TABLAS DE CONVERSION SISTEMA INTERNACIONAL DE
PRESION bar > Pa > psi(libras/pulgada cuadrada). 1 bar = 100.00 Pa = 100 k Pa = 145 psi. 1 Pa = 0
Tablas de Conversion
bar psi kPa/MPa Kg/cm2 Mbar
Page 1. bar psi. kPa/MPa. Kg/cm2 100 MPa. 1019.579. 1000000. Pressure Conversion Table. We're the experts... ...talk to us 01628 531166.
pdf pressure card
Conversions
PSI) - A basic unit of pressure or tension measurement in the Imperial or. English System of Weights and Measures. 1 psi = .006895 MPa. 1000 psi = 1 ksi.
page
APPENDIX: UNIT CONVERSION FACTORS
UNIT CONVERSION FACTORS1. 1 Adapted from 1 megapascal = 1 MPa = 106 Pa. 1 gigapascal = 1 GPa = 109 ... 1 pound‐force per square inch = 1 psi = 6894.8 Pa.
Factores de conversión
1 g/cm3 = 62.428 lbm/ft3 = 0.036127 lbm/in3 1 kPa = 103 Pa = 10−3 MPa. = 0.020886 lbf/ft2 ... 1 psi = 144 lbf/ft2 = 6.894757 kPa.
conversiones
Electro-pneumatic Regulator
∗3 The minimum unit for 0.9 MPa (130 psi) types is 1 psi. ∗ The above characteristics are confined to the static state. When air is consumed on the output
SP X E ITV
Tech Bulletin - Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
To convert PSI to Megapascals (MPa) multiply by 0.006895. To convert from PSI to PROBLEM 1: Find the size hose required to operate a paint spray gun.
TB
www.ryerson.com METRIC SYSTEM
1 Joule = .7376 ft. lb. To Convert psi to MPa multiply by .006894757 ksi to MPa multiply by. 6.894757. MPa to psi multiply by. 145.0377. MPa to ksi.
CONVERSION FACTORS To Convert:
Date: 6/28/2015 Page 1 of 2. CONVERSION FACTORS lbf. Pounds force pli. Pounds per inch g/cc. Grams per cubic centimeter _____ psi X .006895 = ____ Mpa.
Conversion Factors Armacell InfoSheet.EN.US.
Appendix H: Conversion Factors
1 g/cm3 = 62.428 lbm/ft3 = 0.036127 lbm/in.3 1 kPa= 103 Pa = 10 3 Mpa. 1 bar = 105 Pa ... 1 psi = 144 lbf/ft2 = 6.894757 kPa. 1 in. Hg = 3.387 kPa.
 Reelcraft Industries, Inc. • 2842 E Business Hwy 30, Columbia City,
Reelcraft Industries, Inc. • 2842 E Business Hwy 30, Columbia City, IN 46725
Ph: 800-444-3134 / 260-248-8188 • Fax: 800-444-4587 / 260-248-2605 Customer Service: 855-634-9109 • reelcraft@reelcraft.com • www .reelcraft.comForm # TB0001 Rev: 1/2020
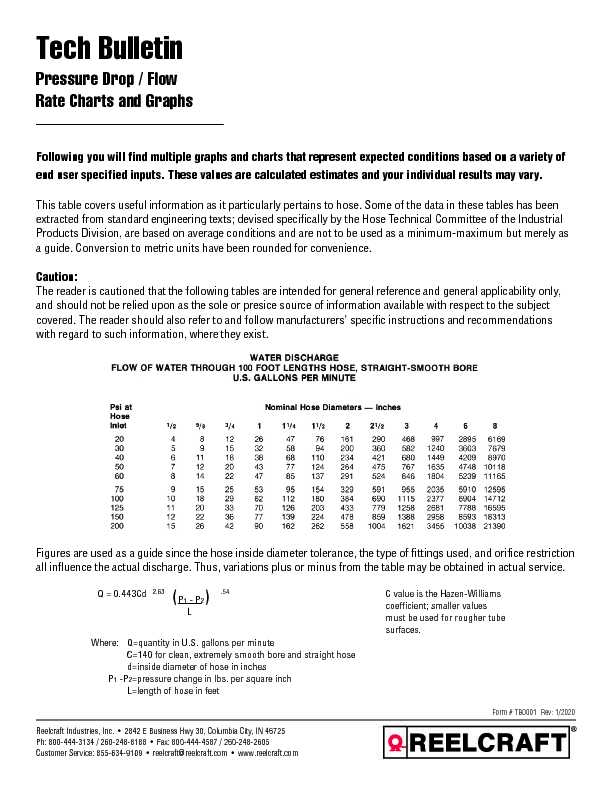
Tech Bulletin
Pressure Drop / FlowRate Charts and Graphs
Following you will find multiple graphs and charts that represent expect ed conditions based on a variety of end user specified inputs. These values are calculated estimates and you r individual results may vary. This table covers useful information as it particularly pertains to hose . Some of the data in these tables has been extracted from standard engineering texts; devised specifically by the H ose Technical Committee of the Industrial Products Division, are based on average conditions and are not to be use d as a minimum-maximum but merely as a guide. Conversion to metric units have been rounded for convenience.Caution:
The reader is cautioned that the following tables are intended for gener al reference and general applicability only,and should not be relied upon as the sole or presice source of information available with respect to the subject
