 Questions - C08 Separation Techniques II - Section 2 Chemistry
Questions - C08 Separation Techniques II - Section 2 Chemistry
C8: Separation Techniques II - Question by Topic. (Mark Scheme and explanations Answers and Explanations. 1. The answer is A. Common sulfates nitrates and ...
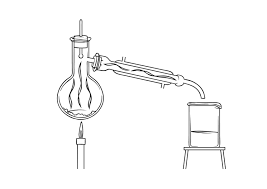 Separation Techniques Exam Style Questions 1
Separation Techniques Exam Style Questions 1
In the space below draw and label the apparatus required to separate a soluble substance from an insoluble substance. A. B. Page 2. Answers. 1. Distillation is
 Separation Techniques Chemistry Questions with Solutions
Separation Techniques Chemistry Questions with Solutions
Which method can be used to separate a mixture of two solids? Answer: All mixtures of two solid substances can be separated using: ○ Using a suitable solvent.
 SEPARATION TECHNIQUES – IGCSE (MCQS)
SEPARATION TECHNIQUES – IGCSE (MCQS)
SEPARATION TECHNIQUES – IGCSE (MCQS). 0620_s/12/qp11. 0620_s/11/qp11. 0620_s/11/qp11. Page 2. 0620_s/10/qp11. 0620_s/09/qp11. 0620_s/08/qp1. Page 3
 National Quali cations 2018 X707/77/02 Biology Section 1
National Quali cations 2018 X707/77/02 Biology Section 1
15 May 2018 Record your answers on the answer grid on page 03 of your question and answer booklet. ... Protein separation technique. Centrifugation. Gel ...
 Questions and Answers
Questions and Answers
4 Apr 2017 MiFID I required firms to “take all reasonable steps to obtain when executing orders
 Separating Mixtures – Exam Questions - Ms Finnegans Science
Separating Mixtures – Exam Questions - Ms Finnegans Science
Questions. Page 2. 2012 - Higher. Paper chromatography was used to find the Name the separation technique shown in the diagram. In which labelled part ...
 Home learning activities Subject Science Year Group Year 8 Unit of
Home learning activities Subject Science Year Group Year 8 Unit of
Complete the exam question on 'Mixtures and Separation Techniques'. Use the mark scheme (once you have tried the question) to mark your answers carefully
 Spring Term 1 Year 8 Separation techniques and Energy Extended
Spring Term 1 Year 8 Separation techniques and Energy Extended
Year 8 Separation techniques and Energy. Extended Homework Assignment. Name Look at the table of information below and answer the questions. Food or ...
 Solution Using Separation of Variables
Solution Using Separation of Variables
However the separation of variables technique does give some useful solutions to Now write down the final answer for u(x
 Questions - C08 Separation Techniques II - Section 2 Chemistry
Questions - C08 Separation Techniques II - Section 2 Chemistry
C8: Separation Techniques II - Question by Topic What is the best method to perform this separation? ... Answers and Explanations. 1. The answer is A.
 Spring Term 1 Year 8 Separation techniques and Energy Extended
Spring Term 1 Year 8 Separation techniques and Energy Extended
1 Match the name of the separation technique to the correct experimental set up below. Look at the table of information below and answer the questions.
 Separation purification and identification of the components of a
Separation purification and identification of the components of a
Hints for the answers to the proposed questions and topics to discussion: principles and practice of purification and separation techniques in Organic ...
 Separating Mixtures – Exam Questions - Ms Finnegans Science
Separating Mixtures – Exam Questions - Ms Finnegans Science
Name the separation technique shown in the diagram. In which labelled part would you expect to find most of the dye at the end of the experiment?
 Separation Techniques
Separation Techniques
Question: Why is table salt (sodium chloride) added to water that is used for cooking? Answer: The sodium chloride is an impurity that will increase the boiling
 GCSE T?ME
GCSE T?ME
Separation Techniques Exam Style Questions 1 Answers. 1. Distillation is a method that can be used to obtain drinking water from a sample of salt water.
 Multiple choice questions on separation techniques pdf
Multiple choice questions on separation techniques pdf
Multiple Choice Question Separation Techniques (MCQ) the separation techniques quiz answers pdf to study grade 6 science for online undergraduate courses.
 Sample Practice Questions Answers
Sample Practice Questions Answers
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/9781119204206.oth01
 Lab #2
Lab #2
Techniques useful for the separation of mixtures include the following: DISTILLATION is the purification of a liquid techniques shown as question marks.
 Year 8 Science Distance Learning Quiz and Learn Booklet Part 1
Year 8 Science Distance Learning Quiz and Learn Booklet Part 1
20 May 2020 Practice questions and answers for you to complete and self mark ... ANSWERS: Separation techniques: Week 4 (22nd June) ...
