 Well What Will We Drink
Well What Will We Drink
www.epa.gov/safewater/consumer/pdf/mcl.pdf. Individual Water Supply Wells Sample Students Answers: ppm ppb
 PREPARING SOLUTIONS AND MAKING DILUTIONS
PREPARING SOLUTIONS AND MAKING DILUTIONS
Final dilution factor (DF) = DF1 * DF2 * DF3 etc. Example: In the microbiology lab BIOLOGY 201 the students perform a three step 1:100 serial dilution of a
 Beers Law: Determining the Concentration of a Solution
Beers Law: Determining the Concentration of a Solution
Don't forget: Attach a copy of your graph to the lab report sheets. Page 8 This experiment covers the concept of molarity dilution
 National Functional Guidelines for Inorganic Superfund Methods
National Functional Guidelines for Inorganic Superfund Methods
Nov 2 2020 Laboratory serial dilution reports (if available)
 lab 9 serial dilution pour plates
lab 9 serial dilution pour plates
https://people.fmarion.edu/gpryor/LAB%209%20BIO%20215L.pdf
 Laboratory Math II: Solutions and Dilutions
Laboratory Math II: Solutions and Dilutions
Molarity is used to report molecules of a substance per unit volume. While serial dilutions are a great way to save on both reagents and space in the ...
 Serial Dilution Lab
Serial Dilution Lab
This exercise is intended to familiarize us with using scientific notation (to express big and small number easily) and the process of using serial dilutions to
 lab 9 serial dilution pour plates
lab 9 serial dilution pour plates
https://people.fmarion.edu/gpryor/LAB%209%20BIO%20215L.pdf
 PREPARING SOLUTIONS AND MAKING DILUTIONS
PREPARING SOLUTIONS AND MAKING DILUTIONS
Final dilution factor (DF) = DF1 * DF2 * DF3 etc. Example: In the microbiology lab BIOLOGY 201 the students perform a three step 1:100 serial dilution of a
 Suggested Reporting Language for Syphilis Serological Testing
Suggested Reporting Language for Syphilis Serological Testing
Guidance on Laboratory Reporting for Surveillance . Measurement of antibodies (i.e. nontreponemal) through serial dilution of the patient specimen to.
 Lab Report
Lab Report
Individual lab reports sharing same data. The lab report and marks can be viewed
 Laboratory Exercises in Microbiology: Discovering the Unseen
Laboratory Exercises in Microbiology: Discovering the Unseen
Scientific Notation and Serial Dilution …………………………..………… 177 Lab 1 of the lab manual. Report any problems with your microscope to your instructor.
 Lab #4 SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
Lab #4 SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
Serial Dilutions (Background). A dilution series is a succession of step dilutions each with the same dilution factor
 Lab Math Solutions Dilutions
Lab Math Solutions Dilutions
https://www.aphl.org/programs/newborn_screening/Documents/2016%20Molecular%20Workshop/5%20-%20Lab%20Math%20%20Molarity.pdf
 BIL 151 - General Biology Laboratory Dilutions: Simple and Serial
BIL 151 - General Biology Laboratory Dilutions: Simple and Serial
Serial dilutions can be used to prepare solutions of any desired concentration no matter how dilute You will perform a simple exercise to be sure you understand how to do this as it will be important in your future biological research endeavors In a pinch here’s a Serial Dilution Calculator: https://www aatbio com/tools/serial-dilution
 LAB 9 SERIAL DILUTION POUR PLATES AND ENUMERATION OF BACTERIA
LAB 9 SERIAL DILUTION POUR PLATES AND ENUMERATION OF BACTERIA
A serial dilution is the dilution of a sample in 10-fold dilutions As shown in the illustration below it begins when 1 mL of the bacterial sample is added to 9 mL and it is mixed together (creating a 10-1 dilution) Then 1 mL from that mixture is added to 9 mL and it is mixed together (a 10-2 dilution) That
 How to Do Serial Dilutions: 9 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow
How to Do Serial Dilutions: 9 Steps (with Pictures) - wikiHow
prepare a dilute solution from a more concentrated one perform serial dilutions use volumetric and Mohr pipets and a volumetric flask DISCUSSION Solutions are an important part of chemistry In this lab you will practice preparing solutions of different concentrations
 Microbiology BIOL 275 DILUTIONS - University of Pennsylvania
Microbiology BIOL 275 DILUTIONS - University of Pennsylvania
The serum dilution is the amount of serum in the amount of total solution; hence this is a 5/25 serum dilution which would equal a 1/5 dilution Titer The titer is the smallest amount or concentration that will produce a particular effect or endpoint
 LAB 8 SERIAL DILUTION POUR PLATES AND ENUMERATION OF BACTERIA
LAB 8 SERIAL DILUTION POUR PLATES AND ENUMERATION OF BACTERIA
A serial dilution is the dilution of a sample in 10-fold dilutions As shown in the illustration below it begins when 1 mL of the bacterial sample is added to 9 mL and it is mixed together (creating a 10-1 dilution) Then 1 mL from that -mixture is added to 9 mL and it is mixed together (a 10 2 dilution) That
 Searches related to serial dilution lab report pdf filetype:pdf
Searches related to serial dilution lab report pdf filetype:pdf
Activity 1 1 5 Student Resource Sheet Serial Dilutions In the lab scientists often need to make dilutions of the same solution Producing samples with different concentrations in a series is more time efficient than trying to prepare each sample one by one A serial dilution is a stepwise dilution of a substance in solution
How to calculate the serial dilution?
- Calculate the final dilution ratio in a serial dilution. The total dilution ratio can be determined by multiplying the dilution factor of each step leading up to the final step. This can be mathematically illustrated with the equation D t = D 1 x D 2 x D 3 x … x D n where D t is the total dilution factor and D n is the dilution ratio.
Why is serial dilution necessary?
- serial dilutions are necessary to count cfus because they estimate the concentration (the number of bacteria or colonies) of a sample by diluting the original culture until you have a serial dilution that results in a countable number of colonies on a plate (usually between 30 to 300 cfus), which will be used to determine the cfu/ml count of the …
What does serial dilution mean?
- In a single and very simple word, Serial dilution is a laboratory technique, in which a stepwise dilution process is performed on a solution with an associated dilution factor. In the laboratory, this method is used to decrease the counts of cells within a culture to simplify the operation.
3590/3550 -Laboratory
Time:Monday to Thursday 2:30 5:30
Location:318 Parker Bldg.
Five two week labs must be completed. Two students per experiment. Individual lab reports, sharing same data.
There are prefab questions which are to be answered (in paragraph form) and are due at start of each new laboratory experiment.
Lab reports are due the beginning of the following lab period the week after the lab is completed.
The lab report and marks can be viewed, but labs are not returned until the end of the course.Lab Report Overview
Each student is responsible for 50% of lab work,and for individual, original reports.The lab report constitutes 50%of the final grade. The organization, accuracy, completeness, interest in topic, results and explanations determine report grade.
The format of the report is that of a journal submission. Check out a Chemistry or Science journal to see how the report should be written.
Grading
Graded on:
Readability-good graphs, well made, self explanatoryCompleteness
Flow of report.
Interest in researching subject.
Accuracy of results. Explanations of results. Good standard curves. Accurate and/or precise analysis of unknown
Discussion of results. Why results are as seen. IfComprehensive conclusion. Questions answered.
References on similar material
Introduction
Description of problem.
Importance of solution of problem. Why are you
working on the problem?Why use this instrument to solve the problem?
Some theory and advantage of using instrument.
Do not give basic description of instrument
operation. This is usually part of prelab questions.Include reference to other work done.
Materials and Methods
List in paragraph format all methodology,
including instruments used with model and manufacturer, columns, solvent systems, reagents (supplier). Methods should be detailed and complete, but not a copy of lab manual. Should notinclude particulars of operating the equipment from the laboratory manual. Do not explain which buttons you pushed on the instrument.Results
All the pertinent data needed for understanding
of experiment. Include tables and/or graphs, sample calculations.Each table or graph should have a paragraph of
explanation in the results section. No graph or table should stand alone without detailed description of what the reader is seeing.If you are comparing results, for example, you
can show % differences. You can include standard deviation if you have multiple results.Discussion: (Separate from results)
Discuss the results and the explanations
Interpret the meaning of the results.
If problem in results explain and give
solution.Refer to other work on the subject
Conclusion
What was demonstrated by experiment.
A short summary of what you found or
accomplished. Was experiment a success?Why? Why not?
Advantage of this method and instrument.
What additional experiment(s) could tell you
more about result you are looking for?Questions and References
Questions:Answer the questions at the end
of experiment. The answers to the questions are in addition to the conclusions even if the answer is covered in the conclusions.References: References you used to
interpret results. Do not reference lab manual. MarksTotal 20
Course Comment
The information you learn in lectures and lab
applies to real job situations.Know the material (theory) from the lectures and
understand the labs before you come to lab.Much of theory of instruments were presented in
second year analytical course (look up notes)Laboratory Procedure
There is only six hoursfor each experiment.
Read and understand experiment before lab.
Summarizeexp. (in hard covered lab book) before
lab.Dilution tables (In your lab book) can be made-up
ahead of lab.Be familiar with theoryof operation of instrument
before lab.Understand which aspect of the instrument used is
being demonstrated by the experiment you are running.Pipetting and Dilution
Students should be familiar with automatic
pipettes for making up specified concentrations or diluting samples.Students should be familiar with standard
and serial dilution techniques.Normal Dilution
Dilution*Mls
sample Mls solvent Total volume1 to 101
0.1 0.5 9 1.9 4.5 10 1 51 to 20 0.5
0.05 0.25 9.5 1.95 4.75 10 1 5 *Dilutions are normally done with auto pipettesSerial Dilution
Housekeeping Comments:
All glassware and equipment used must be cleaned at the end of each lab period and vials emptied and cleaned or disposed of. If you are short of time you may come in following day to finish cleaning.
Chemicals should be put away.
Lab coats, goggles, closed toed shoes, eye wash station, use fume hood of volatiles, care in handling chemicals
Most of the instruments available in the MCAL arevery expensive; please treat them carefully. If you do not understand something, please feel free to ask for help.
The experiments must be recorded in a bound lab bookas the work is done (not on a loose piece of paper).
Please clean-upyour work area before you leave (this is strictly enforced). Remove any waste papers, spills etc. and clean-up all the glassware used. All the chemicals and equipments must be returned to their proper location. You have to get the signatureof one of the demonstrators on your lab book before leaving the lab.
Do not eat or drink in the lab.
IN THE CASE OF A FIRE ALARM:
REMAIN
CALMIF IT IS SAFE, EVACUATE THE CLASSROOM OR LAB
GO TO THE CLOSEST FIRE EXIT
DO NOT USE THE ELEVATORS
IF YOU NEED ASSISTANCE TO EVACUATE THE BUILDING,
INFORM THE INSTRUCTOR
NOW IFYOU NEED TO REPORT AN INCIDENT OR A PERSON LEFT
BEHIND DURING A BUILDING EVACUATION,
CALLSECURITY
SERVICES
204474
9341
DO NOT REENTER THE BUILDING
UNTIL THEIS DECLARED BY A FIRE WARDEN,
SECURITY SERVICES OR THE FIRE
DEPARTMENT
Laboratory Experiments
The five experiments include:
Spectrophotometry Experiment
Gas Chromatograhy Experiment
HPLC Experiment
Mass spctrophotometry (LC) Experiment
ICP Experiment
Gas Chromatography
(GC) ExperimentAutosampler
Injector port
GasChromatograph
Oven &ColumnGC Column
Oven ECD detectorFID Detector
Injectors
GC 3900
GC Experiment
Seperationof alcohols to determine effect
of chain length and boiling point on retention time.Determine separation of polar and non-
polar compounds on different columnsOptimizingthe 3800 GC for analysis
Determining the sensitivity(LOD) of a GC
with microbore column.High Precision Liquid
Chromatography
Experiment
(HPLC) HPLCExperiment
Solvents
pumpsFluorescence
detectorUv-Vis
detectorPump head
Outlet valve
Inlet valve
HPLC columnsManual
Injector
Solvent Mixer
HPLC Experiment
The MCAL HPLC is a automated binary pump
system, using a reverse phase C18 analytical column, with manual and automated sampling.The LC experiment consists of:
¾The identification and seperationof UV absorbing and fluorescing compounds found in common beverages. ¾The determination of the concentrationof beverage constituents by preparation of external standards.¾The optimizingof the LC seperation method
GC-MSExperiment
There is no GC-MS Experiment
Combipal
Mixer-heater
Syringe-tenex-heater
GC Mass Spec.
