Scatterplots and Correlation
The most useful graph for displaying the relationship between two For a correlation coefficient of zero the points have no direction
scatterplots and correlation notes
Pearson's correlation
examination of a scatterplot. Examples of negative no and positive correlation are as follows. Negative. No. Positive correlation correlation correlation
pearsons
Spearman's correlation
does not imply there is no relationship between the variables. For example in the following scatterplot which implies no (monotonic) correlation however
spearmans
Quickest Hub Discovery in Correlation Graphs
4 févr. 2017 isolation of hubs in a correlation graph. ... of the random vector X is nonzero i.e.
> 0
Determine whether each graph shows a positive negative
https://www.waynesville.k12.mo.us/cms/lib07/MO01910216/Centricity/Domain/603/A1%20C4%20L5%20SOLUTION%20KEY%20WORKED%20OUT.pdf
A Guide to Scatter and Line Graphs
Scatter graphs and line graphs are used to show the potential correlation can appear on a graph along with a key
Eight things you need to know about interpreting correlations:
It ranges from +1 (perfect positive correlation) through 0 (no correlation at the bottom left of the graph there is clearly no correlation between X ...
Eight things you need to know about interpreting correlations
Correlation between short-term blood pressure variability
Open Access. Correlation between short-term blood pressure variability parameters with mobil-. O-graph pulse wave velocity. Marco Antonio Vieira Silva12*.
s x
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ON QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES
Zero correlation d. None of these. 9. Scatter diagram is also called ................... a. Dot chart b. Correlation graph c. Both a and b.
Quantitative Techniques for Business Decision
From Distance Correlation to Multiscale Graph Correlation arXiv
30 sept. 2018 variance equals 0 if and only if the random variable is a constant in which case distance correlation shall be set to 0.
Spearma
Introduction
correlation which is a statistical measure of the strength of a linear relationship between paired data. Its calculation and subsequent significance testing of it requires the following data assumptions to hold: interval or ratio level; linearly related; bivariate normally distributed. correlation!Monotonic function
function is. A monotonic function is one that either never increases or never decreases as its independent variable increases. The following graphs illustrate monotonic functions: Monotonically increasing Monotonically decreasing Not monotonic Monotonically increasing - as the x variable increases the y variable never decreases; Monotonically decreasing - as the x variable increases the y variable never increases; Not monotonic - as the x variable increases the y variable sometimes decreases and sometimes increases. lation coefficient rrelation coefficient is a statistical measure of the strength of a monotonic relationship between paired data. In a sample it is denoted by ݎ௦ and is by design constrained as follows െsQN௦s
And its interpretation is similar to that of Pearsons, e.g. the closer ݎ௦ is to േs the stronger the monotonic relationship. Correlation is an effect size and so we can verbally describe the strength of the correlation using the following guide for the absolute value of N௦: .00-.19 .20-.39 .40-.59 .60-.79 .80-1.0 testing of it requires the following data assumptions to hold: interval or ratio level or ordinal; monotonically related. is a nonparametric statistic. Let us consider some examples to illustrate it. The following table gives x and y values for the relationship ݕ perfectly increasing monotonic relationship. does not reflect that there is indeed a perfect correlation for this data however is 1, reflecting the perfect monotonic relationship. by calcula on the ranked values of this data. Ranking (from low to high) is obtained by assigning a rank of 1 to the lowest value, 2 to the next lowest and so on. If we look at the plot of the ranked data, then we see that they are perfectly linearly related. In the figures below various samples and their corresponding sample correlation monotonic correlation values of -1, 0 and 1:N௦ൌ
FsN௦ൌrN௦ൌs
perfect ve no correlation perfect +vemonotonic correlation monotonic correlation
Invariably what we observe in a sample are values as follows:N௦ൌ
F
Spearma
Introduction
correlation which is a statistical measure of the strength of a linear relationship between paired data. Its calculation and subsequent significance testing of it requires the following data assumptions to hold: interval or ratio level; linearly related; bivariate normally distributed. correlation! Monotonic function
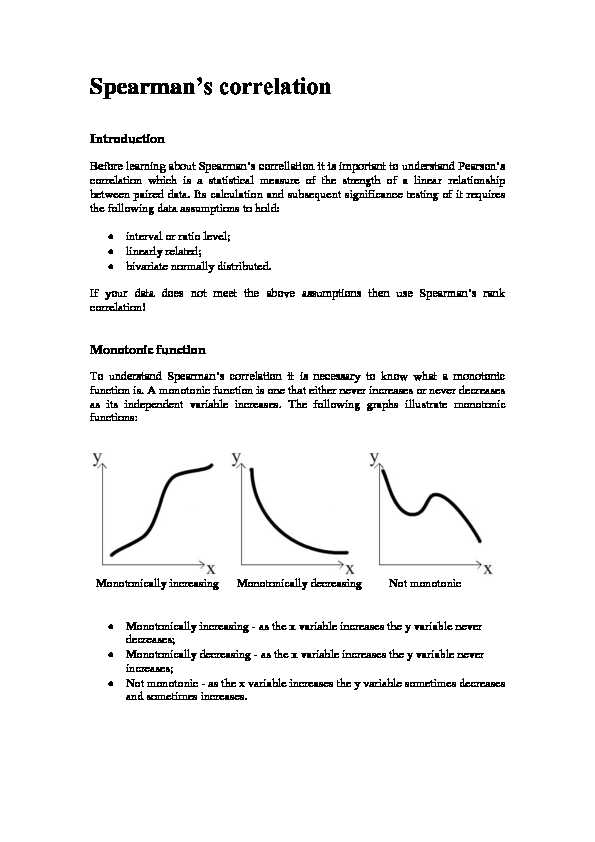
function is. A monotonic function is one that either never increases or never decreases as its independent variable increases. The following graphs illustrate monotonic functions: Monotonically increasing Monotonically decreasing Not monotonic Monotonically increasing - as the x variable increases the y variable never decreases; Monotonically decreasing - as the x variable increases the y variable never increases; Not monotonic - as the x variable increases the y variable sometimes decreases and sometimes increases. lation coefficient rrelation coefficient is a statistical measure of the strength of a monotonic relationship between paired data. In a sample it is denoted by ݎ௦ and is by design constrained as follows െs QN௦s
And its interpretation is similar to that of Pearsons, e.g. the closer ݎ௦ is to േs the stronger the monotonic relationship. Correlation is an effect size and so we can verbally describe the strength of the correlation using the following guide for the absolute value of N௦: .00-.19 .20-.39 .40-.59 .60-.79 .80-1.0 testing of it requires the following data assumptions to hold: interval or ratio level or ordinal; monotonically related. is a nonparametric statistic. Let us consider some examples to illustrate it. The following table gives x and y values for the relationship ݕ perfectly increasing monotonic relationship. does not reflect that there is indeed a perfect correlation for this data however is 1, reflecting the perfect monotonic relationship. by calcula on the ranked values of this data. Ranking (from low to high) is obtained by assigning a rank of 1 to the lowest value, 2 to the next lowest and so on. If we look at the plot of the ranked data, then we see that they are perfectly linearly related. In the figures below various samples and their corresponding sample correlation monotonic correlation values of -1, 0 and 1: N௦ൌ
FsN௦ൌrN௦ൌs
perfect ve no correlation perfect +ve
monotonic correlation monotonic correlation
Invariably what we observe in a sample are values as follows: