 Verb Acquisition in English and Turkish: The Role of Processing
Verb Acquisition in English and Turkish: The Role of Processing
Abstract. To determine the effects of processing load on verb acquisition within and across languages we manipulated whether English- and Turkish-acquiring.
 Unaccusative/Unergative Distinction in Turkish: A Connectionist
Unaccusative/Unergative Distinction in Turkish: A Connectionist
Aug 22 2010 verbs that were reported to show variable be- havior (kana- 'bleed'
 TURKISH GRAMMAR
TURKISH GRAMMAR
TURKISH GRAMMAR ACADEMIC EDITION 2012. 3. TURKISH GRAMMAR. FOREWORD. The Turkish ... verbs constitude a verb composition concept and called a verb "V". All ...
 A Learner Corpus-Based Study on Verb Errors of Turkish EFL
A Learner Corpus-Based Study on Verb Errors of Turkish EFL
Aug 21 2017 ... verb errors
 TRopBank: Turkish PropBank V2.0
TRopBank: Turkish PropBank V2.0
May 16 2020 Being the complements of a verb
 Acquisition of English ergative verbs by Turkish students: yesterday
Acquisition of English ergative verbs by Turkish students: yesterday
Abstract. This study tries to diagnose the acquisition of a special subclass of intransitive verbs namely ergatives
 turkish-verbs.pdf
turkish-verbs.pdf
Turkish Verbs. Modification. Meaning. Suffix. Use. Negative. -me-. For general tense only add -mez. -n-. Stems ending in vowels. Passive. -il-. Stems ending in
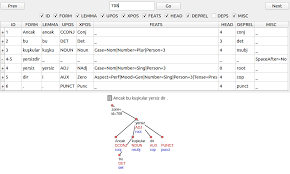 Turkish Treebanking: Unifying and Constructing Efforts
Turkish Treebanking: Unifying and Constructing Efforts
Following the discussion of compounds the light verb constructions were also problematic in the Turkish PUD Treebank as seen in Exam- ple 3. They were
 English-Turkish Parallel Semantic Annotation of Penn-Treebank
English-Turkish Parallel Semantic Annotation of Penn-Treebank
Another exemplary corpus for Turkish is the. Turkish Lexical Sample Dataset (TLSD) (˙Ilgen et al. 2012). It includes noun and verb sets and both sets have 15
 A Syntactically Expressive Morphological Analyzer for Turkish
A Syntactically Expressive Morphological Analyzer for Turkish
Sep 23 2019 tion of Turkish verb lexicon (excluding light verb constructions)
 TURKISH GRAMMAR
TURKISH GRAMMAR
The Verbs That Are Not Used in the Simple Present in Turkish. 146. Turkish Verb Frames (Türkçede Fiil Çat?lar?). 148. Transitive and Intransitive Verb
 50R TURKISH
50R TURKISH
The ones that are most frequently used are nouns adjectives and noun phrases; others are rarely used. Some suffixes
 turkish-verbs.pdf
turkish-verbs.pdf
Turkish Verbs. Modification. Meaning. Suffix. Use. Negative. -me-. For general tense only add -mez. -n-. Stems ending in vowels. Passive.
 TRopBank: Turkish PropBank V2.0
TRopBank: Turkish PropBank V2.0
Note that each verb has a different argument structure and requires a dif- ferent number of arguments in various semantic roles. With. TRropBank annotations
 The Logic of Turkish
The Logic of Turkish
Unlike French Turkish has only one way to conjugate a verb. words have been retained in the language of the Turkish Republic since its founding in.
 English-Turkish Parallel Semantic Annotation of Penn-Treebank
English-Turkish Parallel Semantic Annotation of Penn-Treebank
Turkish Lexical Sample Dataset (TLSD) (?Ilgen et al. 2012). It includes noun and verb sets and both sets have 15 words each with high poly- semy degree.
 On Single Argument Verbs in Turkish*
On Single Argument Verbs in Turkish*
reflexive verbs in Turkish. The article proposes that verbs of emission seem to be unaccusative while reflexives behave more like unergatives.
 Expressing manner and path in English and Turkish: Differences in
Expressing manner and path in English and Turkish: Differences in
Since satellite-framed languages do not prefer to encode path in the main verb this slot is available for manner verbs (e.g.
 Unaccusative/Unergative Distinction in Turkish: A Connectionist
Unaccusative/Unergative Distinction in Turkish: A Connectionist
Aug 22 2010 sues surrounding SI in Turkish and present a novel computational approach that decides ... that unaccusative verbs have an underlying ob-.
 1 A CONTRASTIVE STUDY OF TURKISH AND ENGLISH
1 A CONTRASTIVE STUDY OF TURKISH AND ENGLISH
Nov 3 2011 modalities in both Turkish and English; b) to describe modal verbs with reference to the speech-act theory. Languages.
 Turkish nite verbs
Turkish nite verbs
Turkish nite verbs David Pierce 2004 1 26 Contents 0 Introduction 1 1 Alphabet 1 2 Sounds 2 3 Writing 4 4 Words 4 5 Verbs: Stems 5 6 Verbs: bases 8 0 Introduction As a student of Turkish I make these notes in an e ort to understand the logic of Turkish verbs This is not the account of an expert I gathered the
 Searches related to turkish verbs pdf PDF
Searches related to turkish verbs pdf PDF
This book consists of 114 units each on a grammaical topic The units cover the main areas of Turkish grammar The explanaions are on the let-hand page and the exercises are on the right-hand page Plenty of sample sentences and conversaions help you use grammar in real- life situaions
What is the Turkish conjugation for the past tense?