MS Q 1 Q 3 Q 2Detector
Foreline pumpIon
Volume
Filament
GCProbe (solid
samples)Sample
ProbeICP Experiment
ICP-OES
RF voltage
Plasma
Sample
ArgonNebulizerPump
ICP-OES
Elemental analysis of a liquidsample
¾Must be solubilized,with conc. acid.
Experiment measures the presenceand
concentrationof elements (in ppb). ¾Look at conc. of minerals in water, in food, in rock, in sediment, in metals.Must use standards(purchased or made up)
¾weigh and dilute accurately.
Spectrophotometry
Experiment
Cuvette
Cuvette holder
UV/Vis Fluorescence Experiment
Spectroscopy experiments
Measure UV absortionof vitamin B1 (thiamine)
and B6 (pyridoxine) at differentwavelengths.UV-Vis measuring absorptionand relates to
concentrationby Beer-Lambert Law.Fluorometer measures emmissionof light from
energized fluorescing B6 (pyridoxine) solution.LC-MS Experiment
LC-MS LCPumpsAutosampler
Electrospray
chamberInfusion pumpColumn
LC-MSLC for seperation and ESImass spec with
an ion trapas detector.Measures polar, water soluble
compounds.Compared to GC-MSsystem which works
well with volatile, non-polar samples.LC-MS Experiment
Optimization of the LC for the components
of interest in the analgesicSeperation of the components of the
medication.Quantitation of the medication
componentsquotesdbs_dbs12.pdfusesText_18[PDF] serializable is an class inside io package. say true or false.
[PDF] serif fonts for screen reading
[PDF] seronegative spondyloarthropathy hla b27 negative
[PDF] serpa holster
[PDF] serpa l2 tactical holsters
[PDF] serpa p365 holster
[PDF] serre chevalier ski pass
[PDF] sers plop
[PDF] server jobs portland maine craigslist
[PDF] server side scripting languages
[PDF] serverless architecture
[PDF] serverless architecture aws lambda
[PDF] service a honda accord 2008
[PDF] service a honda accord 2012
 DATA VALIDATION REPORT
DATA VALIDATION REPORT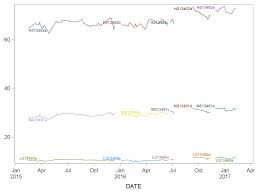 Ferritin Laboratory Procedure Manual
Ferritin Laboratory Procedure Manual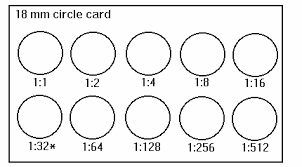 Lab 36 Syphillis Rapid Plasma Reagin
Lab 36 Syphillis Rapid Plasma Reagin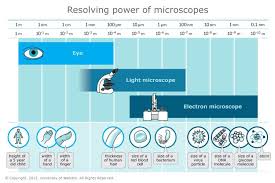 Laboratory Exercises in Microbiology: Discovering the Unseen
Laboratory Exercises in Microbiology: Discovering the Unseen BIOL 3702 Lab Exercise - Dilution Counting - 2019
BIOL 3702 Lab Exercise - Dilution Counting - 2019