body and 6) histoid type granuloma (3,4)..
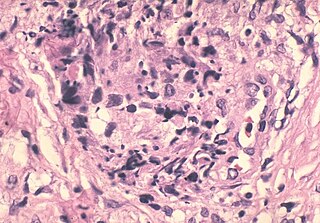
What is a granuloma histology?
A granuloma is a focal aggregate of immune cells that forms in response to a persistent inflammatory stimulus.
It characteristically demonstrates the compact organization of mature macrophages, which may or may not be associated with other inflammatory cell types..
What is a granuloma?
A granuloma is a tiny cluster of white blood cells and other tissue.
It can be found in the lungs, skin or other parts of the body.
They form as a reaction to infections, inflammation, irritants or foreign objects.
Granulomas aren't cancerous..
What is the histologic appearance of granuloma?
Histologic subtypes.
Granulomatous inflammation is commonly characterized by the formation of distinct granulomas composed of aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes, with a peripheral cuff of lymphocytes and plasma cells, and occasionally a necrotic center (Fig. 1)..
What is the process of granuloma?
Granuloma formation begins with an inflammatory trigger, such as an infectious pathogen or a foreign body.
Macrophages are recruited to the site of inflammation and activated as part of the innate immune response..
What type of cell is a granuloma?
Granulomas are a tight collection of macrophages, often surrounded by helper T-cells.
Most granulomas fall into one of two categories: caseating, with a necrotic center, or non-caseating, without any necrosis..
The following are important examples of conditions associated with granuloma formation.
Tuberculosis. Sarcoidosis. Crohn Disease. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis.- Conclusion: A significant number of cases of FNAC diagnosed granulomatous lymphadenitis have an identifiable underlying cause.
Patients with reactive cytological changes, who clinically appear benign, can avoid unnecessary surgery. - Granulomas in cytological specimens from sarcoidosis patients are quite small [median (IQR) largest diameter: 0.478 (0.318–0.701) mm] and appear as well-defined, tiny nodules somehow 'popping out' of the slide, and they are easily appreciated even at low power ( fig.Dec 29, 2012