If the very last letter of the verb root contains the rest of the consonants. Below are some examples that will help you understand the Turkish conjugation for the past tense better: Ben satt?m. (“I sold.”) Ben temizledim. (“I cleaned.”) Ben oturdum.
Are there separate words for modal verbs in Turkish?
In Turkish, there aren’t separate words for the modal verbs. To form modal verbs, certain suffixes are added to the verbs. For example: In Turkish, we express “can” using the suffix -abil or -ebil.
What is Turkish grammar in pracice?
Turkish Grammar in Pracice introduces grammar to learners at beginner to intermediate level. It is not a course book, but a reference and pracice book which can be used by learners atending classes or working alone. What does the book consist of? This book consists of 114 units, each on a grammaical topic.
What are units in Turkish grammar?
Unit itles tell you the main grammar point whose brackets. Unit secions (A, B, C, etc.) give you informaion about the form and meaning of the grammar, as well as its diferent uses. Tips in the form of ? and X,highlight common errors and characterisics of Turkish grammar. Illustraions show you how to use grammar in everyday conversaional Turkish.
Turkish VerbsModification
MeaningSuffixUse
Negative-me-For general tense only, add-mez
-n-Stems ending in vowelsPassive-il-Stems ending in consonants other thanl
-in-Stems ending inl -dir-Most verbsCausative-t-Stems ending in a vowel
-it-Stems ending in ¸s or ¸cReflexive-in-... to yourself
Mutual action-i¸s-... to each other
g¨ormekto see g¨or¨u¸smekto see one another or to converse g¨or¨u¸s¨ulmekto be conversed about g¨or¨u¸st¨urmekto make to converse with one another g¨or¨u¸st¨ur¨ulmekto be made to converse with one another giymekto wear clothes giyinmekto dress oneself giyindirmekto dress someone else giyindirilmekto be dressed by someone else giyindirildirmekto be forced to be dressed by someone elseConjugation
1. Drop-mekfrom the infinitive to get the stem.
2. Modify for meaning, as above
3. Select the tense and append something:
TenseAppendMeaning
Present-(i)yorActions happening right now -I am writing (now). General (Aorist)-(i)r-Things generally true -I am a writer.Future-(y)ecek-Actions that will happen
mi¸s-past-mi¸s-Present state caused by past action, or things the speaker is reporting without having seen. di-past-di-Both simple past -did- and past perfect -have done Necessity-meli-Actions that must, or should, be taken Conditional-se-If .... (with non-simple moods, expresses unfulfilled conditions, hopeless wishes of the past, etc.) Subjunctive-e-No statement of fact, things that might happen or have happened (with non-simple moods, expresses unfulfillable past wishes, or quotes of those expressions)4. Select the mood and append something:
MoodAppendConjugation pattern
Simple-I (mostly)
Past-idi-II
Conditional-ise-II
Past conditional-idi- + -isi-II
Inferential-imi¸s-I
Inferential conditional-imi¸s- + -ise-II
5. Apply the appropriate conjugation ending:
-im -izType I-sin -siniz
-(dir) -(dir)ler -m -kType II-n -niz
- -ler -eyim -elimType III-eyin -esiniz
-e -eler6. Entire pattern:
SimplePastConditionalPast conditionalInferentialInferential conditionalPresent-(i)yor + I-(i)yordi + II-(i)yorse + II-(i)yordise + II-(i)yormi¸s + I-(i)yormi¸sse + II
General (aorist)-ir + I-irdi + II-irse + II-irdise + II-irmi¸s + I-irmi¸sse + II Future-ecek + I-ecekti + II-ecekse + II-ecektiyse + II-ecekmi¸s + I-ecekmi¸sse + IImi¸s-past-mi¸s + I-mi¸sti + II-mi¸sse + II-mi¸s idiyse + II-mi¸s imi¸s + I-mi¸s imi¸sse + II
di-past-di + II-diydi + II-diyse + II-di idiyse + II---- Necessity-meli + I-meliydi + II-----meliymi¸s + I-- Conditional-se + I-seydi + II-----seymi¸s + I--Subjunctive-e + III-edi + II-----eymi¸s + I--
Participles
Present-eng¨oren= seeing (right now)
Aorist-irg¨or¨ur= seeing (in general)
Future-ecekg¨orecekwhich-will-be-seen
mi¸s-past-mi¸sg¨orm¨u¸s= seen di-past-dikg¨or¨ulmedik= extraordinary (unseen)Imperative
-[y]in -[y]iniz -sin -sinlerTo be - past pos
idim idik idin idiniz idi idilerTo be - past neg
degildim degildik degildin degildiniz degildi degildilerAbility (to be able to ...)
Append this to the stem:
-[y]ebilmek withbilmekconjugated some way 1quotesdbs_dbs11.pdfusesText_17[PDF] turn off accessibility windows 7
[PDF] turn off exposure notification android
[PDF] turn your android phone into a webcam
[PDF] turnitin download
[PDF] turnitin free account
[PDF] tuticorin air pollution
[PDF] tuto pour apprendre le ukulele
[PDF] tutorial adobe illustrator cc 2017 bahasa indonesia
[PDF] tutorial adobe illustrator cc 2017 bahasa indonesia pdf
[PDF] tutorial adobe illustrator cc 2018 bahasa indonesia
[PDF] tutorial adobe premiere
[PDF] tutorial android studio pdf
[PDF] tutorial gimp 2.8 pdf
[PDF] tutorials on the use of sql to write queries or stored procedures