covered. The reader should also refer to and follow manufacturers' sp ecific instructions and recommendations en-USwith regard to such information, where they exist. Figures are used as a guide since the hose inside diameter tolerance, th e type of fittings used, and orifice restriction all influence the actual discharge. Thus, variations plus or minus from the table may be obtained in actual service.C value is the Hazen-Williams
coefficient; smaller values must be used for rougher tube surfaces.Where:
Q=quantity in U.S. gallons per minute
C=140 for clean, extremely smooth bore and straight hose d=inside diameter of hose in inchesP1 -P2=pressure change in lbs. per square inch
L=length of hose in feet
(P1 - P2) LQ = 0.443Cd
2.63 .54Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
Page 2www.reelcraft.com
*Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers AssociationPressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
www.reelcraft.comPage 3 To convert PSI to Megapascals (MPa) multiply by 0.006895 To convert from PSI to feet of Hydraulic Head multiply by 2.309 To convert from U.S. gallons per minute to cubic feet per minute multiply by 0.1337 To convert from U.S. gallons per minute to cubic meters per second multiply by .00006309NOTE: Friction loss can vary by 20% due to
temperature. Bends can increase friction loss by 50%.C value is the Hazen-Williams coefficient;
smaller values must be used for rougher tube surfaces. where : P= pressure loss in lbs. per square inchQ=quantity in U.S. gallons per minute
C=140 for clean, extremely smooth bore and straight hoseL=Length of hose in feet
d=inside diameter of hose in inchesP=4.51(Q/C)
1.85 x L d 4.87 orP=0.0483Q
d4.87 @60F (15.6
C) *Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers AssociationPage 4www.reelcraft.com
Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
*Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers Association www.reelcraft.comPage 5Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
*Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers AssociationPage 6www.reelcraft.com
Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
PROBLEM 1: Find the size hose required to operate a paint spray gun (production type) that requires 8 C.F.M. of "free air" at 80 to 100p.s.i. pressure. Using the above curve-based on 90 p.s.i. inlet pressure and a recom- mended maximum pressure drop of 10 p.s.i. follow the 10 p.s.i. verti- cal line upward until it intersects with the horizontal line representing the 8 C.F.M. air flow. Note that this point is above the 1/4" I.D. hose range and that if co n- tinued further to the right, intersects the 1/4 I.D. hose curve at 15 p.s.i. pressure loss. The 1/4" I.D. hose cannot be recommended. Next larger size hose 3/8" must be recommended. PROBLEM 2: Find the maximum cubic feet of "free air" flow through a
1/2" I.D. hose with a 10 p.s.i. pressure loss at 90 p.s.i. inlet pres
sure. Follow the 10 p.s.i. vertical line upward until it intersects with the1/2" I.D. curve, follow horizontal line left for cubic feet per minut
e air flow. Approximately 50 C.F.M. is indicated for 1/2" I.D. hose.To select the proper size for a particular reel,
it is essential to know the following: 1. Cubic feet per min. "free air" requirements of the equipment to be used. 2.The minimum pressure at which the equipment
will operate efficiently. (If this is not available, it is recommended that the pressure drop not exceed10 p.s.i. at 90 p.s.i. inlet pressure.)
3.Pressure loss, p.s.i. per 50 ft of hose, coupled
each end. Note: 1. Pressure loss is directly proportional to the length. For example, if the pressure loss is given for50 feet of hose, the loss for 100 feet will be twice as
much, and the loss for 25 feet will be half as much. Note: 2. Above curve is based on inlet pressure - 90 p.s.i. (Standard pressure for shop purposes.) *Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers Association Reelcraft Industries, Inc. • 2842 E Business Hwy 30, Columbia City,IN 46725
Ph: 800-444-3134 / 260-248-8188 • Fax: 800-444-4587 / 260-248-2605 Customer Service: 855-634-9109 • reelcraft@reelcraft.com • www .reelcraft.comForm # TB0001 Rev: 1/2020
Tech Bulletin
Pressure Drop / FlowRate Charts and Graphs
Following you will find multiple graphs and charts that represent expect ed conditions based on a variety of end user specified inputs. These values are calculated estimates and you r individual results may vary. This table covers useful information as it particularly pertains to hose . Some of the data in these tables has been extracted from standard engineering texts; devised specifically by the H ose Technical Committee of the Industrial Products Division, are based on average conditions and are not to be use d as a minimum-maximum but merely as a guide. Conversion to metric units have been rounded for convenience.Caution:
The reader is cautioned that the following tables are intended for gener al reference and general applicability only,and should not be relied upon as the sole or presice source of information available with respect to the subject
covered. The reader should also refer to and follow manufacturers' sp ecific instructions and recommendations en-USwith regard to such information, where they exist. Figures are used as a guide since the hose inside diameter tolerance, th e type of fittings used, and orifice restriction all influence the actual discharge. Thus, variations plus or minus from the table may be obtained in actual service.C value is the Hazen-Williams
coefficient; smaller values must be used for rougher tube surfaces.Where:
Q=quantity in U.S. gallons per minute
C=140 for clean, extremely smooth bore and straight hose d=inside diameter of hose in inchesP1 -P2=pressure change in lbs. per square inch
L=length of hose in feet
(P1 - P2) LQ = 0.443Cd
2.63 .54Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
Page 2www.reelcraft.com
*Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers AssociationPressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
www.reelcraft.comPage 3 To convert PSI to Megapascals (MPa) multiply by 0.006895 To convert from PSI to feet of Hydraulic Head multiply by 2.309 To convert from U.S. gallons per minute to cubic feet per minute multiply by 0.1337 To convert from U.S. gallons per minute to cubic meters per second multiply by .00006309NOTE: Friction loss can vary by 20% due to
temperature. Bends can increase friction loss by 50%.C value is the Hazen-Williams coefficient;
smaller values must be used for rougher tube surfaces. where : P= pressure loss in lbs. per square inchQ=quantity in U.S. gallons per minute
C=140 for clean, extremely smooth bore and straight hoseL=Length of hose in feet
d=inside diameter of hose in inchesP=4.51(Q/C)
1.85 x L d 4.87 orP=0.0483Q
d4.87 @60F (15.6
C) *Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers AssociationPage 4www.reelcraft.com
Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
*Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers Association www.reelcraft.comPage 5Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
*Charts are provided by Rubber Manufacturers AssociationPage 6www.reelcraft.com
Pressure Drop / Flow Rate Charts and Graphs
PROBLEM 1: Find the size hose required to operate a paint spray gun (production type) that requires 8 C.F.M. of "free air" at 80 to 100p.s.i. pressure. Using the above curve-based on 90 p.s.i. inlet pressure and a recom- mended maximum pressure drop of 10 p.s.i. follow the 10 p.s.i. verti- cal line upward until it intersects with the horizontal line representing the 8 C.F.M. air flow. Note that this point is above the 1/4" I.D. hose range and that if co n- tinued further to the right, intersects the 1/4 I.D. hose curve at 15 p.s.i. pressure loss. The 1/4" I.D. hose cannot be recommended. Next larger size hose 3/8" must be recommended. PROBLEM 2: Find the maximum cubic feet of "free air" flow through a