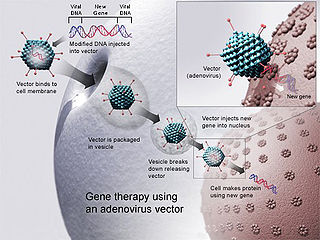
Ethics and genetics research topics
Ethical Issues regarding the Environment: The release of GMOs into the environment has the potential to cause ecological damage.
For example, a common fear is that genetically modified crops may cross-breed with any wild relatives, resulting in the spread of modified genes and the creation of invasive species..
Genetically engineered animals examples
The ethical questions surrounding gene therapy and genome editing include:
How can “good” and “bad” uses of these technologies be distinguished?Who decides which traits are normal and which constitute a disability or disorder?Will the high costs of gene therapy make it available only to the wealthy?.Genetically engineered animals examples
Bioethics examines the ethical and philosophical issues surrounding biological and medical research, technologies, and treatments.
These issues include informed consent, patient safety, conflicts of interest, and the broader social and political consequences of biotechnologies..
Genetically modified animals list
00:00.
Genetic engineering (also called genetic modification) is a process that uses laboratory-based technologies to alter the DNA makeup of an organism.
This may involve changing a single base pair (A-T or C-G), deleting a region of DNA or adding a new segment of DNA..
GMO animals examples
From a rights perspective, based on the right not to be harmed, the answer would also be yes.
But from the perspective of a virtue ethics that promotes respect for species' integrity and regards inter-species gene splicing as genetic pollution and contamination of germ-lines, the answer is no..
How ethical is genetic engineering?
There are a lot of different opinions out there about whether genetic engineering is ethical or not.
Some people believe that it is a helpful tool that can be used to improve the lives of people who have genetic disorders.
Others believe that it is morally wrong to “play with God” and change a person's DNA..
How is genetic engineering an ethical issue?
For instance, there is a chance that genetic alterations could have unintended consequences or that parents may not be able to control which traits their child inherits.
Some people believe that designer babies are morally wrong because they involve manipulating the genes of a human embryo..
How is genetic engineering an ethical issue?
For instance, there is a chance that genetic alterations could have unintended consequences or that parents may not be able to control which traits their child inherits.
Some people believe that designer babies are morally wrong because they involve manipulating the genes of a human embryo.Dec 10, 2022.
Is genetic engineering ethically right?
From a rights perspective, based on the right not to be harmed, the answer would also be yes.
But from the perspective of a virtue ethics that promotes respect for species' integrity and regards inter-species gene splicing as genetic pollution and contamination of germ-lines, the answer is no..
What are the ethical issues with genetic engineering?
For instance, there is a chance that genetic alterations could have unintended consequences or that parents may not be able to control which traits their child inherits.
Some people believe that designer babies are morally wrong because they involve manipulating the genes of a human embryo.Dec 10, 2022.
What are two bioethical concerns for genetic engineering?
The ethical questions surrounding gene therapy and genome editing include:
How can “good” and “bad” uses of these technologies be distinguished?Who decides which traits are normal and which constitute a disability or disorder?Will the high costs of gene therapy make it available only to the wealthy?.What are two bioethical concerns for genetic engineering?
Genetic engineering also brings with it concerns over intellectual property, and patenting of created animals and/or the techniques used to create them.
Preserving intellectual property can breed a culture of confidentiality within the scientific community, which in turn limits data and animal sharing..
What are two bioethical concerns for genetic engineering?
There are a lot of different opinions out there about whether genetic engineering is ethical or not.
Some people believe that it is a helpful tool that can be used to improve the lives of people who have genetic disorders.
Others believe that it is morally wrong to “play with God” and change a person's DNA.Dec 10, 2022.
What is bio genetic engineering?
00:00.
Genetic engineering (also called genetic modification) is a process that uses laboratory-based technologies to alter the DNA makeup of an organism.
This may involve changing a single base pair (A-T or C-G), deleting a region of DNA or adding a new segment of DNA..
What is the ethical issues of genetic engineering?
For instance, there is a chance that genetic alterations could have unintended consequences or that parents may not be able to control which traits their child inherits.
Some people believe that designer babies are morally wrong because they involve manipulating the genes of a human embryo.Dec 10, 2022.
What is the ethics of genetic engineering?
Ethical Issues Associated with GMOs
It is a common fear that genetic modification may result in unintended consequences, such as the creation of new allergens or toxins, the spread of modified genes to wild relatives, or the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria..
When did genetic engineering become a thing?
1973: Biochemists Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen develop genetic engineering by inserting DNA from one bacteria into another. 1982: FDA approves the first consumer GMO product developed through genetic engineering: human insulin to treat diabetes..
Where can we find genetic engineering?
Used in research and industry, genetic engineering has been applied to the production of cancer therapies, brewing yeasts, genetically modified plants and livestock, and more..
Why is bioethics important in biotechnology?
Because biotech innovations may eventually involve germ-line manipulation, the actions we take today may affect every future generation of human beings, making the coming generations stakeholders in our ethical analysis..
Why is genetic engineering an ethical issue?
For instance, there is a chance that genetic alterations could have unintended consequences or that parents may not be able to control which traits their child inherits.
Some people believe that designer babies are morally wrong because they involve manipulating the genes of a human embryo.Dec 10, 2022.
Why is GMO a bioethical issue?
From a rights perspective, based on the right not to be harmed, the answer would also be yes.
But from the perspective of a virtue ethics that promotes respect for species' integrity and regards inter-species gene splicing as genetic pollution and contamination of germ-lines, the answer is no..
- Ethical Issues Associated with GMOs
It is a common fear that genetic modification may result in unintended consequences, such as the creation of new allergens or toxins, the spread of modified genes to wild relatives, or the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.