 Unit 7 SEPARATION TECHNIQUES Question Bank - Miss Pirulli
Unit 7 SEPARATION TECHNIQUES Question Bank - Miss Pirulli
SEPARATION TECHNIQUES A)chromatography B)electrolysis C)distillation D)titration 23 Given the diagram representing a process being used to separate the colored dyes in food coloring: Which process is represented by this diagram? A)elements with identical boiling points B)elements with different boiling points C)compounds with identical boiling
 SEPARATION TECHNIQUES - Sepali's Chemistry Guide
SEPARATION TECHNIQUES - Sepali's Chemistry Guide
Separation Techniques Exam Style Questions 1 1 Distillation is a method that can be used to obtain drinking water from a sample of salt water Two different examples of distillation apparatus are shown below • Which apparatus A or B will produce the drinking water the quickest? Give a reason for your choice
 SEPARATION TECHNIQUES - Sepali's Chemistry Guide
SEPARATION TECHNIQUES - Sepali's Chemistry Guide
SEPARATION TECHNIQUES If a substance does not dissolve in a solvent we say that it is insoluble For example sand does not dissolve in water – it is insoluble Filtration is a method for separating an insoluble solid from a liquid When a mixture of sand and water is filtered: • the sand stays behind in the filter paper (it becomes the
 Separating Mixtures - CSIRO
Separating Mixtures - CSIRO
substances that can be separated using a range of techniques (ACSSU113) -recognising the differences between pure substances and mixtures and identifying examples of each -identifying the solvent and solute in solutions -investigating and using a range of physical separation techniques such as filtration
 Unit 7 SEPARATION TECHNIQUES Question Bank
Unit 7 SEPARATION TECHNIQUES Question Bank
SEPARATION TECHNIQUES A)chromatography B)electrolysis C)distillation D)titration 23 Given the diagram representing a process being used to separate the colored dyes in food coloring: Which process is represented by this diagram? A)elements with identical boiling points B)elements with different boiling points C)compounds with identical boiling
 Searches related to separation techniques questions and answers filetype:pdf
Searches related to separation techniques questions and answers filetype:pdf
What name is given to this separation technique? The salt and water was collected at X Explain why the insoluble impurities (dirt) were held at Y 2011 - Ordinary To get the salt from the mixture of salt and water the water was removed This could be done by either evaporation or distillation
How can mixtures of liquids be separated according to their properties?
- Mixtures of liquids can be separated according to their properties. The technique used depends on whether the liquids dissolve in each other, and so are miscible, or if they are immiscible. Fractional distillation is a technique used to separate miscible liquids according to their boiling points.
Which mixtures are suitable for separation by chromatography?
- Mixtures that are suitable for separation by chromatography include inks, dyes and colouring agents in food. Simple chromatography is carried out on paper. A spot of the mixture is placed near the bottom of a piece of chromatography paper and the paper is then placed upright in a suitable solvent, eg water.
How do you separate a soluble solid from a liquid?
- Pour the mixture through the filter funnel. Let the water drain and leave the insoluble solid to dry. Eg. Separating sand from Salt water. Evaporation is used to separate a soluble solid from a liquid. For example, copper sulfate is soluble in water – its crystals dissolve in water to form copper sulfate solution.
Spring Term 1
Year 8 Separation techniques
and EnergyExtended Homework Assignment
Name: _____________________
Teacher: ___________________
Instructions
Please complete all sections
You will need to complete sections as you work through the topic A printed copy should be handed into your teacher.Separation techniques
Task 1: Identifying mixtures
1 Draw particle diagrams in the boxes below to represent an element, a compound,
and a mixture. element compound mixture2 The graph below shows the heating curves of two substances.
a The two substances shown in the graph are water and chocolate.Label the graph.
b State the name of the substance that is pure. Explain your answer using the graph provided. c Label the different states (solid, liquid, or gas) shown on this graph. Identify the changes of state. Label appropriately as boiling, freezing, and so on, as appropriate. d Describe how an experiment can be set up to provide data for this graph.Task 2: Solutions
1 a Use the words solute, solvent, and solution to describe how a solution is made.
b Use the diagrams below to explain in detail what happens to particles when a substance dissolves.2 The table below gives information on the solubility of sugar and salt in water.
Substance Solubility at 20 °C (g/100g of water) sugar (sucrose) 202 salt (sodium chloride) 36 a State what is meant by solubility. Give an example using the data provided. b Explain what is meant by a saturated solution.Task 3: Separation techniques
1 Match the name of the separation technique to the correct experimental set up below. Your
choices are: chromatography filtration evaporation distillation2 Rearrange the sentences below to describe and explain how filtration can be used to
separate sand from a mixture of sand and sugar. OrderSugar dissolves in water. Sand does not.
Sand is left as the residue in the filter funnel.
Add water to the mixture. Stir.
