Chapitre 3 Dérivabilité des fonctions réelles
(2) On définit de même la dérivée `a droite que l'on note fd(x0). on applique le théor`eme pour la fonction log sur l'intervalle [x
MHT chap
6.2 Properties of Logarithms
Once we get the x2 by itself inside the log we may apply the Power Rule with u = x and w = 2 and simplify. log0.1(10x2) = log0.1(10) + log0.1(x2). Product Rule.
S&Z . & .
4-Partial Derivatives and their Applications.pdf
them one is called partial derivative of z(x y) with respect to x denoted by one of the symbols *(i) u = (tan–1a) [log(x2 + y2)] + btan–1(y/x)
Partial Derivatives and their Applications
Appendix: algebra and calculus basics
28 sept. 2005 2. Logarithms convert products to sums: log(ab) = log(a) + log(b). ... The derivative of the logarithm d(log x)/dx
algnotes
CONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY
(ii) The function y = f (x) is said to be differentiable in the closed interval [a b] The derivative of logx. w.r.t.
leep
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
An equation involving derivative (derivatives) of the dependent variable with log x. Example 18 A solution of the differential equation. 2.
leep
formulaire.pdf
Logarithme et Exponentielle : eln x = ln(ex) = x e−x = 1/ex. √ex = ex/2. (ex) y. = exy lim x→−∞ ex = 0 lim x→+∞ ... R`egles de dérivation.
formulaire
1. If log x2 – y2 = a then dy / dx = x2 + y2
1. If log x2 – y2. = a then x2 + y2. Solution : Take y /x = k → y = k x. → dy/dx = k. → dy/dx = y / x The derivative of an even function is always.
mat c
Untitled
%20Samples.pdf
New sharp bounds for the logarithmic function
5 mar. 2019 log(x + 1) i. e. log(1 + x) ⩾ 2x/(2 + x) for x ⩾ 0. ... and by another differentiation
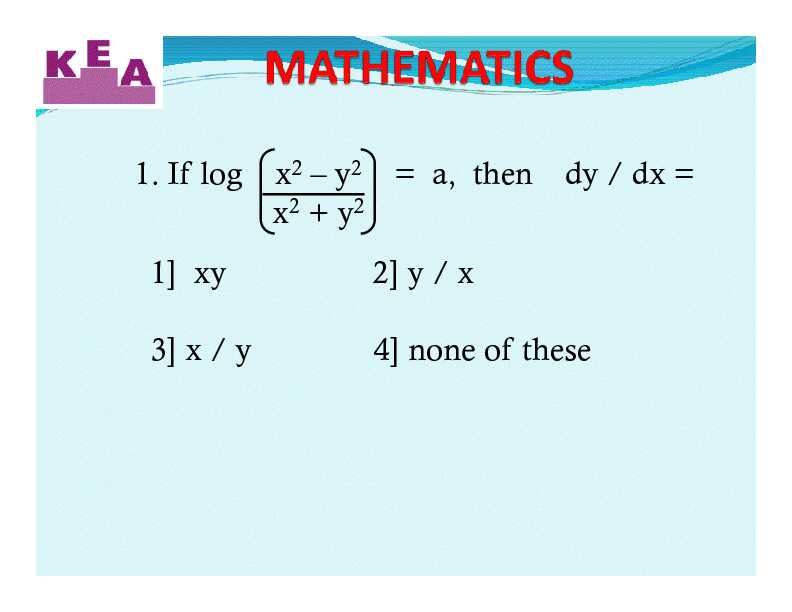
1. If log x2- y2= a, then dy / dx =
x 2+ y21] xy 2] y / x
3] x / y 4] none of these
1. If log x2- y2= a, then
x 2+ y2Solution :Take y /x = k y = k x
dy /dx = k dy /dx = k dy/dx = y / xAnswer : 2] y / x
Ќ͵LŅ Ņ ΛǣΜ ў Ļǣŭ ΛǣΜͲ ŭΛЉΜ ў ЋͲ ŭЊ
8. If x
y= e x - y, then dy / dx is equal to1] y 2] x
(1 + log x) 2 (1 + logx) 23] log x 4] none of these
( 1 + logx ) 28. Solution :
Given that : xy= ex - y
y log x = (x - y) log ee y log x + y = x y ( 1 + log x ) = x y = x y = x1 + log x
Diff. y w.r.t 'x"
dy log x dx (1 + logx) 2Answer : 3] log x
(1 + logx) 25źŅŅ͵
5źŅŅ͵
terms then dy/dx =1] sec2x 2] sec2x2y-1 1-2y
3] Tanx 4] -Tan x
2y-1 2y-1
y = f(x) + f(x) + .........to ∞ dy f1(x) dy f(x) dx 2y - 1 dy sec2x -1 Tan x
dx 2y-1 2y-1Answer : 3] Tan x
2y-1YўЊ
YўЊ
2 3!
terms then d2y /dx2
1] 1 / x
1] 1 / x 2] 2 / x 3] 1 4] 0
2 3!
e x= 1 + x + x2+ x3+ .......... to ∞2! 3!
y = elog x y = elog x y = x dy/dx = 1 d 2y dx 2= 0Answer: 4] 0
secx - Tanx dx1] sec x [
secx -Tanx1] sec x [
secx -Tanx2] Tan x [ secx + tanx ]
3] secx [secx + Tanx]
4] Tan x [ secx - Tanx]
secx - Tanx sec2x - Tan2x
y = secx + Tan x1. If log x2- y2= a, then dy / dx =
x 2+ y21] xy 2] y / x
3] x / y 4] none of these
1. If log x2- y2= a, then
x 2+ y2Solution :Take y /x = k y = k x
dy /dx = k dy /dx = k dy/dx = y / xAnswer : 2] y / x
Ќ͵LŅ Ņ ΛǣΜ ў Ļǣŭ ΛǣΜͲ ŭΛЉΜ ў ЋͲ ŭЊ
8. If x
y= e x - y, then dy / dx is equal to1] y 2] x
(1 + log x) 2 (1 + logx) 23] log x 4] none of these
( 1 + logx ) 28. Solution :
Given that : xy= ex - y
y log x = (x - y) log ee y log x + y = x y ( 1 + log x ) = x y = x y = x1 + log x
Diff. y w.r.t 'x"
dy log x dx (1 + logx) 2Answer : 3] log x
(1 + logx) 25źŅŅ͵
5źŅŅ͵
terms then dy/dx =1] sec2x 2] sec2x2y-1 1-2y
3] Tanx 4] -Tan x
2y-1 2y-1
y = f(x) + f(x) + .........to ∞ dy f1(x) dy f(x) dx 2y - 1 dy sec2x -1 Tan x
dx 2y-1 2y-1Answer : 3] Tan x
2y-1YўЊ
YўЊ
2 3!
terms then d2y /dx2
1] 1 / x
1] 1 / x 2] 2 / x 3] 1 4] 0
2 3!
e x= 1 + x + x2+ x3+ .......... to ∞2! 3!
y = elog x y = elog x y = x dy/dx = 1 d 2y dx 2= 0Answer: 4] 0
secx - Tanx dx1] sec x [
secx -Tanx1] sec x [
secx -Tanx2] Tan x [ secx + tanx ]
3] secx [secx + Tanx]
4] Tan x [ secx - Tanx]
secx - Tanx sec2x - Tan2x
y = secx + Tan x- log(1+x^2) derivative
- log x base 2 derivative
- log(x^2+y^2) derivative
- log x^2 differentiation
- log(sec x^2) derivative
- log(sec x^2) derivative by first principle
- log tan x/2 differentiation
- log base x 2 differentiation