Sugar solution passes through the filter paper as filtrate. Fold the filter paper, place in funnel, and pour the mixture into the filter funnel.3 Fill in the gaps below to explain why you can use evaporation to obtain salt from sea water
but not water from an inky solution. Evaporation can be used to remove a s from a solution. This is the case when removing salt from sea water. In this example, s is the solute, water is the s , and sea water is the s . Salt can be obtained simply by leaving sea water in an e b until the water e . On the other hand, evaporation cannot be used to obtain water from an inky solution as only the i would be left at the end. In order to obtain pure water from an inky solution, d must be used. This is a technique where the substance with the l boiling point evaporates first, and as its vapours enter the c , the gas condenses into a l , ready to be collected in a beaker.4 Match the halves of the following sentences together to explain how chromatography
works.Place a sample of each ink
you would like testing on so the mixture separates.Place the chromatography
paper in a beaker of solvent, for example, water.The level of solvent in the
beaker must dissolve in the solvent.The solvent moves the pencil line of the
chromatography paper.The ink samples with the solvent up the
chromatography paper.The solvent carries the
samples up the chromatography paper.Some dyes move faster than
others, and some dissolve better than others, not be above the pencil line.5 The chromatogram below show the separation of ink from four different felt-tip pens.
a State the only coloured pen whose ink does not appear in the brown felt-tip pen. b Suggest whether a brown pen made by a different company would produce the same result on a similar chromatogram. Explain your answer.Energy
Task 1: Energy in food and in fuels
Look at the table of information below and answer the questions.Food or fuel Energy (J/kg)
coal 30 000 000 wood 15 000 000 petrol 46 000 000 cheese 16 000 000 bread 9 500 000 lettuce 550 0001 A new power station is opening in your local area. State the fuel you would choose for this
power station using the table above. Explain your answer. Leon and James students are in the same class. Leon is very sporty while James likes to play on his games console in his spare time. Their typical daily energy requirements are 8700 kJ and 12 400 kJ.2 a Link the correct energy requirement for each student.
Leon:James:
b Describe the types of food you would recommend to Leon and James as part of their diet using the table above. Explain your answer.Task 2: Conservation of energy
1 State the law of conservation of energy.
2 A coal fire is burning in the fireplace. Describe the energy before and after this
change.3 The diagram below shows a lever in action. Explain how this lever follows the law of
conservation of energy.Fill in the gaps using the following words:
force multiplier force distance pivot simple machine bigger smaller A lever is a . In this example, a screwdriver is used to open a paint tin. The is where the end of the screwdriver is resting on the edge of the paint tin. The applied to the lid by the lever is than the that you apply with just your hand. This means that a lever is a . Energy is conserved because the the lid moves up is than the moved by your hand.Task 3: Energy transfers
1 Link each key word with the correct definition provided.
2 Complete the diagram to describe what happens during changes of state. Fill in the gaps
and label each arrow using the words and phrases below. melting evaporation or boiling sublimation condensation freezing to from water steam energy temperature A measure associated with changes in temperature or with work, measured in joules.A measure of how hot or cold something is,
measured in degrees Celsius.The energy in the store associated with the
temperature of an object. internal energy3 Two objects are in contact with each other. Explain what brings about the transfer of
energy between the two objects using the term equilibrium.4 Use the image below to answer the following questions.
a Draw an arrow on the diagram to show the direction of energy transfer. b Describe how conduction occurs through the sides of the cup. You should include the phrase vibration of particles in your answer. c Suggest a suitable material for the manufacture of this cup. Explain your answer in terms of conduction and insulation.5 a Choose from the following list sources of infrared radiation.
Circle the correct answers.
ice cube the Sun a metal saucer a lamp a fire b Describe what all sources of infrared radiation have in common. c Explain how energy is transferred by radiation. State whether particles are required for this method of energy transfer.Task 4: Energy resources
1 Wood and coal are two different types of energy resources. Describe the difference
between them in terms of renewable and non-renewable energy sources.2 Describe how electricity is generated in a power station by completing the table below. Use
these phrases: heats water to steam generates electricity spins the generator burns the fuelPart of the power station Function
furnace boiler turbine generatorTask 5: Energy, power, and work done
1 Explain the difference between energy and power by filling in the table below. Use the
following phrases to help you: increases joule stays the same wattEnergy Power
UnitHow this quantity changes as the
circuit component is left running2 An incandescent light bulb and an energy-saving light bulb have power ratings of
40 W and 12 W respectively.
a Calculate the energy transferred by both light bulbs over 10 hours in kWh. Show your working.Remember: 1000 W = 1 kW
energy (kWh) = power (kW) × time (h) b Compare the costs of running these two light bulbs over a 10-hour period. You should include the relative amounts of fuel used in each case.3 a Pete pulls a pulley and lifts a 20 N weight by 0.5 m. Calculate the work done.
Work done = force (N) × distance moved (m)
= J b the weight. The weight gains 30 J. Calculate the amount of energy dissipated to the surroundings. Show your working.quotesdbs_dbs10.pdfusesText_16[PDF] sept cent euros en lettre
[PDF] september 11 in history
[PDF] september 2016 movies in theaters
[PDF] september 2017 movies in theaters
[PDF] sequel viewpoint case statement
[PDF] sequel viewpoint date functions
[PDF] sequel viewpoint script examples
[PDF] sequence control statements in java
[PDF] sequence of basic feasible solution
[PDF] sequences (xn) and (yn)
[PDF] sequencing speech therapy goals
[PDF] serial dilution and plating
[PDF] serial dilution calculations microbiology
[PDF] serial dilution calculator cells
